- Introduction
Many business owners and senior managers are accepting the principles of lean management. Most do apply them in their waste management strategies without knowing it. However, the difficulties are realized at the implementation stage of the lean technique. The lean method ensures easier identification of the waste material within the final products and the appropriate tool to be used for their elimination from the required products [1]. It is majorly used in the industrial firm to ensure the final product produced meets the customer requirement in terms of quality and pricing. Many lean tools can be used to realize this.
- Theoretical content
Problem statement
A lot of production time is used in the material handling and the assembly section which decreases the rate of production process. To increase the quantity produced, the production time should be reduced to the minimal value possible. However productivity should not be increased at the expense of the customers’ quality requirement of the final product
Methodology
The reduction of the cycle time in the assembly line using the lean techniques mainly work based on waste minimization while maximizing the value of the customer. The word lean is used within the industrial or manufacturing sector to mean using the limited available resources to create higher value for the consumers of the product. An organization or industry using this lean technique for the cycle time reduction must appreciate what role the value of the customer plays in the production processes and work continuously towards increasing it to maximize the value of the customer at zero waste production [2].The lean technique uses the horizontal system of product flow, in which the products produced flow across the various assets within the industry to the established technologies than to the multiple departments and finally to the customers.
This horizontal system is preferred to the vertical workflow as it produces a process that is cheaper in terms of the human labor required, the space required, the capital requirement production time as the well as the number defects produced [1]. Furthermore, the use of a horizontal system enables a quicker and continuous response to the customers continues to change in customers’ product requirements in terms of the quality, variety, and pricing.
The lean technique was first introduced in the late 1980s for use in the Toyota business by a group of researchers headed by Jim Womack [3].
Assembly types
The assembly type of the lean technique uses two models, the SUB frame model and the SLF type model. SUB frame model involves a reduction of the production time and costs through the batch time elimination, mixed model processing, land grouping, and control chart [4]. The model requires cutting, welding, quality check as well as painting among many other activities. Examples of the SUB frame models include, just in time JIT, Interpretive Structural Models, Structural Self-Interaction Matrix.
Obtaining average cycle time in the sub-frame models
The average cycle time for each of the activities involved in the sub-frame models can be obtained by summing up the value added time ,non-value added time and the total cycle time then dividing by three to get the average for the each activities involved. This is given as Value added time (sec) + none—value added time (sec) + Total cycle time (sec)/3. To reduce the total cost involved in the production process, there should be minimum number of workers per work station .To get the least number of workers per station total time taken to produce a given product is dived by the cycle time.
, this will enable the company to evaluate the least number of workers to be stationed in each of the workstations. Also the workstation involved in the production process should be very minimal to reduce the total production cost. To obtain the least number of workstation in sub-frame model, the total time taken in completing one cycle is divided by the time available.
. Minimum workstation ensures the customer requirements are achieved at a minimum cost to enable the company realize profit per unit produced.
SLF model, on the other hand, tends to continuously eliminate unevenness in the workflow through the system to improve the flow of work. SLF models include interpretive structural model, end cutting, child part setting [3]. SUB frame models differ from the SLF models, mainly in terms of the activities involved in the two models of the lean techniques. SLF model, for example, uses child part cutting, child part setting and cutting in achieving the primary goal of time reduction by exposing mechanical problems at every process of the production which is not applicable in the SUB frame model [5]. However, both SUB frame models and SLF model presents issues in the quality of the product produced that already exist within limited control on the amount of the waste produced.
Literature review
Toyota firm was the first to employ the use of the lean manufacturing concept in their production processes. Generally, this technique is applied in the industrial production processes to improve production processes as well as increasing the employee’s morale [6]. Lean manufacturing was adapted to replaces the older traditional system that uses the inventory system, which was time-consuming and expensive to apply. For any manufacturing firm to effectively adopt the use of this technique, the company must understand how lean method differs from the traditional construction type [7]. Better and appropriate manufacturing system design requires that an elaborate analysis of the constant fluctuating marketing dynamics as well as appreciating the market volatility. The use of lean techniques in the production processes ensures that the firm meets the customer’s requirement for the products since consumers of the product are for the values of the services they get from the company but not for errors committed by the producing firm. Waste, according to Diestel and Panizzolo [7]. Waste is anything that does not add any value to the final products produced, Lean manufacturing technique when used together with the SWOT aim at a total waste reduction for the end product to meet customer requirements as the product reliability is only achieved from the customers’ side and not on the company’s side [8]. Moreover, this technique also increases the final production output per head as well as inventory reduction for the total goods produced.
Companies adopting this lean technique in their production processes produce products of higher quality at the lowest production time and cost by reducing the total amount of waste produced [9]. The implementation of this technique in the manufacturing firms occurs in various steps; the identification step, the solution step, implementation step, and finally follow up and training.
The identification process entails identification of the various types of waste produced, their possible cause within the production processes and finally a way out for their permanent elimination at the lowest cost and time. Solution step, on the other hand, involves finding the exact solution and the possible root cause to the various waste type identified [11]. These solutions found are then tested, and if found to be applicable for total waste reduction, they are then implemented.
Experimental methodology
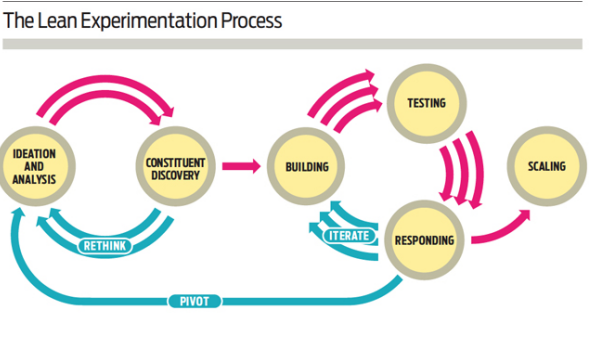
Fig 1: Showing steps involved in the waste identification processes as drafted from [10].
Ideation and analysis stage in the lean experimentation tend to create the picture of the program involved the possible solutions that can be applicable in waste reduction and elimination process. These ideas are then analyzed with program and solutions addressing the same problems. Constituents discovery involves careful listening to the comments of the client of the product produced [11].
. The building, in this case, includes risk identification, the risk that is approximately close to the idea identified in the analysis process. Once these various ideas have been analyzed and the risks involved identified, Testing of the ideas is then followed, where a cheaper testing tool such as; MVP tool of the lean technique is used in the testing for the hypothesis validation process[12]. Once the hypothesis is tested analysis is done to either accept it or ignore it based on the findings of the investigation.
- Results and Discussion
The application of the lean technique in an organization enables the firm to have their various strategies tested in the least time possible within the aim of getting well defined short terms results. These short terms out can include, the school attendance list, the rate of reading, placement in various job vacancies as well as in the health sectors (Elbert, 2018). Lean outcome testing tool such as A-B testing can be applied by multiple organization to test and analyze the different alternative available approaches available on the constituents of the sample.
4. Case Study
Production of textile products, for example, is an example of the manufacturing firm that uses lean technique system to reduce the cycle time in the waste elimination process to achieve a total waste reduction in their final product at the lowest cost and time. The dye and other chemicals used in the manufacturing process are treated as waste as they don’t form part of the final textile products produced [7]. The garbage generated within the textile industry is identified using the lean technique analyzed and appropriate lean technique tool used to eliminate the waste identified. Each type of waste produced is reduced using a specific lean technique tool. The table below shows the various categories of wastes produced in the textile industries.
| Constituents | Cycle Time (min) | Change Over Time (min) |
| Heavy metals | 11 | 20 |
| Suspended solids | 10 | 12 |
| Sulfates | 20 | 22 |
| Oil and grease | 15 | 16 |
| Surfactants | 18 | 19 |
Table 2; Showing the various waste categories that can be identified and eliminated using the lean technique in the textile industry at a given cycle time.
Each waste identified has its unique lean tool for the removal at the cheapest cost and at the least time to ensure that the final product is of the right requirement for the ultimate user.
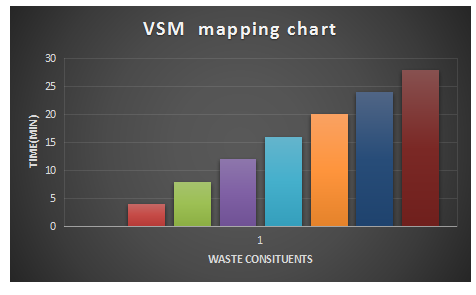
From the table 2 above the total change over time , waste waiting time in min , WIP time and the Takt time could be obatained and the cycle time , lead time and the takt time compared in the VSM mapping chart as shown below.
Fig 3, the red bar represent , the cycle time, the green bar represent the lead time , the purple bar represent the Takt time, yellow bar represent the waste waiting time while the blue and the brown bar represent change over time and WIP time respectively.
Problems encountered
Lean technique is very new into the industries, and its implementation requires a lot of finance in terms of training the staff to adopt it. Moreover lean technique can reduce the staff morale since some of the employees are resistance to change and therefore implementation of this technique would reduce their work morale. Lean technique still need further improvement to ensure total time reduction in the production process. Lastly, in the process of time reduction to reduce the production cost, most company tend to ignore the customer requirements’ of the product in terms of the quality of the product.
Conclusion
The lean technique is majorly used in various industries such as the textile industries to reduce the time of production through a secure and cheaper method of identification of the unwanted products within the final product and the appropriate tool for their elimination [11]. The lean experiment described above illustrates how various lean parameters can be used to reduce the time used in waste elimination while meeting the consumer’s requirement for the products.
Bibliography
[1] Correia, D., Silva, F.J.G., Gouveia, R.M., Pereira, T., and Ferreira, L.P., 2018. Improving manual assembly lines devoted to sophisticated electronic devices by applying Lean tools. Procedia Manufacturing, 17, pp.663-671.
[2] Deokar, A., Raj, S.A., Jayakrishna, K., and Zubar, H.A., 2019. Implementation of Lean Concepts Using Value Stream Mapping in Automotive Firm. Advances in Manufacturing Technology (pp. 141-147). Springer, Singapore.
[3] Dieste, M., and Panizzolo, R., 2019. The Effect of Lean Practices on Environmental Performance: An Empirical Study. In Lean Engineering for Global Development (pp. 225-258). Springer, Cham.
[4] Elbert, M., 2018. Lean production for the small company. Productivity Press.
[5] Ghiyasinasab, M., Lehoux, N., Ménard, S., and Cloutier, C., 2018. Using Lean Techniques and Simulation to Improve the Efficiency of Engineered Wood Production: A Case Study in a Small Factory. Ind Eng Manage, 7(269), pp.2169-0316.
[6] Gibson, M., and Mrugalska, B., 2019. Lean Production and Its Impact on Worker Health: Force and Fatigue-Based Evaluation Approaches. In Advanced Macroergonomics and Sociotechnical Approaches for Optimal Organizational Performance (pp. 118-127). IGI Global.
[7] Nguyen, M.N., and Do, N.H., 2016. Re-engineering Assembly Line with Lean Techniques. Procedia CIRP, 40, pp.590-595.
[8] Rohani, J.M., and Zahraee, S.M., 2015. Production line analysis via value stream mapping: a lean manufacturing process of the color industry. Procedia Manufacturing, 2, pp.6-10.
[9] Satoglu, S., Ustundag, A., Cevikcan, E., and Durmusoglu, M.B., 2018. Lean Transformation Integrated with Industry 4.0 Implementation Methodology. In Industrial Engineering in the Industry 4.0 Era (pp. 97-107). Springer, Cham.
[10] Seth, D., Seth, N., and Dhariwal, P., 2017. Application of value stream mapping (VSM) for lean and cycle time reduction in complex production environments: a case study. Production Planning & Control, 28(5), pp.398-419.
[11] Singh, J., Singh, H., and Singh, G., 2018. Productivity improvement using lean manufacturing in the manufacturing industry of Northern India: A case study. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 67(8), pp.1394-1415.
[12] Yamazaki, Y., Shigematsu, K., Kato, S., Kojima, F., Onari, H., and Takata, S., 2017. The design method of material handling systems for lean automation—Integrating equipment for reducing wasted waiting time. CIRP Annals, 66pp.449-452.