Part A
1. Introduction
Market expansion has evolved as a crucial growth strategy for businesses of all sizes in the present era with the advent of rapid industrialization and technological advancement. By going global, it has been evident that organisations not only benefited from a competitive edge in their operation with access to unexplored resources, consumers, markets and others but are also able to retain long-term operational sustainability. In this report, an attempt will be made to critically assess the effectiveness of the market expansion with a special reference to Uber, an American multinational transportation company. Following this, a market expansion plan will be developed here to contextualise how an American company like Uber would be able to enter the Cuban market even with the conflict between the two countries. The first section of the report will incorporate a detailed discussion of the international expansion, key rationale, market analysis, external and internal market factors and others to make the discussion of the report more comprehensive. A personal reflection on self-employability will also be depicted at the end section of the report.
2. Company Background
Uber is a renowned American-based global transportation network that offers on-demand transportation services like ride-sharing and food delivery. The company has grown as a global platform connecting the digital and physical worlds to help movement happen at the tap of a button (Uber, 2024). Uber strategized on strengthening the local economies and improving access to transportation as reliable as running water, so everyone benefits. It is one of the most valuable start-ups globally with approx. 75 million global consumers and three million dedicated drivers in 83 countries. The organisational mission includes improving the quality of life for all people by providing accessible and affordable transportation (Uber, 2024). As per organisational data, movement is the lifeblood of the firm which pushes the firm constantly to reimagine how to move better. Uber’s history started in 2008 on a snowy evening in Paris, when Garret Camp and Travis Kalamick found themselves stuck and unable to find a taxi. Their idea was to simply invent something that eased transportation with a tap of a button and since ever, the DNA of Uber’s reinvention and re-imagination carried on gracefully (Uber, 2024). In 2010, the first-ever Uber trip was taken across San Francisco and by December 2015, the company successfully reached 1 billion trios both nationally and internationally.
3. Products or services
Uber offers a vast range of transport services focusing on consumers’ comfortability. Organisational technology helps to maintain as well as build multisided platforms which focuses on meeting consumers need for independent ride services including bikes, scooters, public transit and others. Services offering also focus on connecting rides on 4 wheels to 2 wheels to 18-wheel freight deliveries (Help. uber, 2024). Different types of Uber rides include Uber X which is a 4-seater passenger car, Uber XL, a six-passenger seat SUV, Uber Comfort and others. Uber Green is a newly introduced initiative focusing on low emissions by Uber. Based on the market demand, a different range of services was also launched by the firm to capture the market. Uber Taxi is one of the popular product offerings where the upfront fare is mainly calculated after entering the drop-off and pick-up locations through the app. Organisational data also highlight that the company connect consumers and grocers, restaurants and other merchants to widen its offering (Uber, 2024). At present, Uber helps people move and connect in over 70 countries including approximately 10,000 cities around the world.

4. Country Overview
Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean which has long been operated as a closed economy. Since 2010, the government has been encouraging private ownership of businesses to bring change to its economic image. A shift has also been evident in the Cuban economy from an agricultural-based economy to a large service-oriented economy. Since, 2011, the country started to reform its economic model to engage more foreign direct investment as well as enhance national production by developing the state-owned businesses wider and more efficient (Romanò and Barrera, 2021). Cuba is also a Spanish-speaking one with a population of 11,047, 252. The country’s relations with other neighbouring ones have created a significant impact on the political and socio-economic landscape. As per market data, the country’s service industry accounts for 75.2% of the economy. Cuba offers mainly two types of transportation systems, one is traditional government-run cabs which serve tourists and the other is on-demand rides for individual patrons. The best proposition of the country’s market is that it leaves space for all entities of businesses from start-ups to large operations, since collaboration is the key to sustaining business here.
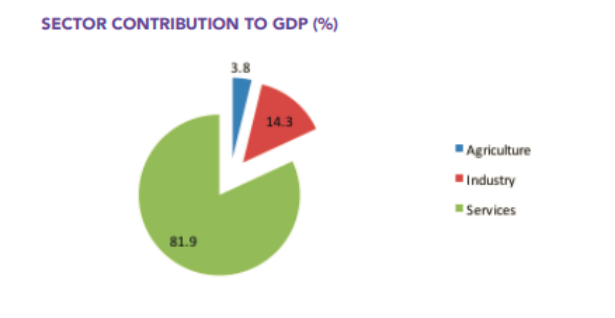
Figure 2: Overview of Cuban economy
(Source: Dobusinessjamaica, 2021)
The above figure shows the sector-wise contribution to the country’s economy and indicates the significant proposition of the service industry. A rise in middle-class consumers has profoundly benefitted the service sector in higher per capita revenue growth as well. China also made significant investments in Cuba specifically in infrastructure. However, a lack of a market-based foundation affected foreign investment in the market (Pedraza and Romero, 2023). As Cuba has begun to liberalize its economy, U.S. companies have shown significant interest in expansion as well. Regulatory compliance in this country also impacted business operations by creating both opportunities and threats.
5. Market research/analysis
Market size
The ride-hailing market in Cuba is projected to reach US $17.55k by 2024 ending with a culmination of the market volume, of US 3.60k (Statista, 2024). Secondary findings also indicate that the global ride-hailing market grew by $70.13 billion in 2023 to $ 80.46 billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 14.8%. The forecast market growth can also be attributed to factors such as environmental sustainability, multimodal transportation, adherence to regulatory framework and others (Spadoni, 2023). It is also stated that the anticipated growth of the ride-hailing market can be further fuelled by increasing fuel prices. The market is also moderately fragmented as the players in the respective region have a significant market share compared to the overall region.

Figure 2: The Ride-hailing market size in Cuba
(Source: Statista, 2024)
Growth drivers and potential
On-demand transportation services remain one of the key market drivers to the Ride-hailing market’s growth in Cuba. Besides, the global surge in urbanization coupled with traffic congestion has effectively fuelled the demand for traditional transportation alternatives. Bebbington et al. (2020) also examined that the ubiquity of smartphones as well as the widespread availability of mobile applications have dramatically reshaped commuting habits and rendered ride-hailing services as a convenient one. The cost of owning a personal vehicle also fuels the market growth of the Ride-hailing market’s growth. However, ride-hailing services come up as a value-based ride with additional options such as driver reviews, e-transactions, location tracking and others. The market also reflects effective growth potential as the online ride-hailing market is on an upward slope of growth due to the digitized economy (Worldfinance, 2024). An opportunity for more innovation and renewable resources used in the ride-hailing market also opens windows of new opportunities.
Market trends
The ride-hailing market in Cuba is also expected to rise over the projected horizon with the changing economy, especially after the pandemic. Electrification of the ride-hailing services set a key trend of adopting electric vehicles for companies which anticipated the consumer’s needs and environmental sustainability. A recent study by Fernández (2022) also highlights the increase in demand for electric vehicles as an anticipated factor behind the hike in the upcoming future. The market also witnessed significant growth in the number of strategic partnerships and alliances which act as a key trend for the ride-hailing service providers.
Key success factors
In the Cuba market, the potential to present new sales opportunities for businesses is comparatively high due to the existing closed economy and attractive foreign direct investment (Salas Vargas et al. 2021). One of the key success factors in this market is compliance with government regulations as it comprises a dominant state-based economy. Apart from that as few market players are there that provide ride-hailing services, a high likelihood of success is also there (Rottig et al. 2020). Continuous innovation and strategic partnership also remain considerable factors for the market success of the ride-hailing service provider in the market of Cuba.
6. The rationale for expansion
In the present day, with the advent of the digitized economy and rapid technological growth, a shift has been evident in the way to operating businesses triggered by increasing market expansion and limitless growth opportunities. Shenkar et al. (2021) have mentioned the concept of market expansion as a procedure through which economies, cultures, societies and regions become consolidated by the global-spanning network for trade and communication. Perhaps, Romanò and Barrera (2021) stated that expansion to the international market mostly takes place in business operations if businesses already reached a certain standard of growth and actively looking for additional opportunities in order to generate higher profits. Being a market leader, Uber successfully operate in several markets including domestic and multinational. It has been seen that the company is able to retain a strong market position by having a diversified services or product portfolio, full-service distribution channels and a strategic model. Under the operational strategy of Uber, the strategy of market expansion would undoubtedly give a new direction to the company amidst the wave of liberalization and industrialization (Li et al. 2021). Since the ride-hailing market of Cuba is dynamic both in terms of supply and demand it will undoubtedly benefit Uber in improving its sales economy within a short period of time (Nahrstedt, 2021).
The prime reason behind entering the Cuba market despite existing political tensions remains to bring an improvement in the strategic positioning through grabbing competitive advantages which will lead the firm to stay ahead of niche market competition and marginalise the profit. Expansion to the Cuba market would also allow the firm to reduce the threat of being dependent on one specific market segment by extending their services or product’s wideness (Ghauri et al. 2021). Along with that, Uber can also access human capital and other unexplored resources through an expansion which aids in competitive advantage for its operation as well as at the same time reduces operational costs (Sinha, 2020). The rising price of raw material sourcing also puts immense pressure on the company’s overall expansion which can be mentioned as another key rationale for expansion. Cuba is an important emerging market for consumer goods which presents the opportunity for capitalization as well (García-Rodríguez et al. 2021). By expanding its operation, thereafter, Uber can solidify its business positioning and such an augmentation of the distribution and service network in multiple countries can also act as one of the key growth strategies for Uber.
7. Factors to consider
a. Macro environmental factors
PESTLE analysis
Political factors
Cuba is a unitary republic and communist state with administration subdivisions which outlaw political pluralism. All the departments of state and the Cuban communist party are also closely connected and their power is beloved by the executive committee of the Council of Ministers (Williams, 2022). Since the country is experiencing a socialist political climate with moderate stability, Uber can exhibit an operational environment which is not risk-free. However, the country’s good relationships with its neighbouring ones can allow the firm to grab the trading benefit. Cuba’s strategic geo-political location also helps businesses to take advantage of international commerce and trade (Pertierra, 2020). Despite having a stable socialist political system, the unpredictable political climate and the impact of having a strained relationship with the U.S. often also discourage new business development.
Economic factors
Cuba is a centralized “socialist economy” dominated by state-owned enterprises which are around 90% of the economy and employ 70% of the workforce (Martinez, 2022). The GDP per capita in 2022 was $7,173 which represents a change of 1.8% per capita yearly change compared to the past year (Statista, 2024). As per the market data, the country’s economy is also expected to grow at a rate of €7.67k in the forecasting period with a consumer price index of 0.98k. Since 2014, the government has substantially improved the operating environment for the country through introducing new laws on foreign investment (Rodríguez, 2024). The corporate tax rate of Cuba also ranges from 15% to 30% and is levied on both the domestic and foreign companies conducting business activities within the country (Tradeclub. standardbank, 2024). The country’s economy also depends on import activities from China, Venezuela, Spain, the USA and Canada. The presence of such a degree of positive and economic indicators allows the country to be an appealing one for new business ventures. The unemployment rate of Cuba is comparatively low to other countries, only having 1,6% jobless people which ranks 13th globally (Agbarakwe and Bredino,2024). Operating in such a dynamic economy with growth possibilities, Uber will also be able to effectively higher its sales economy. However, the economic activity on the island is still dominated by the government by both directly and heavily subsidized state-owned enterprises which may affect the company’s operation. The rising inflation rate remains another area of concern for the sustainable operation in Cuba.

Social factors
Cuba is a multi-ethnic country comprising customs and cultures derived from diverse origins and rich history. The country has a population of approx. 11,451, 653 with an average growth rate of 0.233% annually (Statista, 2024). Protestants and Roman Catholics are the most dominant religions in the country. Due to having a literacy rate of 99.67% in 2022, the country indicates a moderate to high living standard which can benefit Uber in accelerating substantial sales growth. The presence of rich and diverse cultures and ethnicities can develop both opportunities and challenges for Uber as well (Pérez-Campdesuñer et al. 2021). As consumer behaviour in this country is somewhat guided by ethnicity, the company needs to take into consideration their preferences while introducing any services or products. Since, social inequality is also there, even after high disposable income, Uber can exhibit fluctuated consumer spending behaviours as well.

Figure 4: The current population rate in Cuba
(Source: Statista, 2024)
Technological factors
The Cuban government has made a significant improvement in its technological infrastructure with a high internet penetration rate (Henken and Santamaria, 2022). As the technology’s growth upholds a significant contribution to the country’s economy, thereafter Uber can effectively benefit and grab a competitive edge in its operation by utilizing such infrastructure. Despite the advanced information system, Cuba still has to improve in different sectors which lack development. The country’s focus towards a digitized economy can also boost Uber’s market growth rate.
Legal factors
The legal environment of Cuba is mainly outlined by a robust legal framework which includes business laws, labour laws, consumer and business rights and others (Cowling, 2020). Complying with the country’s law will help Uber provide a safe and fair work environment as well as foster equal employment opportunities in the new market. The country’s employment legislation also emphasizes work-life balance for employees. In order to avoid legal complications, Uber thereafter needs to design a code of ethics aligned with the country’s federal regulations.
Environmental factors
Climate change has brought a massive shift in the weather pattern of the country which profoundly impacts the business operation as well (Milanés et al. 2020). As per the findings, soil and desertification remained the main causes of the country’s environmental problem. Cuba is also experiencing water pollution, loss of biodiversity, air pollution and other combined factors. It has been evident that the government has taken multiple initiatives under the environmental protection policy and set boundaries for businesses as well (González, 2023). Uber thereafter should comply with the standard of business operation to avoid any kind of penalty.
Micro environmental factors


Table 1: SWOT analysis
(Source: self-created)
Uber has positioned itself as the largest ride-sharing technology globally with strong brand recognition in over 50 countries. One of the key strengths of the firm is its operation on low fixed investment and easily accessed communicative networks. Apart from that the company has remained an effective consistency in its dynamic pricing strategy which allows the firm to grab a competitive edge in its operation. Compared to other traditional taxi services, Uber also offers low prices which act as a key strength to boost high consumer engagement. The business model of Uber is also ideal for the consumers to drive the interaction, Uber also enjoys the primary advantage of the first mover with the first ride-hailing service with a widely available app. The innovative nature of the business model also allows the firm to maintain a low-cost contractual agreement with drivers with a high market valuation.
Despite its success, Uber also received multiple negative coverage over controversies and scandals. Frequent scandals lead the firm to witness a substantial loss in its market avenues. Along with that, having a dependency on the workforce has not been advantageous for Uber and has caused damage to the brand name. A lack of consistency in maintaining the market profitability also acts as a weakness of the firm. It can also be added that Uber employees are classified as independent contractors instead of full-time employees in several regions which has created some unfavourable employment practices for the firm as well. The company also struggled with consumer loyalty due to its exploitative business model.
Though. Uber has immense opportunities to improve its reputation through greater performance and accountability. It can grab the opportunity to expand its operation in the international market by utilizing digitalisation and other innovative technologies (Lisa et al. 2020). Diversifying offerings through strategic acquisition can allow the firm to stay ahead of its market competitors as well. Uber also has an opportunity to improve its investment in green technology to grab the consumer’s attention and reduce operational costs. The company can also launch different ventures into driverless technologies as it sets a key trend in the marketplace. Having good relationships with suppliers, the firm can also strengthen the delivery services which will benefit the firm to higher revenue growth. Consideration of the sustainability factors in the business operation can also help the firm to improve its brand image in both the existing and new marketplace.
On the other hand, the rising market competition imposed a potential threat to the operation of Uber. The threat in the form of reputation loss is also there as approx. 300, 00 drivers of Uber filed lawsuits against the minimum wage policy of the firm. In recent days economic uncertainty also become a threat for the market success for the firm. Along with that as the organizational operation relies heavily on its workforce thereafter employee strikes often act as a key threat to the market operation of Uber. Several stringent regulations also imposed negative pressure on the operation of Uber.
8. Competitor analysis
In the market of Cuba, Uber can face intense competition from private-owned taxis, state-owned taxis and others. Ride-hailing services to locals are also offered by Almendrones and Ruteros. Almendrones are shared taxis which operate specific routes in Havana and other cities. Those are vintage cars painted in bright colours with a fixed fare rate of 10 to 20 Cuban pesos. On the other hand, Ruteros are small buses that have a seat fare of 1 Cuban peso per ride. This service is popular with locals and often crowded during the peak hours. As not many flexible rise service providers are there, Uber can face comparatively low competition in the Cuban market. By considering a low-fare offering and leveraging flexible operating features, Uber is also able to grab the market attention and build consumer loyalty in this market effectively.
Porter Diamond Model
In order to analyse the competitive environment, a Porter Diamond Model is incorporated here as such a model is effective in identifying competitive advantage for the firm. The model places emphasis on the four key factors such as “company strategy”, “structure and rivalry”, “factor conditions”, related and supporting activities and “demand conditions”.
Organizational structure, rivalry and strategy
Uber’s strategy mainly focuses on providing high-quality services to consumers to retain consistent profitability (Uber, 2024). The company also promises value for money and consumer satisfaction through efficient processes which lead to cost saving for the company. Uber also comprises a flatter organizational structure which supports free and open communication. Managers and supervisors also work closely with employees to foster both professional and personal growth apart from the profit building. It is also stated that with the global competition, the company has gained an understanding of different international and regional business practices.
Factor conditions
Uber strategically uses its available natural resources to set up production and operational plants. The company also has capital resources in the form of debt financial resources and equity capital resources (Uber, 2024). Skilled human resources availability also allows the firm to meet the consumer’s expectations. Infrastructural support and technological innovation profoundly help Uber to achieve economies of scale and reduce overall operational costs as well.
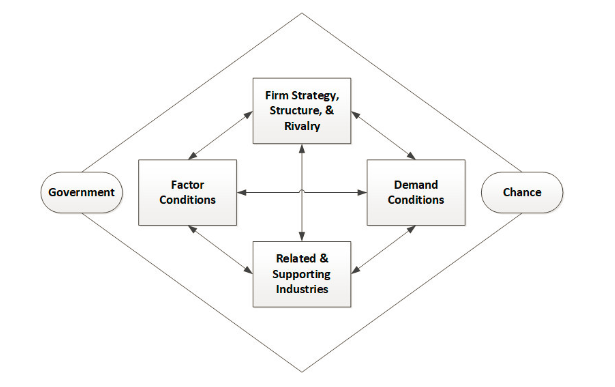
Demand conditions
The increasing size of the local markets and domestic consumers remain important for Uber to enhance their product or service demand. Apart from that, sophisticated and demanding domestic consumers of Uber pushed the firm to develop unique products to stay competitive in the market. Apart from that, the firm can able to influence the behaviour of the consumers in the market based on the market response.
Supporting and related industries
The presence of similar industries in the international and domestic markets has also been a source of ‘development and growth’ in terms of expansion for the firm. Rival industries also remain an important factor in the development of Uber’s internationality (Djuraeva, 2021). Global suppliers also help the firm to build a strong network of supply on time which in turn boosts the consumer’s loyalty.
Government
Government policies also remain supportive of Uber in their way of growth as well as setting up different plants in various regions. Uber also benefited from the existing industry regulations and was able to maintain the quality of Uber products or services. Different government-level initiatives remain catalysts for the firm as well.
Chance
Random events have an adverse impact on Uber’s operation and are influenced in different manners. The occurrence of natural disasters also blocks the service provision of Uber in the market. Uber also benefited from scientific breakthroughs by developing technological knowledge regarding new service offerings.
9. Mode of entry
Cuba’s natural beauty, proximity to the U.S. and the ideal weather make it a great destination for new business ventures. In order to enter the Cuban market, Under can go for utilizing a joint venture strategy, collaboration with a Cuban-based company. As a market expansion strategy, a joint venture is basically an endorsement between two or more business to form a completely new entity which shares resources, knowledge, rewards, profits, risks and others involved within the venture (Paul, 2020). Since, segmenting the Cuban market can be challenging for Uber thereafter, taking support from the already existing companies with theestablishment of ‘joint venture’ can benefit the firm effectively. Another key benefit of such an expansion strategy includes high flexibility to manage risk in the new market and conduct operations in a cost-effective way. Meyer and Nguyen (2020) also noted that joint ventures lead businesses to gain success in their operation by minimizing the effort to find investors, building a distributor network and offering much time to understand and capture the market need by delivering innovative solutions. On the other hand, Uber can also imply a strategic alliance as a market entry mode in the Cuban market. Since such a strategy would benefit the firm in gaining easy access to human resources, capital and others which in turn allows it to offer diversified services, it is stated that such a selected strategy can prove beneficial for the firm effectively.
Barriers related to expansion
In light of expanding to the Cuba market, Uber can also face certain hindrances in its operation due to market uncertainty and political risks. It can be added that Cuba has one of the globally few remaining centrally planned economies where the government controls 90% of the economy. All trade with that country is majorly conducted through the state thereafter goods imported into Cuba by government entities can act as a key limitation of businesses (Pedraza and Romero, 2023). Besides, fixed capital investment in Cuba represents only 10% of its GDP which is half the regional average. Such conditions can hinder the development of new foreign capital for Uber. Apart from that, the dual currency system of the country created confusion in the trade operation. In order to gain success in this market, Uber thereafter needs to take into consideration such key factors to ensure a smooth operation as well.
Conclusion and recommendation
On a conclusory remark, based on the above discussion it is stated that the development of an effective market expansion plan would benefit Uber to retain its operational sustainability as well as market competency. Since going new marketplace can leverage potential growth opportunities for the company as the target market possesses a growing economy, thereafter is stated that expansion from the U.S. to Cuba can result in high business profitability. Despite the existing conflict between the two countries, new policies have helped turn on the business venture’s growth. In light of Uber’s case, it is also added that strategic collaboration, as well as the incorporation of digital marketing can help the firm to capture its target market seamlessly.
Based on the above discussion, here some recommendation is also developed as follows:
In order to greater international success, it is recommended that Uber be more careful in integrated planning and preparation to comply with the country’s regulations as different countries have different rules and legislation. Along with that, the conduction of market research can also help the firm to better meet the consumer’s demand in the target marketplace as well as stay ahead of their key competitors
Another recommendation includes improving the investment in designing a robust digital marketing strategy to keep their consumers aware of the product offering of the firm. By widening its reach in the target market, the company can witness a high sale in the economy as well. Marketers also need to incorporated innovative and creative solution to content and campaign designing
It is also recommended that Uber laid emphasis on the provision of training and development opportunities for its employees to improve service quality. Besides maintaining of an open communication channel can help the firm to avoid the lawsuits. In that prospect developing strategic collaboration with any private training provider firm can help the firm to maintain a cost effectiveness in that initiatives
Part B
Personal reflection
In order to better reflect on employability in the international business context, here Kolb’s reflective model is depicted as the model is simple yet effective for developing self-reflection.
Concrete experience
During the internship, I worked in DPD courier Waitrose delivery service and Amazon delivery driver in the UK. Work experience in both work areas is different from my point of view as I am able to learn several new things through hands-on practice. I feel I am fortunate that I have a scope to turn my learning into practical and an opportunity to know better the professional environment at this age.
Reflective observation
In my opinion, while working at DPD Courier Waitrose delivery service, I had to maintain a strict routine and be punctual to the time. Delivering service has helped me to understand the significance of operational collaboration while performing the logistic operation. As quality consumers deliver remains the main motto for all organizations irrespective of size, thereafter maintaining collaboration and communication is effective in my opinion. While working as an Amazon delivery driver, I identified the importance of both verbal and written communication skills. I also realized the effectiveness of technological skill and open sharing of knowledge for both professional and personal growth at the individual level despite the profit gained and others.
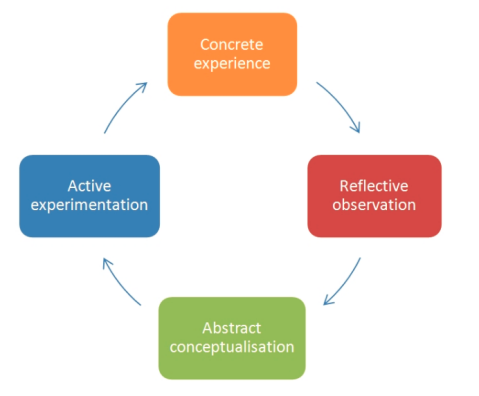
Figure 6: Kolb’s reflective model
(Source: self-created)
Abstract conceptualisation
Both employability experiences were new for me in different aspects including organizational structure, policies, work culture and others. What I found similar is that both experiences allowed me to better reflect on my existing personality traits and better shape my future career vision to work hard. At the starting phase of my first work experience, I found that I had poor communication skills and collaboration abilities. Due to this despite different positive experiences, I exhibited potential hindrances in the group activities to convey my opinion or accept the instructions of others. Besides, employability experiences, especially international business context, led me to refine my personality traits and improve my confidence in my
working pattern. I feel now I am much more confident in making my future decisions which help me to achieve my future target.
Active experimentation
Focusing on the all-over employability experiences, I can say that I need to work more to bring an improvement in both areas including my existing skill sets and vision towards the globe. The development of an action plan can help me to bring significant improvement in the area of communication and collaboration. Strategies such as going for listening more yet remaining specific, conducting more group work, thinking before speaking, and others can help me enhance my communication ability. Besides, engaging with different online courses can also help me to be a better version of myself and ensure high self-esteem.
References
Agbarakwe, U.H. and Bredino, M.S., 2024. Perspectives on Unemployment in Nigeria: Lessons from Cuban Economy. International Journal of Development and Economic Sustainability, 12(1), pp.52-61.
Bebbington, A., Chicchon, A., Cuba, N., Greenspan, E., Hecht, S., Bebbington, D.H., Kandel, S., Osborne, T., Ray, R., Rogan, J. and Sauls, L., 2020. Priorities for governing large-scale infrastructure in the tropics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(36), pp.21829-21833.
Cornelissen, J. and Cholakova, M., 2021. Profits Uber everything? The gig economy and the morality of category work. Strategic Organization, 19(4), pp.722-731.
Cowling, C., 2020. Gendered geographies: motherhood, slavery, law, and space in mid-nineteenth-century Cuba. In Motherhood, Childlessness and the Care of Children in Atlantic Slave Societies (pp. 236-250). Routledge.
Delgado, I.P., 2023. Cuban industrial development and its heritage. In Social Struggle and Civil Society in Nineteenth-Century Cuba (pp. 103-124). Routledge.
Djuraeva, L., 2021. Importance of the Innovative Business Models for the Future Success of the Company. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 100, p. 01013). EDP Sciences.
Dobusinessjamaica, 2021. MARKET ASSESSMENT CUBA. Available at:https://dobusinessjamaica.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/Market_Assessment_Cuba.pdf[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Drewniak, R., 2020. Strategic Alliance and Process Innovation: The Moderating Role of the Alliance Duration and the Firm Size. Building Future Competences. Challenges and Opportunities for Skilled Crafts and Trades in the Knowledge Economy, 2, pp.74-93.
Fernández, M.C., 2022. V. 1. Electric vehicles in the Cuban transport system. Copyright© 2022 Writers & Finland Futures Research Centre, University of Turku, p.309.
García-Rodríguez, F.J., Ruiz-Rosa, I., Gutiérrez-Taño, D. and Gil-Soto, E., 2020. Entrepreneurial intentions in the context of a collectivist economy: a comparison between Cuba and Spain. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, pp.1-19.
Ghauri, P., Strange, R. and Cooke, F.L., 2021. Research on international business: The new realities. International Business Review, 30(2), p.101794.
González, D.C., 2023. Present and Future of Environmental Law in Cuba. FIU L. Rev., 17, p.507.
Grabher, G. and van Tuijl, E., 2020. Uber-production: From global networks to digital platforms. Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space, 52(5), pp.1005-1016.
Griffin, R.W. and Pustay, M.W., 2020. International business: a managerial perspective. Pearson.
Help.uber, 2024. Uber Products and Services. Available at:https://help.uber.com/riders/article/uber-products-and-services?nodeId=1b505b35-7f14-4b04-a3c5-dc656d7787ed[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Henken, T.A. and Santamaria, S.G. eds., 2022. Cuba’s Digital Revolution: Citizen Innovation and State Policy. University Press of Florida.
Hill, C., 2008. International business: Competing in the global market place. Strategic Direction, 24(9).
Hill, C.W., 2022. Global business today. McGraw-Hill.
Khozen, I., Setianty, I. and Meiriza, F.D., 2021. What can we learn from business innovation fail-ure of uber in Southeast Asia market?. Inovbiz: Jurnal Inovasi Bisnis, 9(1), pp.124-132.
Li, J., Ding, H., Hu, Y. and Wan, G., 2021. Dealing with dynamic endogeneity in international business research. Journal of International Business Studies, 52, pp.339-362.
Lisa, S., Ibrahim, D.Y. and Borges, G.L., 2020. The success of startups through digital transformation. International Journal of Open Information Technologies, 8(5), pp.53-56.
Martinez, J.L., 2022. The Political Economy of Contemporary Cuba. (Post-) colonial Archipelagos: Comparing the Legacies of Spanish Colonialism in Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines, p.76.
Meyer, K.E. and Nguyen, H.V., 2020. Foreign investment strategies and sub-national institutions in emerging markets: Evidence from Vietnam. In Multinational Enterprises and Emerging Economies (pp. 67-97). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Milanés, C.B., Montero, O.P., Szlafsztein, C.F. and Pimentel, M.A.D.S., 2020. Climate change and spatial justice in coastal planning in Cuba and Brazil. Ambiente & Sociedade, 23, p.e01841.
Nahrstedt, J., 2021. US economic sanctions on Cuba: An analysis of the reasons for their maintenance (No. 162/2021). Working Paper.
Paul, J., 2020. Marketing in emerging markets: A review, theoretical synthesis and extension. International Journal of Emerging Markets, 15(3), pp.446-468.
Pedraza, S. and Romero, C.A., 2023. Contemporary Crises in Cuba: Economic, Political, and Social. FIU L. Rev., 17, p.609.
Pérez-Campdesuñer, R., García-Vidal, G., Sánchez-Rodríguez, A., Martínez-Vivar, R., de Miguel-Guzmán, M. and Guilarte-Barinaga, E., 2021. Influence of the socio-economic environment on the entrepreneurs behavior. Cases of cuba and ecuador. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 13, p.1847979021994509.
Pertierra, A., 2020. Creating order through struggle in revolutionary Cuba. In Anthropology and the individual (pp. 145-158). Routledge.
Rangaswamy, A., Moch, N., Felten, C., Van Bruggen, G., Wieringa, J.E. and Wirtz, J., 2020. The role of marketing in digital business platforms. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 51(1), pp.72-90.
Rodríguez, J.L., 2024. The Cuban Economy in the Last Decade: Balance and Outlook. Science & Society, 88(1), pp.27-48.
Romanò, S. and Barrera, D., 2021. The impact of market-oriented reforms on inequality in transitional countries: new evidence from Cuba. Socio-Economic Review, 19(2), pp.765-787.
Rottig, D., Muscarella, S. and Torres de Oliveira, R., 2020. Managing formal institutional challenges when entering Cuba: a multinational corporation perspective. International Journal of Emerging Markets, 15(1), pp.24-49.
Salas Vargas, N., García Gómez, D.A., Romero Romero, O. and Kiran Schulz, R., 2021. Marketing for business opportunities management on foreign investment and productive enchainments. In Social Innovation and Entrepreneurship in the Fourth Sector: Sustainable Best-Practices from Across the World (pp. 299-331). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Santos, F.A.D.N., Mayer, V.F. and Marques, O.R.B., 2020. Dynamic pricing and price fairness perceptions: a study of the use of the Uber app in travels. Turismo: Visão e Ação, 21, pp.239-264.
Sgrlaw, 2024. Opening the Door to Business Between the U.S. and Cuba. Available at:https://www.sgrlaw.com/ttl-articles/recent-developments-in-art-law/ [Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Shenkar, O., Luo, Y. and Chi, T., 2021. International business. Routledge.
Sinha, V.C., 2020. International business. SBPD Publishing House.
Spadoni, P., 2023. The external sector of Cuba’s economy: Performance and challenges. FIU Law Review, 17(3), p.635.
Statista, 2024. Cuba: Growth rate of the real gross domestic product (GDP) from 2012 to 2022. Available at:https://www.statista.com/statistics/388618/gross-domestic-product-gdp-growth-rate-in-cuba/[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Statista, 2024. Cuba: Total population from 2012 to 2022. Available at:https://www.statista.com/statistics/388512/total-population-of-cuba/[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Statista, 2024.Ride-hailing – Cuba. Available at:https://www.statista.com/outlook/mmo/shared-mobility/ride-hailing/cuba#:~:text=Cuba%20is%20expected%20to%20witness,US%243.60k%20by%202028.[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Tien, N.H., Ngoc, N.M. and Anh, D.B.H., 2021. Change of consumer behaviour in the post Covid-19 period. Change, 2(1), p.53.
Tradeclub.standardbank, 2024. Tax rates in Cuba. Available at:https://www.tradeclub.standardbank.com/portal/en/market-potential/cuba/taxes[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Uber 2022. Annual Report.Available at:https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1543151/000155278123000195/e23076_uber-ars.pdf[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Uber, 2024. About us. Available at:https://www.uber.com/in/en/about/[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Uber, 2024.Uber’s technology offerings. Available at:https://www.uber.com/in/en/about/uber-offerings/?uclick_id=f9b17fca-8eaa-47b0-be0a-684db7340ff2[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Uber, 2024.What is Uber all about? Fun facts about Uber’s history. Available at:https://www.uber.com/en-ZA/blog/what-is-uber-facts/[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Williams, R.G., 2022. The Political Economy. In The Oxford Handbook of Central American History (p. 253). Oxford University Press.
Worldfinance, 2024. Cuba and US become stronger neighbours. Available at:https://www.worldfinance.com/special-reports/cuba-and-us-become-stronger-neighbours[Accessed on: April 15 th, 2024]
Yun, J.J., Zhao, X., Wu, J., Yi, J.C., Park, K. and Jung, W., 2020. Business model, open innovation, and sustainability in car sharing industry—Comparing three economies. Sustainability, 12(5), p.1883.