Question 1
| Trait | Will West | William West | Person 1 | Person 2 |
| Height (fig 1) | 178.5 | 177.5 | 179.1 | 178.1 |
| Arm Width (fig 2) | 187.0 | 188.0 | 186.5 | 187.5 |
| Height seated (fig 3) | 91.2 | 91.3 | 90.3 | 90.5 |
| Head width (fig 4) | 19.7 | 19.8 | 19.7 | 19.7 |
| Head length (fig 5) | 15.8 | 15.9 | 16.0 | 16.1 |
| Cheek width (fig 6) | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.7 | 14.7 |
| Right ear length (fig 6) | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.6 | 6.4 |
| Left foot length (fig 7) | 28.2 | 27.5 | 28.0 | 27.8 |
| Third left finger length (fig 8) | 12.3 | 12.2 | 12.3 | 12.3 |
| Small left finger length (fig 8) | 9.7 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 9.7 |
| Left forearm length (fig 9) | 50.2 | 50.3 | 50.1 | 50.3 |
| Distance | Will West | William West | Person 1 | Person 2 |
| Will West | 0 | 0.1 | ||
| William West | 1.0 | 0 | ||
| Person 1 | 1.0 | 0 | ||
| Person 2 | 0 |
Question 3
Verifications
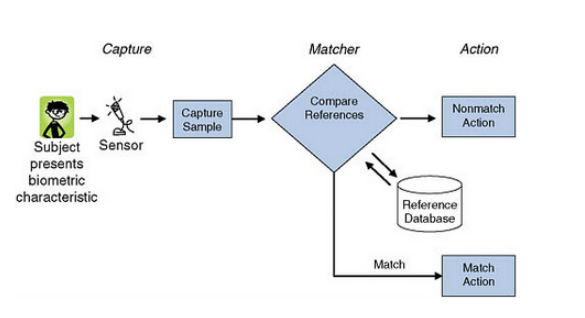
Verification frameworks look to respond to the inquiry “Is this individual who they state they are?” in the verification framework, an individual presents oneself as a particular individual. The framework checks their biometric against a biometric profile that as of now exists in the database connected to that individual’s record so as to discover a match. Verification frameworks are commonly portrayed as a 1-to-1 coordinating framework on the grounds that the framework attempts to coordinate the biometric displayed by the person against a particular biometric as of now on document. Since verification frameworks just need to contrast the given biometrics. A biometric reference put away in the framework, they can produce results more rapidly and are more precise than distinguishing proof frameworks, in any event, when the size of the database increments.
Identification systems
Distinguishing proof frameworks are not the same as confirmation frameworks in light of the fact that an ID framework tries to recognize an obscure individual, or obscure biometric. The framework attempts to address the inquiries “Who is this individual?” or “Who produced this biometric?” and must check the biometric introduced against all others as of now in the database. Recognizable proof frameworks are depicted as a 1-to-n coordinating framework, where n is the all-out number of biometrics in the database. Criminological databases, where an administration attempts to recognize an inactive print or DNA disposed of at a wrongdoing scene, frequently work as distinguishing proof frameworks
Question 5
A biometric framework is a framework that permits the acknowledgment of a specific normal for an individual utilizing scientific calculations and biometric information. There are a few employments of biometric frameworks. There are frameworks that require enlistment upstream of clients. Other recognizable proof frameworks don’t require this stage.
Enlistment mode is a learning stage that plans to gather biometric data about who to distinguish. A few information procurement battles can be done to guarantee a specific vigor of the acknowledgment framework to transient varieties of the information. During this stage, the biometric attributes of people are caught by a biometric sensor, and afterward spoke to in computerized structure (marks), lastly put away in the database. The preparing identified with the enlistment has no time imperative, since it is performed “disconnected.”
The check or verification mode is a “coordinated” correlation, in which the framework approves the personality of an individual by contrasting the biometric information entered and the biometric format of that individual put away in the framework’s database. In such a mode, the framework should then respond to the inquiry identified with the character of the client. Right now the check is completed through an individual distinguishing proof number, a client name, or a keen card.
The ID mode is a “one-to-N” examination, in which the framework perceives a person by coordinating it with one of the models in the database. The individual may not be in the database. This mode comprises of partner a character with an individual.
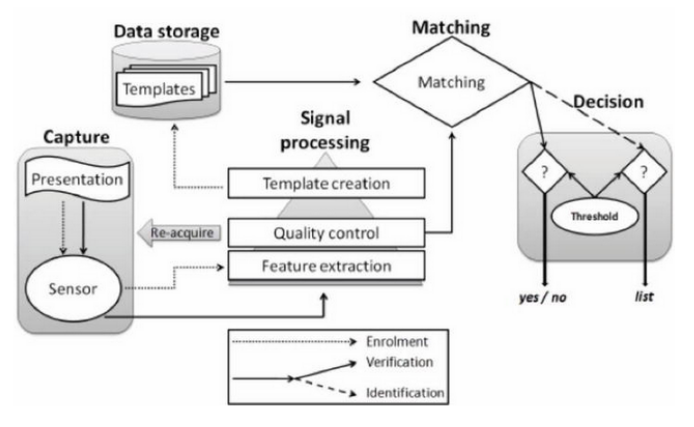
The catch module that speaks to the passage purpose of the biometric framework and comprises in obtaining the biometric information so as to separate a computerized portrayal. This portrayal is utilized later in the accompanying stages.
The module of sign preparing makes it conceivable to advance the handling time and the computerized portrayal procured in the enlistment stage so as to upgrade the preparing time of the check stage and the ID.
The capacity module that contains the biometric layouts of the framework enrollees. The coordinating module that looks at the information removed by the extraction module with the information of the enrolled models and decides the level of comparability between the two biometric information.
The choice module that decides if the comparability record returns through the coordinating module is adequate to settle on a choice about the character of a person.
Biometric Framework
Question 6
The six processes through which identification, verification and registration are required include the following;
- A lockable, and Operational barricade
- Devices or methods which need to be verified
- A mechanism which requires locking
- Devices which are used to sense alarms
- When one is requesting to exit the sensor
- When one has to sign in through access controls
Question 7
Application that does not require the internet to allow users to get access into the system are referred to as offline application systems. They use a standalone system to populate data into the database while the online system requires the internet for its use. For it to save the data on the server, internet is required. Most of this applications are cloud based meaning that they rely on the data being stored on the cloud.
Question 8
(a) Verification. For instance, an individual cases that he isunique and offers his unique finger impression; the framework at that point either acknowledges or dismisses the case dependent on contrasting the offered example and the enlisted example related with the guaranteed character. Numerous business applications, for example, physical or consistent access control, exchanges at a bank, charge card buys, and therapeutic records the executives are instances of check applications.
(b) Identification. Given an info biometric test, the framework decides whether this example is related with any of a typically enormous number of selected characters. There are two sorts of distinguishing proof situations. In constructive recognizable proof, the individual states that the biometric framework knows him. In antagonistic recognizable proof, the individual declares that the biometric framework doesn’t have any acquaintance with him. In the two situations, the framework affirms or discredits the individual’s affirmation by procuring his biometric test and looking at it against all formats in the database.
Question 9
To begin with, various kinds of exceptionalism might be predominant in a given nation simultaneously, and all through various periods of its history. Our typology will be useful in ordering, looking at, and imagining the assortments of exceptionalism crosswise over time and world locales. A closer assessment of exceptionality talks should likewise reveal more insight into the significant inquiry as to under what conditions what sort of exceptionalism perhaps develops. At the end of the day, does exceptionalism regardless of how non-exceptionality it is at one point in time fundamentally joined an inclination toward exceptionalism and, along these lines, the contention inclined attributes of the settler type? How strong are considerate types of exceptionalism?
Question 10
Biometrics is the specialized term for body estimations and fingerprints It alludes to measurements identified with human attributes. Biometrics confirmation is utilized in software engineering as a type of ID and access control. It is additionally used to recognize people in bunches that are under reconnaissance.
Biometric identifiers are the unmistakable, quantifiable attributes used to name and portray people. Biometric identifiers are regularly sorted as physiological versus social attributes. Physiological qualities are identified with the state of the body. Models incorporate, however are not restricted to unique mark, palm veins, face acknowledgment, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris acknowledgment, retina and smell/fragrance. Conduct qualities are identified with the example of conduct of an individual, including yet not constrained to composing cadence, stride, and voice. A few scientists have authored the term behavior-metrics to depict the last class of biometrics.
Question 11
Performance means the ability for the biometrics to be detected by the device. In this case the performance of the device gadget used depends on the screening ability of the cameras use to scan biometrics. On the other hand acceptability is the ability to reject or accept the biometrics provided to an individual. In biometrics each file is stored on a personal file which the system has to check for it.
Question 12
Conduct identifiers are a more up to date approach and are normally being utilized related to another strategy in view of lower unwavering quality. Be that as it may, as innovation improves, these conduct identifiers may increment in noticeable quality. In contrast to physical identifiers, which are constrained to a specific fixed arrangement of human attributes, as far as possible to conduct identifiers is the human creative mind. Physical biometrics identifiers are, for the most part, immutable and device independent
Question 13
The difference between behavioral biometrics and physical biometrics is that physical biometrics include biometrics such as fingerprints, Irish and facial scans while behavioral biometrics are those features in biometrics which imitate changes in the environmental factors. Examples include the DNA strands which are identical in human factors.
Here are some examples of physical biometrics
- Face;
- Fingerprint;
- Iris;
- Hand geometry; and,
- Retina.
The best examples of behavioral biometrics include
- Dynamic signature;
- Gait recognition
- Keystroke recognition; and,
- Speaker verification.
Question 15
Human acknowledgment frameworks are intrinsically probabilistic, and consequently characteristically uncertain. The possibility of blunder can be made little however not disposed of. Framework planners and administrators ought to foresee and anticipate the event of blunders, regardless of whether mistakes are required to be inconsistent.
The logical premise of biometrics – from understanding the appropriations of biometric characteristics inside offered populaces to how people
Question 16
Horizontal biometrics include the biometrics such as the fingerprints, iris and DNA strands recognition. They system will have to check whether they are matching with the extracted sample in the system. The individual file is stored in the databases.
Question 17
Examples of the vertical biometrics include the height measurements, armpits length, and the size of the retinal Iris. The main functions leading to implementation of the vertical biometrics is to ensure that the mutated gene which are carried from parents to offspring are. Examples include the height, face recognition and the facial detection.
Question 18
In the year 1960s when the modern and high speed computers were invented is when the actual biometric system began to takes its way into the computing security environments. This is because biometrics rely on computers and the high speed servers for storage. This could not be possible while using computers which were slower in its processing speed.
Question 19
I don’t think they were the biometrics used for verification but was just a way the scientists were coming up with various theories to come up with the way in which they can handle the security issues to do with biometrics.
Question 20
Phrenology implies the psychology which is the art of analytical methods based on the beliefs by different people regarding the human features in the body. Hence it is not a science but just a theoretical beliefs of human nature.
Question 21
Anthropometry is a science which deals with measurements involving human beings. It is a science because it involves measuring which is consists of unit measurements used.
Question 22
The first biometric system to be implemented uses fingerprinting technique and was established in the year 1960s. it was the first geometry to be used commercially by the developers to provide security problems solution in different institutions. It was used both to verify and identify the users within the system boundaries.
Question 23
Yes at the areas of war, it is advisable that we can use biometric system in schools because it will help to identify intruders who may be entering into the school in cases they may be terrorists. Biometric systems will help to gap the issue of terrorism because only registered and verified individuals are recognized by the system.
Part 2
Question 1
Technology: these are the biometrics related to the change in the technology. For example modern mobile phones uses face recognition to verify the users of the mobile phone.
Scenario: these is the application of the biometrics depending on the situation which is in. scenario based biometrics include the biometrics taken for a particular reason such as the DNA for cases of child birth issues.
Operational: this is the use of biometrics for operational reasons. For example in schools where wars do happen can apply biometrics systems. The main reason why this is applied is to gap the cases of terrorism in certain areas of wars.
Question 2
System error: in biometrics system, errors normally occur due to the fact they the fingerprints may not be detected due to lose of fingerprints through friction by participating in heavy works which may cause crutches on your fingers. Also the age of an individual matters when it comes to face recognition because of the wrinkles appearing unusual in the face. This will cause the multifunctioning of the face.
Another system error is the tilted angle at which the object is taken a scan in. this is because the system recognizes these objects up to a certain angle.
Question 3
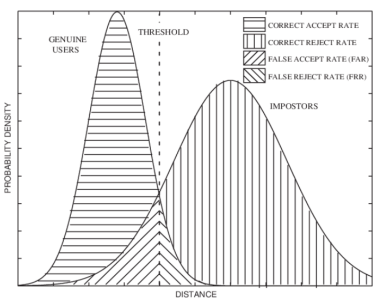
Biometrics are designed in such a way that it only accepts the traits between a certain threshold limits. This limit threshold can only be understood by the system but not seen by any individual. If the set of instruction are within the threshold limit, the system is set to accept the inputs which calls for false acceptance and if it is below or above the threshold, the system rejects the input data hence false rejection.
Question 4
For identification, the same applies only that the system is set to accept the entry of data within a certain threshold. Such that if the data has to be verified it will only accept the data within the threshold limit. In the case of false acceptance, the system will not be able to accept the input that does not meet certain visibility and vice versa for false rejection.
5. Explain the two levels of representations of fingerprint: local and global level.
Biometrics is the most widely used security measure in IT environment because it is considered as a unique element in nature. Fingerprints is one of the most known biometric measure which can be used to make our systems secure. Every human being is known to have an identical fingerprints. Fingerprints are classified into two categories which include;
- The global level structure – which has many ridges which forms specific shape which looks like arch, loop and whorl.
- The local level structure which is also known as minutiae. This class is categorized into two categories which are the endpoints and bifurcations. The two are used to identify the fingerprint.
Question 6
Coordinating score level combination methods in multimodal individual check traditionally use worldwide score measurements in the standardization and combination stages. In this paper, novel standardization and combination strategies are displayed to exploit the different insights of the monomial scores so as to decrease the real and impostor PDF projection covering and improve the check rate. Ioint mean standardization is a relative change that standardizes the mean of the monomial biometrics scores independently for the real and impostor people. Histogram evening out is utilized to adjust the factual appropriation of the monomial scores and make the entire separate insights practically identical. The displayed weighting combination strategies have been intended to limit the fluctuations of the different multimodal insights and diminish the multimodal PDF projection covering.
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Question 10
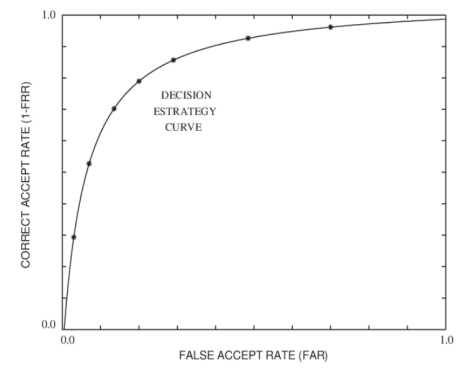
ROC Figure
REC Figure
Question 11
Technology: these are the biometrics related to the change in the technology. For example modern mobile phones uses face recognition to verify the users of the mobile phone.
Scenario: these is the application of the biometrics depending on the situation which is in. scenario based biometrics include the biometrics taken for a particular reason such as the DNA for cases of child birth issues.
Operational: this is the use of biometrics for operational reasons. For example in schools where wars do happen can apply biometrics systems. The main reason why this is applied is to gap the cases of terrorism in certain areas of wars.
Question 12
Here are some examples of physical biometrics
- Face;
- Fingerprint;
- Iris;
- Hand geometry; and,
- Retina.
The best examples of behavioral biometrics include
- Dynamic signature;
- Gait recognition
- Keystroke recognition; and,
- Speaker verification.