Introduction
The digital technology has made an entry into our life with an intention to solve certain traditional problems. However, with a passage of time, most of the solutions became a mainstream culture in themselves. At the turn of this century, software developers were designing digital solutions that can be accommodated in the real world, however, in the coming future when solutions developed by Artificial Intelligence (AI) will make a mark in the marquee, humans will learn the methods to find their space in a digital or virtual domain.
This is why most of the leaders are aware of the fact that digital transformation or switch over is not a destination, it is a journey. It is the formation of a new working culture and a distinctive world of new-age solutions which will weave around a new set of practices. It can, therefore, be understood as a process of insightful transformation that leverages the changes and opens up new possibilities (Matt and Benlian, 2015).
The public organizations in UAE are also working hard in the direction of a digital adaptation of the services, apart from catering to the needs of the efficiency and accuracy; these digital interfaces are generating unparalleled connectivity associated with the operations. The parameters of the service charters are changing, in a similar fashion, the satisfaction levels of the customers are changing because the technology is raising the bar to a new level. As a leader, it is a challenging face, the process of digital enablement is taking place in parts, striking a coherence among all the segments is a big challenge because sometimes the results of the endeavor are out of control for a leader.
The primary area where they need to work in the area of the familiarity level of the service providers and receivers with the digital transformation. Dealing with the digital technology is a two-way partnership, during the initial run, a person has to learn the technology in the second run technology takes the charge and changes everything, the systems, the processes, and the outputs. This constant change in the methods is adding a dynamism in the processes which is leading towards the generation of temporary needs related to the effective implementation of the technologies. As the leader, an individual is duty-bound to follow a contingency-based approach to understand these technology-based needs of various stakeholders. These needs arise for a passage of time, acts as a roadblock and disappear.
There is no denial to the fact that digital transformation is beneficial in most of the possible ways, still many stakeholders are not happy with this change because of they are required to come out of their comfort zones. As an effective leadership tactic, it is important for a leader to design and formulate some messages establishing it as a journey from “one comfort zone” to the “other swift and easy comfort zone.”
A failure in the deliverance of these messages can expose the exercise of change management into a zone where many risk factors can jeopardize its smooth growth. Apart from these processes generated threats many more deliberated roadblocks and traps are also blocking the path of the digital solutions. Most of the countries of the world faced these problems and now UAE is also facing the same problems. Cybercrimes, data breaches, and theft of sensitive data are primary among them. Cybersecurity is a sensitive issue; it demands the attentive nature of the employees to prevent unpleasant conditions. It is very important to understand the fact that digital transformation demands a constant increase in the competency levels of the employees and other stakeholders, the presence of anti-social elements makes it a complicated deal for the stakeholders, as a leader it is important for an individual to motivate the employees on the road of the development of new competency levels (Madichie and Al Athmay, 2013).
Monitoring and the injunction of the right methods at the right time is a necessary action that is required. Here a leader should remember the fact that he or she is not leading the pack by the virtue of “leading by an example.” Here the leader is required to look at it from the point of view of a contingency, in case he fails to come up with risk mitigation mechanisms or the methods that can serve as an injunction then it will be known as inefficient leadership at his part and it can show some adverse effects on the development of the process (AlaaEldin Ragab, 2014). It is very important for a leader to come up with some pro-active steps to salvage the situation, the exercise of contingency sometimes demands control as the primary exercise, as a leader practicing the contingency leadership a leader can rise up to the occasion and ensure control over the security needs and other risks.
As a contingency leader, it is important for an individual to have a look at the macro picture of the projects, a concise perspective on the key result areas can be the next step to mitigate the negative impact of the change. Most of the change management firms recommend a comparative analysis of the transformation of the business process on the scale of before and after.
When we consider this recommendation from the point of view of the public sector enterprises, we find an additional strength attached to the system. This strength is an outcome of the whole and sole control of the government over the matters. They can change the entire system in phases without facing any pangs of the competition. In other words, we can also say that the government sector can introduce better control over the issues and act as a leader to ensure a smooth transition from one phase of the technology to the other.
When we have a glance at the current preferences of the centralized bodies working in the direction of digital transformation we find that policymakers are inclined towards the introduction of technologies like “blockchain,” “analytics” and “IOT.” The introduction of the Artificial intelligence and enablement of the IoT solutions can certainly make a huge difference in the functioning of the government sector. The cumulative impact of these arrangements will bring down the numbers of the humans or the manual labors from the systems and decrease the margin of the errors to a minimal level. This transformation will also introduce a change in the business environment, the introduction of the automation in the system will write the new rules associated with the functionality and these new rules will also ensure cost-effectiveness in the process (Demirkan et al., 2016).
The role of leadership is pivotal during the course of change management, it is pivotal because apart from the technical and functional aspects of the operations the system demands a certain dose of organizational values, traits, and characteristics. In general conditions, leaders become the primary carrier of these values and represent these values as a trait of their own personality in order to become the face of the organization. During the phase of change management, it becomes important for them to be the “face of the change.” It is necessary because the employees look upon him for the direction, the model of contingency prescribes a different role for a leader.

Image1. Retrieved from https://businessjargons.com/fiedlers-contingency-model.html
This model clearly indicates that during the course of the contingency leadership situational variables guide the conduct and the decisions of a leader. The contingency style of leadership also forces a leader to adopt different roles and styles during the course of the progression of a change based project.
We can also term it as “Transformational leadership” this type of leadership makes it sure that all fractions of the stakeholders are involved in the process of the decision making.
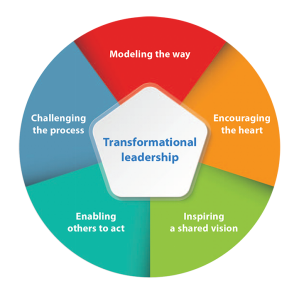
Image 2: Responsibility matrix associated with the Transformational leadership, Retrieved from https://www.americannursetoday.com/inspire-transformational-leadership/
In image 2 we can see a set of tasks or the areas where a transformational leader has to keep an eye. In the present context, transformational leadership is the best option. Under this type of leadership, it is required to think from the perspective of a team because a change in the behavior and the attitude of the team is the primary goal of the exercise. As we can see in image 2, the model of transformative leadership enables an individual to have a look at all the aspects of the problems from a distinctive point of views, it allows a leader to be ready with the necessary tools to handle certain conditions.
Transformational leadership ensures that a leader is switching his personality and focus in accordance with the best needs of the setup and matching steps in accordance with the dynamic needs of an evolving system and surrounding business environment (Awofeso et al., 2016).
In the year 2013, the ruler of the UAE Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum mentioned about the digital revolution in one of the speeches made by him. He said, “We want to relocate citizen service centers into every citizen device, enabling them to obtain their desired service through their mobile phones anywhere at any time”.
Under this spirit of reform, the government of UAE launched a series of digitally enabled products like refillable debits cards, Electronic voting machines, and many more films. Most of these services were following web-based and mobile-based service models. (Hessa Buhumaid, Margaux Constantin, and Jörg Schuber). The performance of these products came under scanner because of the
Transformational leadership is one of the most effective leadership approaches in this context. This approach ensures that all employees are involved in the decision-making processes and states the enormous importance of teamwork to fulfill the aims of digital transformation. This ensures that the employees get work according to their varying job roles in the company. Therefore, it can be stated that for public organizations, transformational leadership is one of the
The problem statement of this research states that adoption of traditional techniques or wrong techniques is causing delays and detrimental impacts on the digital transformation of the public sector in UAE, techniques like the contingency model can help the leaders in picking up the right preferences on the merit of the evolution of the situations in accordance with available tools, resources and affinity levels of stakeholders.
Although the overall review of the previous studies has been up to the mark there are still certain gaps in the existing literature. A detailed literature review of the available literature is apt to study the success of digital transformations that took place in other parts of the world. The focus of most of the literature is more on the process rather than the role of the leader or the people. Every country may have its own model of change in accordance with the education level and information levels of the employees. The process of this change is an interaction between the human ware and the software, the contingency model described by Stace and Dunphy describes a dynamic role for the leaders during each step, in the image 3 we can observe four quadrants representing the stages of the evolutions, as it is evident each quadrant demands a different type of leadership style.
Image 3: Contingency change model, retrieved from https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-3-319-52878-6_76
This model clearly states that it is the duty of the leaders to ensure that they clearly communicate the digital change vision and create appropriate channels of communication to ensure the success of the change occurring.
Furthermore, with effective leadership in place, the public organizations of the UAE could easily ensure the success of the digital transformation. It is of high significance for the public organizations of the UAE to increase the effectiveness of their leaders instead of totally focusing on the integration of advanced technologies. Image 3 describes four types of the style of change; ideally a transformation should focus on all the styles of the changes. The present literature review signifies the fact that currently the leaders are more focused on the integration of the technology and ignoring other aspects of the change. Style of the change is one such area, the demographic details of the UAE present an interesting spectrum of the population, this population can be termed as the causative factor behind the scale of the change.
Image 4: Scale of change at a micro-level for each phase and procedure, image retrieved from https://www.chinaabout.net/tofflers-model-on-akzos-case-of-leadership-change/
Image 4 presents a breakdown of the processes and methods to fix the scale of the changes at the level of each unit of the change. The contingency model allows a leader to monitor the program under the purview of its variable state and fix a turnaround time for a process implied by him. In the case of the UAE, the demographic spectrum of the population can force a leader to come up with some special programs or steps to remove the barriers.
Leaders with effective leadership abilities can make it possible for public organizations to integrate emerging technologies in the most appropriate and systematic way. The organizations would be capable of comprehending the dos and don’ts associated with digital transformation. The leaders will be responsible for influencing the workers to assist the change and provide them with a comprehensive knowledge regarding the aspects associated with digital transformation. Image 4 can be developed for each process separately. The contingency model purviews a change from the point of view of the jigsaw puzzle, the scale management diagrams can be considered as the parts of the macro picture, each fitting in a jigsaw puzzle to complete it.
Although it seems quite complex that what are leaders supposed to do with technologies, but it has to be observed that digital transformation is a sort of change and it is of utmost importance for the organizations to leverage the organization’s leaders in the process of digital transformation. The leaders devise clear and realistic change vision and communicate with the workers to make them comprehend the significance of the change. The leaders are the ones who would motivate the employees of the public organization to support the change and get involved. Overall, it would make it feasible for the public organizations of the UAE to receive active participation and assistance from the employees throughout the process of change. The leaders will be the ones reporting to the managers regarding the progress of the digital transformation and devise effective strategies in order to prevail over the barriers in the process of change. It is essential for the UAE public organizations to make sure that their leaders are actively involved in the process of digital transformation to mitigate the risks associated and the challenges related to the overall change process for accomplishing the change of proper digital transformation extensively.
The research question determined for this particular research has been presented in the section below:
- The implementation of a new digital domain is changing the dynamism of the change for the organizations of the UAE. What should be the criteria to fix the roles of leaders in this new domain where the technology experts and the process experts are on a different page of information?
- What is the response of the public organizations of the UAE in terms of the adaptation of new technology by the public organization? If the choices are variable then how a technology leader can ensure a smooth transition between the technologies?
- What are the key factors that public organizations of the UAE are facing in regard to the clash between technological leadership and procedure based leadership? How does a leader can find a role for him during this transition phase with the help of various management and leadership models?
- What are the technological leadership approaches adopted by the public organizations in UAE?
- How has the approach towards the adoption of technological leadership affected the technological preferences of the public organization in the UAE?
- What challenges are associated with the technologies preferred by the public organizations in UAE?
- How can a leader, mitigate these challenges and ensure a smooth transition by adopting certain change management tactics to mitigate the shocks and the negative impacts of the process of the change?
Research Aim and objectives
The primary aim of this research program is associated with the dynamic role of leadership in the process of the digital transformation in UAE public organizations. Furthermore, the research also aims in identifying different technological leadership approaches and the breakdown of the processes in accordance with the contingency model to serve certain situations to move the changes on an optimum path, favoring all the stakeholders for a smooth transition. In addition to it, this research will also determine fundamental challenges and the root challenges faced by these organizations with a purview of the root causes inflicted by technology adoption. During the course of this research, the researchers will also try to develop a set of recommendations based on the probabilities presented by the analysis given by the contingency model framework.
The objectives formulated for this particular research have been defined in the section below:
- To identify the readiness of UAE public organizations with relation to the acceptance of technological adaptation.
- To identify the preparedness of the leaders in the course of the implementation of the technological leadership approaches in the public organizations of UAE.
- To determine the quantum of the challenges faced due to the technologies preferred by the UAE public organizations.
- To determine the paths of recovery to mitigate the impact of the challenges
- To recommend strategies and methods based on various approved leadership models to mitigate the impacts of the challenges identified regarding changing leadership and technological preferences.
The Significance of the Study
The current research is really significant because it explores the problem caused by the digital transformation of the public sector of the UAE at a different level. Most of the previous works present a standardized account of past success stories. The culture and the demography of UAE are different from the rest of the world and this is why a new and unique set of problems is on the cards. The scope of this study also covers to create and suggest strategies and techniques that must be applied in order to accomplish effective and extensive digital transformation.
The role of leadership is crucial because digital technologies are standardized and approved solutions whereas human behavior and IQ levels are unpredictable, a leader becomes a necessary human link in this process. This is why it also focuses on the role and impact of leadership on digital transformations or change along with the preferences of UAE public organizations concerning the adoption of emerging technologies.
During the last few years, the field of technology has been growing at an exponential rate making it compulsory for every kind of organization to integrate modern technologies to achieve success and operate effectively. This integration is a tough task in many ways because of the previous working cultures that have a strong impact on the working dynamisms.
Failing to adapt the technological and digital changes would put the public organizations of UAE in a trembling position and snatch their ability to compete with the private organizations. It can cause chaos and bring down the credibility of these organizations. Thus, it is of utmost importance for the UAE public organizations to integrate progressive technologies to meet the demand of the people extensively. The definition of the term progressive has a greater meaning attached to it, it signifies the evolution of a society with the digital methods and it can be considered as a major change in the terms of the economic attributes that are surrounding it.
The significance of this study is related to the implementation of this integration with the help of certain leadership and management drove models.
The current technological preferences of the UAE public organizations accentuate on analytics, IoT, and blockchains. All these changes are in the state of experimentation, and the service providers are promising long term gains, for instance, big data can become the key property of the decision-makers, blockchains will allow the local businesses to survive and compete against the onslaught of the “online giants.” The direct impacts of the IoT are visible in the areas of the cost-cutting where human robots and intelligent devices are replacing human beings. For instance, we can take the example of a simple sensor control replacing a watchman from the door.
Apart from the technological preferences of the UAE public organizations, they are facing certain challenges associated with the adoption of technologies. These challenges are making it difficult for organizations to evolve digitally. It is of high importance for the public organizations of UAE to put effective leadership in place to achieve the change of digital transformation successfully. The use of contingency models is the need of the hour because this model has the power to study the roles of various stakeholders and come up with right injunctions for each macro and micro process associated with it. It is very important to understand it from the perspective of project management. The technology-based leadership only instigates a regular project management scheme where one phase is dependent on the other, on the other hand, contingency model allows a leader to pick up the task from the perspective of an agile project management model where all the fractions of the project work simultaneously.
The leaders would make it possible for the UAE public organizations to direct the employees properly towards the digital change. With the help of the tactics involved in the agile project management, under this type of an arrangement leader can keep a check on the scope of the processes and streamline them to ensure smooth and timely delivery of the goods or the changes without affecting the main structure in the terms of the outputs.
The leaders will be the ones responsible for formulating effective digital strategies and execute them to increase the effectiveness of the overall change process. The synchronization of the digital strategies with the main operations is also an area that can be taken up as a loop-based action research program, a lean and mean feedback chain can support both the ends in the terms of the procurement and adaption.
The leaders will be the ones to identify the technological needs of the organization to provide the best quality services to the people of the nation as well as live up to their expectations extensively.
Outline of the thesis
Technological preference can be considered as the preferred medium or device of users based on several technological choices that are available. A leader can inspect the technologies on the merits of the shortest possible route and ease of the adaptation.
The different public organizations take huge measures to be aware of the technological advancements that exist today and their benefits (Choi and Chandler, 2015). The public organizations are capable of bringing in a change at a bigger quantum and this is where the transformation is important for the country. These changes may have a ripple impact on the other sectors of the economy. These ripple effects can further weave around a new economic and administrative setup, as a leader, it is important for a person to consider these changes as well.
The past set of practices suggests that organizations have educated themselves regarding advancements in technology and their benefits for all kinds of businesses (Schwarzmüller et al., 2018). The current technological preferences of public organizations in developed countries lie with analytics, blockchain, and IoT (Internet of Things).
The usage of data analytics has become an important aspect of digital transformation. This is because the increasing number of organizations is viewing data as a commodity and as a result, it has become a significant area of technology investment among these organizations. Most of the companies start their journey at an interface where they collect data as a commodity, however, after a point of time this data becomes capital for them and this capital helps them in the process of decision making and other aspects like an expansion of the business, etc. Data analytics can help in managing the flow of ingredients on the assembly line along with aiding the organization’s automation procedures for several applications. Data analytics have become an important ingredient in the process of the inventory management for various organizations and this high time for the public sector of UAE to churn out the advantage of this new age boon adding an economy in the operations.
Embracing data analytics by the organization will truly improve their productivity and as a result, it will enhance important business decisions. Some of the most significant types of analytics that is used by these organizations are:
- Descriptive analytics: This type of analytics includes foundational reporting and business intelligence conducted by most organizations.
- Prescriptive analytics: This type of analytics involves technology that provides recommendations for human activities.
- Predictive analytics: This type of analytics uses data insights in order to anticipate human activities in the future.
Blockchain technology has helped various organizations in digital transformation because it enabled the organizations in maintaining the records through the decentralized database and distributed ledger on a continuous basis. Today, organizations can synchronize all the information over the internet which is protected by the cryptographically protected block. The cryptographic characteristic of the BlockChain has gained a very high level of trust among organizations as it has eliminated all the security risks. It has become virtually impossible for the hackers to break through the BlockChain because every single transaction over the internet would have to be overwritten and its backups get deleted. Blockchain technology is an attempt to kill the monopolies of the big giants like Amazon.inc and others, although the success of this technology is under suspicion right now, still it is one of the most promising technologies that can gain a great currency in the coming future.
IoT (Internet of Things) has digitally transformed business by the rapid analysis and processing of data in milliseconds. With the evolving customer expectations, more enterprises are forced to transform the existing business with the help of IoT. It has resulted in opening up new business opportunities, delivering tailored and meaningful customer experience, enhancing business efficiency, improving employee productivity and reducing operating costs. The Impacts of the IoT are visible in UAE, it is supporting the administration in bringing down the number of the human beings in the operations and moving ahead in a direction where the standardization of the services will herald a new era of digital technology-enabled tangible advancements.
| Technology | Description of technology | Benefits |
| Analytics | Obtaining data, for the modification of current business methods and practices (Ilias O. PappasPatrick MicallefMichail N. GiannakosJohn KrogstieGeorge Lekakos) | transformation of business and society (Chen et al. 2012; Loebbecke and Picot 2015). It mechanizes processes and transforms businesses (Ng, 2018) Prediction of outcomes (Reed and Dongarra, 2015). |
| blockchain | The blockchain is a distributed database of records of all transactions or digital events that have been executed and shared among participating parties. (Amish Gupta) | It enables the distribution of digital information but prevents it from being copied (Ameer Rosic, 2019) |
| IoT (Internet of Things) (Al-Fuqaha et al., 2015). | Kevin Ashton coined the phrase ‘Internet of Things’ in 1999 and defined it as follows:The IoT is an integration of human culture with the internet. (Steve Ranger,2018) | The main benefits of IoT are identified as Connectivity: (Mok, 2017), Wellness (Lindsay, 2017) Conservation (Hicks, 2017) and Personalization(Lindsay, 2017) and others. |
According to Maja Korica, associate professor at Warwick Business School, in 2017, Amazon introduced over 50,000 new robots in 2017 and the overall technological advancement is estimated to have replaced 20% of its workforce. This signifies that labor has been reduced immensely due to such technologies (Christidis and Devetsikiotis, 2016). As per the theory of technological change, the TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT POSES A DANGER OF REPLACEMENT TO THE LABOUR (Graetz and Michaelis, 2015; Bonin, Gregory, and Zierhahn, 2015, p. 21; Arntz, Gregory, and Zierahn, 2016, p. 25). Technology is expected to replace around 1.5 million laborers in England according to the Office for National Statistics (ONS).
Another preference of technology adopted by public organizations is machine learning through their enterprise applications. In addition, they have initiated the utilization of sensors that can regulate the flow of traffic in an enhanced manner (Bodolica and Spraggon, 2014). Digitalizing and growing technologically is helping them gather various data and information sources. It leads to a better understanding of the gather information amongst various levels and agencies due to which they are able to make well-informed decisions. Blockchain helps these public organizations such as the government for providing transparency while maintaining the security of the transactions. Blockchain helps in offering wide possibilities for these organizations regarding functions that lead to the transfer of funds and storing records in ledger with good security (Broadbent and Lelliott, 2016). The introduction of artificial intelligence or AI can help in automating most of the operations of a business that can ease or reduce the use of manual labor. In addition, it behaves like a cost-effective solution that is gradually changing the concerned business environment.
CHAPTER TWO: DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION IN PUBLIC SECTOR ORGANISATIONS
The theoretical background for this particular research can be established through the review of the literature. A literature review can be considered as an evaluation and search of existing literature for the chosen subject or provided area of topic. It is the documentation of state of the art in alignment with the specific topic or subject. There are four vital objectives of a literature review that include surveying the literature for the selected area of topic and synthesizing the gathered data and information from each literary source into separate summaries. The other objectives include conducting a critical analysis of the gathered information through identification of literature gaps and limitations in the present knowledge and presenting the literature in a systematic manner. The literature review helps in grasping in-depth knowledge regarding the area of the chosen topic or subject (The Royal Literary Fund, 2019). This section is one of the most vital parts of research projects since it helps in moving forward with the available literature and forms a base for research activities.
Introduction
The concept of digital transformation is quite deep in nature. It is the integration of digital technology into all the areas of business through which business leaders get the result in the form of fundamental changes in entire business operations. Such fundamental changes help the business to achieve high business goals along with delivering value to the customers. In this modern digital era, digital transformation has become an imperative for all businesses, either it is a small scale business or a huge enterprise. It is creating an interface where the rest of the businesses are seeking space. In a global world where free skies are all set to become a reality, digital transformation is all poised to set the benchmarks of the services and categories. The contingency model associated with digital transformation can allow a leader to keep a check on these global standards and plan things in accordance.
What is Digital transformation?
Digital transformation refers to the integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, changing the operations of the business and services offered to customers. It requires the organizations to continuously experiment novel technologies and be prepared for the consequences. The same idea is expressed by (Kane et al., 2015) who defines digital transformation as the transformation of an organization along with its processes, activities, models, and competencies for leveraging the opportunities and increasing its influence on the society through a prioritized and strategic manner. However, these transformations are usually made by taking the future and present shifts into consideration (Kane et al., 2015). George Westerman, MIT principal research scientist defined digital transformation as an indicator of fundamental reconsideration of usage of technology, people and processes by an organization for the purpose of modifying business performance.
Usually, digital transformation is mainly used in the context of business. However, recently its impact has been observed on public organizations through the leverages of emerging current technologies. Digital transformation has the capability of altering the various dimensions of the concerned business (Oswald and Kleinemeier, 2017). In other words, digital transformation can be considered as a journey with intermediary goals connected to each other. It strives to maintain constant optimization around divisions, processes, and ecosystems of the business. (Sow and Aborbie, 2018) posted an article on 14 August, 2017 in which he stated that digital transformation is aimed at creating potential capabilities for complete leveraging of opportunities and possibilities through new technologies that can influence the business in a better and faster way along with innovative measures Dr. Chakib Bouhdary the Digital Transformation Officer at SAP asserts that The journey of such transformation requires commitment and clear and appropriate approaches based on the organizational maturity and the goal of digital transformation (Westerman et al., 2012).
According to Bin Taher et al. (2015), digital transformation is present within almost all industries across the globe. It is necessary for an organization to adapt to the changing aspects of the concerned market in order to maintain the stability of its productivity and current position in the market. In the current scenario, organizations that fail to adapt and understand the importance of emerging technologies reached a stagnant point in their business which gradually led to overall organizational failure. As per Wikipedia, Digital transformation originated during the second half of 21th century. It then faced rapid growth throughout the century due to which most of the organizations belonging to any industry have gradually transformed itself digitally. It has become a necessity for organization to transform at an extremely fast pace due to rapid changes and innovations in the technological world that leads to change in the modern expectations of the consumers (Khan, 2016). There are several mobile technologies, cloud computing, artificial intelligence and such other innovations in technology that brings about drastic change with the ways consumers receive information that can help them understand the type of the product or service along with its quality. The impressive technological innovations change their expectations from the business and service providers. Digital tools have transferred the way stakeholders and employees perceive the organization with high level of expectations.
There are several vital technologies that create a sense of urgency regarding digital transformation. Moreover, it supports the concept of digitizing organizations. However, utilizing only one piece of technology or application will not help in the successful digital transformation of an organization. There are a number of vital processes that are necessary for implementing the process of digital transformation. For instance, cloud computing helps in gaining quick access to essential software required for some specific operation along with new updates, functionalities, and data storage. There are several other technologies necessary for carrying out digital transformation such as information technology, machine learning, blockchain, virtual reality, augmented reality, Internet of Things (IoT), and social media (Azmeh and Foster, 2016).
According to (Khan, 2016), in order to understand the importance of these technologies for an organization, it is necessary to understand the features of each of these technologies. For instance, many organizations in the current scenario are shifting to cloud platforms due to the benefits offered by it. In an article published by (ESDS, 2013), the major benefits of cloud platforms were identified to be a reduction in costs, optimization of resources, ease of maintenance, security, scalability, collaboration, and mobility. Information technology is one of the most necessary entities of any organization. It plays a critical role in business organizations. IT is used by most of the departments of an organization. IT provides a competitive edge to the business and facilitates the expansion of products and services. IT helps organizations to monitor the expenses and profits and helps the management to cut costs (Dery et al., 2017). IT also helps the organization to survive in a competitive business environment and accomplish tasks faster by enabling digitalization (Sisk, Annie, 2019). Basic activities can be done virtually due to which information technology is essential for a business. Basic transaction processes and communication with distributors, suppliers, and customers are made easier with the application of information technology. The influence of information technology can be observed through different effects such as easy flow of data and information, efficient and effective process of transaction, interactivity, and flexibility of decision support systems, virtual support through workgroups, executive support, management of data, and communication (Khan, 2016).
Leadership can take the advantage of social media for the purpose of promoting digital transformation in the public sector in UAE since it is the most powerful means of communication in today’s world and has risen hugely in popularity. Various renowned agencies scattered around the web promises business leaders to help them with digital transformation. Furthermore, with the help of social media, communication has become more personalized and targeted than any other form of media where organizations get the chance to receive customer feedback immediately and on daily basis (Berman and Marshall, 2014). Outreaching to the public using traditional measures are very expensive. Social media such as the web 2.0 applications can be utilized by public organizations particularly government agencies to cut the costs related to communications with the citizens and to improve the standard of the services offered to citizens (Nasiopoulos et al., 2011a; Nasiopoulos et al., 2011b).
Social media is highly essential for crisis communication. Before the concept of social media, communication was difficult during emergency situations and reaching out to a maximum number of individuals was a real challenge. Currently, maximum numbers of people are associated with social media due to which it is easy to reach out during emergency situations. Social media instruments can be used for effectively handling communication during a crisis as expressed by (Pera, 2015a, b; 2014) that readiness, knowledge, and participation in crisis reaction can be stimulated by novel social media technologies by facilitating observation and interaction. Moreover, it is easier to engage the citizens around the city by letting them know about the different initiatives taken by the government. It ensures the citizens learn their importance. This leads to better trust-building with the public. It is easier for the government parties to connect to the citizens on low stakes, instant feedback, effective messages, and current social trends (World Economic Forum, 2016). Social media can develop the prospects of communication and reduce the confusion and inaccuracy that may arise during a crisis. (Veil et al, 2011)
What is the Public Sector?
The public sector goes hand in hand with the private sector to contribute to the economic development of a country. According to AlShamsi and Ajmal, (2018), the public sector consists of several organizations that are operated and owned by the government of the host country. The existence of public sector is aligned with need for services for the general public or citizens of the particular country. The public sector has similarities with the organizations of the voluntary sector; however, public organizations usually are not focused on generating profits against their business activities like private businesses. The primary source of public sector in generating the Funds for certain activities are raised through different kinds of sources such as fees, taxes, and financial transfers through other governmental levels. Different public organizations across the globe employ unique ways of raising funds for their operations (Doherty et al., 2018). Public organizations are generally based on education, emergency services, electricity, fire service, oil and gas, infrastructure, healthcare, police services, law enforcement, public transit, postal services, waste management, and social services. Moreover, the presence and existence of public organizations can be observed on three levels that include local that is (county or municipal), regional (provincial or state) and national (federal) (Rosenbloom, 2000).
Management studies of Digital Transformation in the public sector
The public sector has come a long way in terms of digital transformation, the first steps with the beginnings of e-government in the 2000s until today. Indeed, the modernization of infrastructure and trades is a major challenge for the sector, subject to a high level of requirements in terms of public expenditure control, risk management, and compliance standards. It has also had to overcome various cultural, budgetary and structural obstacles related to a very vertical hierarchical model, silo operation and traditionally longer investment and programming cycles.
To this list of constraints is added the technical and technological ones inherent to the aging technologies then in place or to situations of proprietary confinement preventing many public organizations from switching suppliers, even after the expiry of their contractual commitments.
It is interesting to note that the digitization of the public sector and its services constitute a strong expectation on the part of citizens. According to the Digital Barometer 2017, from a study conducted by the Research Center for the study and observation of living conditions (CREDO), the French aspire to a “digitization of civic life”, a reflection a growing use of the internet for other areas of their daily lives. In 2017, they were 67% to perform their administrative or tax procedures online and this figure is growing every year. Results that confirm the need for a quality, reliable and continuously available cloudless service.
Choosing adapted technological solutions, the key to success
Continuing on the road to success their digital transition and optimize their efficiency, for the public actors, by choosing suppliers with an excellent understanding of their issues. There is still progress to be made to ensure that the digital solutions offer answers perfectly to the complex and very specific needs of the sector, inherent to the heterogeneous nature of its various fields such as health, transport, education and or administrations and communities.
While it is difficult to define a common approach that may be suitable for all these markets, there is no doubt that the protection of public data is a priority strategic priority for all public actors, even more than for the private sector. In fact, hospitals, communities, energy suppliers and universities have a wealth of data that they need to protect and exploit to improve their services.
To cope with the explosion in the volume of data they must manage and take advantage of the benefits of digital disruption, these institutions must quickly move towards an intelligent management approach to this data. To do this, it is essential to prioritize the availability of data and to break silos that slow down their access and hinder the effectiveness of the tools. The intelligent data management model relies on the ability to move data agilely, according to events that occur and can be considered abnormal, and also involves rethinking the manual approach to data protection and evolving towards a behavioral model, which is based on automation. This allows the system to detect risks and anomalies on its own.
The digital transformation of the UAE public sector
In the current age, the UAE government has taken initiatives to modernize the services offered to the citizens. According to Ahmed and Abdalla Alfaki (2013), the performance goals of a Government mainly focus on reducing costs and generating revenues on new grounds and benchmarks set through peer government agencies frequently. However, the government in the UAE has adopted a different kind of approach over the last few years. Their main focus is based on delivering services that can compete with the best services offered by private organizations across the country. They aim to provide citizens with services equal to the service offered by five-star hotels with the efficiency and effectiveness of leading banks. It integrated the utilization of technologies in the services offered by the government (Al Athmay, 2013). Around the year, they adopted an initiative to relocate the service centers for citizens into the device of every citizen in the country that can enable them to obtain or avail the required services through any electronic from any location at any time. The success of a government can be determined by their approach to reach out to the citizens before they reach out to the government. For countries like the United Arab Emirates, the primary challenge exists in huge areas of demographic regarding delivery of government services.
As stated by Alameri (2013), the population of the UAE consists of different kinds of nationalities that are mostly transient with a population that natively does not belong to the country. 88% of the total population is nonlocal and transient. Due to such mobility and diversity, it is necessary for the government to deliver services of the best quality and such that cannot be replicated by the topmost private organizations. They can gather resources and knowledge from around the world that can be easily understood and navigated by both old and new residents of the country. Maximum individuals that build the overall population of the country are young due to whom it is necessary to indulge in innovation that can help in catering to the needs and requirements of such a population (Khan et al., 2014). For instance, apart from the call centers and field offices, it is necessary to offer web-based and mobile-based services. In light of such changes, challenges, and goals of the country, the government of the UAE has managed to invest for noteworthy improvements in its services that can contribute to the satisfaction for citizens all around the country.
According to Schiliro (2013), these efforts made by the government include introducing electronic machines for voting purposes, offering debit cards that can be refilled for facilitating the payments towards government fees and announcing awards by the government for the most suitable solutions for services that are technologically driven. For rapid implementation with efficiency and effectiveness, leaders break down typical government groups and unify separate entities for enabling them to work together (Al-Jenaibi, 2015). There are four major sections that have been governed by the government through digitization. These include rewards for innovation for designs of applications and crowdsourcing, advanced e-voting that behaves as a path for greater participation and convenience, introducing convenience for payments to the government through electronic measures, and developing a standard and culture of excellence.
According to Kamali et al. (2015), in their initiative to create a government that is customer-centric, they were able to provide 96% of the crowd with services associated with 337 departments of the government. For their current target of providing 80% of citizens with most of the governmental services, they have started promoting the concept of mobile services with finest user-friendliness. Around the year 2013, they introduced the Best m-Government Award. There were four types of participants for the awards that included Arab, national, and entities of international government along with students pursuing their education in the universities of UAE (Bason, 2018). The awards were based on innovation in education, health, social affairs, environment, security and safety, commerce and economy, tourism, infrastructure, and transportation. The solutions were awarded based on degree of innovation and ease of use along with effectiveness and efficiency. Moreover, these solutions should be associated with the services offered by core government departments and that are essential for the overall country. Four top applications that were awarded included Drive Now Text Later, The Dubai Police, The General Women’s Union app, and Active citizen (Qasim, 2018).
The concept of e-voting was initiated around the year 2011 by the Federal National Council of UAE in order to increase the participation of the citizens through appealing and convenient measures. Proper research had been conducted to set the electronic machines around the cities that could increase the convenience for people. Towards the end of implementing this regime, they were able to install 13 voting stations based on the density of the population in every one of the seven emirates under UAE in comparison to one station in each emirate in 2006 (Al-Jenaibi, 2014). They selected spacious locations for ensuring maximum number of participants and efficient flow of the activities associated with voting. More than hundred personnel were trained to help the individuals participating in the voting system. The campaign for voting was able to explore nontraditional channels that led to increased participation from the youth. The National Election Committee utilized social media for educating and reaching out to eligible voters through articles and videos briefing them regarding the entire process. The significant results of these improvements were measurable (Al Qubaisi et al., 2015).
Around the year 2011, they launched an e-dirham card that was rechargeable at ATMs and could be utilized to pay any kind of fee to the entities of the federal government. These measures replaced the previous process of submitting or mailing cash to governmental sites as fees (Bealer and Bhanugopan, 2014). Since managing, developing, and operating such programs could be time-consuming and expensive, they carried out the operations with company that was state-owned namely National Bank of Abu Dhabi that had the capabilities of operating with e-dirham and ready for delivery. UAE was one of the first developed countries to initiate such a program of payment systems. In order to promote the utilization of e-dirham, the Finance Ministry reduced fees and rates along with a support system that ran 24 hours across seven days in a week. The range of options and services offered by e-dirham is increasing on a day to day basis. Around the year 2015, reports collected regarding these measures suggested that approximately 17 billion dirhams had been collected as government fees.
According to AlMazrouei and Pech (2015), in order to create a standard and culture of excellence, the different entities of the government motivated the UAE leaders to improve their processes for the public through a particular Star Rating Program that utilized standards of private sectors for delivering services of quality while using approaches of private sectors for identification of problems. Around the year 2014, this program was established with a measurable and detailed process for achieving citizen feedback. These entities are tested once in two years based on specific a criterion that includes citizens, alignment, services, citizens, channels, service innovation and efficiency, citizen experience, technology, and people. These entities receive plaques with classification along with a report with recommendations and evaluation for improving their degree of service deliveries.
Digital methods and technologies adopted in the UAE
Technology is changing the UAE rapidly over the last couple of years. An advanced city cannot be determined through free Wi-Fi across the country and remote monitoring. As stated by Pavlik (2015), the UAE is considered as the country that leads the way in adopting the technology. Digitalization of services provided by the government and automated systems for traffic lights seem to be insignificant in the times of smart cities. Individuals are developing technology on a day-to-day basis and improving various sections such as remote monitoring and secure infrastructures, building cities on 3D simulations designs with the prediction of the future that can lead to prevention or mitigation of issues before they can cause any kind of damage or loss. In the current scenario, a city can be called smart if digital technology is making different aspects of lives easier for the citizens of a particular city from education to transport to health. These measures should be more sustainable than efficient.
Every government of every emirate is focused solely on creating the best city for its citizens and staying ahead of the competition. Amongst all the emirates, Dubai has brought about significant changes to the city along with the government. They have managed to improve the overall health of the country. According to reports served by several authors such as Schmidt and Cohen (2014), the impact of technology can widely be observed across Dubai. Due to such reasons, present-day cities have become complex with dense structures where most of the individuals work and live. The speed of global urbanization has increased over the last few decades that pressurize the economic and social structures, infrastructure, and the environment involved through these changes. Currently, the nature of cities is more constrained and compact which intrinsically affects various aspects such as physical expansion, mobility, availability of resources along with provisioning, planning of economic activities along with interconnectivity, environment cleanliness, and urban planning. According to Salem (2016), there are few specific areas that Dubai has focused on and which include fast growth, technology transformation, happiness goal, towards 2021, Smart happiness, unique opportunities, resilient and smart, making connections, climate change, global competitiveness, digital literacy, autonomous transport, smart mobility, the environment and ICT, digital government, and moving forward for the future.
As stated by Al-Khouri (2014), the population of this particular area has increased rapidly more than other places across the globe during the latter half of the previous century. The fast growth was based on the opportunities they sought through the multiple challenges facing the city such as adequate housing, education, healthcare, literacy, infrastructure, jobs, and accessibility to freshwater. Over the last two decades, they sought opportunities in every single challenge due to which they are part of one of the fastest-growing and leading countries through technology across the globe. On a global level, they are considered as the center for investment and economy. According to Dutot and Van Horne (2015), the economy for Dubai was improved by diversifying the economy through significant developments in industries such as real estate, tourism, travel, retail, finance, and logistics. Moreover, they focus on gaining different kinds of talents from around the world that can participate, indulge, and enhance the process of technological transformation for the overall country.
According to World Economic Forum (2019), the technological journey for Dubai was initiated around the year 1999, through their first strategy involving information and communications technology that led to the beginning of Dubai e-government, Dubai Internet city, Dubai Smart government, and the Smart Dubai initiative around the year 2014. Over the last 20 years, the different initiatives involving digital transformation across the city have been able to gain public acceptance along with the implementation of ICT in almost every aspect of life. In the current scenario, Dubai is one of the seven emirates with 2.5 million citizens with highest degrees of implementing ICT both by the government and the public. They have been able to achieve exceptional qualities of life along with an unmatched environment for business. Through the implementation of technology, they seek to make Dubai the happiest place on this planet. Recently, they established and initiated a five-year strategy that aims to transform Dubai technologically completely by the year 2021. The interaction between people, businesses, and the government has increased due to exchange of services, ideas, products, and experiences. Every one of these can behave as consumers and producers at different stages of technological transformation. Moreover, they aim to retain the happiness of the country through these transformations and changes (Elmasryet al., 2016).
Current challenges faced by UAE public organizations regarding technologically preferences
Although the evolution and exponential growth of technologies in the UAE have catered some major benefits to the business and public sector organizations there are still certain challenges that the public organizations require emphasizing on. In the current scenario, the public organizations of the UAE are dealing with the challenges associated with the integration of modern technologies. The privacy issues and cybersecurity along with the management of the infrastructure and emerging technologies are some of the major challenges faced by the UAE public organizations (Al Qubaisi et al., 2015). Besides this, one of the main challenges associated with the technologies is that it is of utmost importance to select the most suitable technologies as per the needs. However, the public organizations of the UAE have been failing at this severely. The majority of the UAE public organizations are accentuating the advancement of the technologies rather the technologies that are suitable for their processes. Since the public organizations are failing at this, it is tending to decrease their potentiality in meeting the needs and demands of the customers as well as increasing the overall expenses of the organization as well. Apart from this, the concerns related to data security are also growing with the adoption of more and more advanced technologies. With the significant amount of data stored and transmitted electronically, the scope for data violation is amplifying drastically. It is highly essential for the organizations of the UAE public sector to anticipate the quick responses and decisive actions in order to satisfy the state patchwork as well as the regulations of the federal data breach (Khan et al., 2014).
On the other hand, the cybercriminals are advancing with the advancement in the field of technology and targeting businesses with low-level security systems integrated. The UAE public organizations with low-level security control are being hacked and a significant amount of data loss is taking place. Such incidents are further leading to damage the reputation of the UAE public organizations among the people and are ruining their trustworthiness. Besides this, another major technological challenge associated with the UAE public organizations is that the private sector companies have skilled employees and expertise possessing vast amount of knowledge regarding technologies, which the public organizations are lacking (Azmeh and Foster, 2016). Due to this along with the pace at which technological change continues is making it necessary for the public organizations to be agile as well. It is because the customers and the other people of the city have high expectations and the competitors or the private companies with the assistance of skilled IT employees are moving faster. Besides this, the challenge of infrastructure management has also caused severe trouble for UAE public organizations. It is because public organizations are highly dependent on third parties for their infrastructure management (Hoberg et al., 2017). It is essential for the public organizations of the country to excel at managing the vendor relationships effectively, as failing to address the maturing practices of vendor management could result in significant business risks.
Digital transformation is the insightful transformation process of the business as well as organizational processes, tasks, models, and competencies in order to leverage the changes along with the opportunities of mingled digital technologies completely. It also plays a substantial role in accelerating the impact all across the society in a prioritized and strategic manner considering current as well as future shifts. The UAE public organizations are seeking to go under a change of digital transformation in order to increase their effectiveness in providing superior quality services to the people. It is because the digital transformation would make it possible for the public organizations to address the needs and wants of the people as well as live up to their expectations extensively. Apart from this, the technological field of the UAE has seen its fair share of evolution and growth over the past years. The extensive growth of technologies has influenced the perspectives of public organizations. Although the technological preferences of the UAE public organizations accentuate on the needs and want of the public, the main area where the organization’s lack is in identifying their needs of the technology. Even if the technologies and digital transformation promise a beneficial future, it also has its own set of cons and causes severe challenges for UAE public organizations. At present, the UAE public organizations are dealing with issues such as data breach, increased cybercrime, complex infrastructure management, lack of skilled IT employees and expertise within the organization. All these combined tends to create an adverse impact on the public organizations of the UAE. Besides this, the organizations are also failing at leveraging the skills of their leaders in the process of digital transformation. It is of utmost significance for the UAE public organizations to get their leaders involved in the process of digital transformation. The involvement of the leaders will make it possible for the public organizations of UAE to accomplish the change of digital transformation extensively. The leaders will be the ones accountable for communicating the significance of the change. With effective leadership in place, it would easier for the public organizations of UAE to decide upon the technical requirements of the organization itself and the manner in which it would help the organization in addressing the issues of people. It is highly imperative for the public organizations to make sure that they integrate effective technologies as per their needs with appropriate security control system in place to avoid potential threats.
CHAPTER THREE: LEADING CHANGE IN ORGANISATIONS
What is leadership?
Leadership is a widely discussed and researched topic across most areas of organizational sciences. However, very rare researches have been conducted regarding its impact on digital transformation (Northouse, 2004). Leadership can be formal happening at all levels of management, maybe emergent and informal, which means not solely conferred by position or title. According to McCleskey (2014), the study and research of leadership extend to over a century. As suggested by Gooty et al (2012), leadership entails a multi-level (collective, group, dyad and person) follower-leader interface process which happens in a specific situation (context) and where followers (direct reports or subordinates) and a leader (supervisor, superior) share a purpose (mission, vision) and collectively achieve things such as objectives, goals, and tasks. Among the earliest studies of leadership was by Galton (1869) who underscored a basic concept that provided a popular notion regarding leadership (Zaccaro, 2007).
In this early conception, leadership was linked to the characteristic of extraordinary individuals known as the great man theory. This theory evolved into a study pertaining to leadership traits (Glynn &DeJordy, 2010). Northouse’s (2004) review of leadership recognized four shared themes in the approach to leadership namely: leadership entails a process; leadership happens in a group context; leadership entails influence, and leadership entails goal accomplishment. Based on this, Northouse (2004) defined leadership as “a process where a person influences a group of persons in order to attain a shared goal. The aspect of the accurate definition of leadership is an important matter because according to Rost (1993), there exist over 221 different conceptions and definitions of leadership where some were broad while others were narrower conceptions. According to Bass (2008), the search and pursuit for a single explanation of leadership are futile.
Leadership plays an essential role and function for the management of any organization in terms of helping to optimize efficiency and to attain set goals (Robbin, 2003). People are largely inert or tend to prefer the status quo but the leadership helps to initiate action which includes communicating plans and policies to followers. According to Robbins (2003), leadership behavior tends to influence the social process in an organization. Leadership entails aspects such as guide, give, build, reward, and motivate, which build a communication network and bring followers to attain an organization’s mission and vision. A leadership that pursues optimal function tends to enhance employee or performance, and vice versa (Robbins et al., 2010). Robbins (2003) suggests that motivation influences an employee’s performance. The leadership of an organization plays an incentive role in the workplace. According to motivational theories such as Maslow (1954) and Herzberg (1966), followers are motivated with both economic and non-economic rewards (intrinsic and extrinsic rewards) in order to perform at their potential (Baard et al, 2004). Essentially, leadership provides the motivation and morale to ensure their followers and subordinates perform at their optimal level.
Besides the role of supervision, the leadership provides guidance for the followers and subordinates. In this context, the guidance suggests giving instructions to subordinates on the way they ought to undertake their work in an efficient and effective manner (Jenster, 2009). The leadership can be a morale booster where they influence their follower’s cooperation towards their duties and winning their trust and confidence and ultimately leveraging their abilities to achieve set goals. The leadership is a symbol and hallmark of creating confidence. The leadership promotes confidence through conveying the work energies to subordinates, clearly explaining their role and providing guidelines on how to attain the goals in an effective manner (Burton & Peachey, 2009). Leadership plays an important role in providing the right and efficient work environment in order to get things done. Essentially, leadership helps to establish and enhance human relations in order to generate the necessary valuable synergy for productivity. From this analysis, it is evident that leadership has an important role in facilitating many aspects in a group especially in relation to the achievement of the mission and vision.
Types of leadership (Leadership Theories)
According to (Zimmermann et al., 2015), the understanding and recognition of different leadership styles are really significant for an organization including the situations in which these leadership styles work best. Although, simply by mimicking these styles, a business leader will unlikely to be successful. Leadership is not about providing certain responses in a certain situation. In fact, it is about using his natural leadership strengths in an appropriate and authentic manner in order to motivate and inspire others.
The concept of leadership was first studied in the 20th century. It was first studied as a trait but later by the start of the 21st century, this concept had evolved as the concept of leadership focusing on the relation between the leader and follower. The main contributions in this evolution were made by Dr. Peter Northouse and Dr. Gary Yukl (Ecoggins, 2016).
Transactional leadership was initially defined by Max Weber (1947) and more recently by Bernard Bass (1981). As the two authors suggested, this leadership style is regularly used by managers in entities and focuses on the primary roles of management process namely planning, organizing and controlling. Transactional leadership dwells on the exchanges that happen between followers and leaders (Burns, 1978; Bass 2000; 2008). In these exchanges, leaders are able to complete required tasks, realize their performance objectives, motivate followers via contractual agreement, maintain the present organizational situation, avoid unnecessary risks, emphasize extrinsic rewards, direct conduct of followers towards the attainment of set goals, and emphasis on improving organizational efficiency (Bass 2000; 2008). In this regard, transactional leadership enables followers to minimize workplace anxiety, accomplish their own self-interest, and focus on clear organizational objectives that include reduced costs, customer service, increased quality, and increased overall productivity and production (Sadeghi &Pihie, 2012). According to Burns (1978), Transactional leadership theory suggested the relationship between followers and leaders as a sequence of exchanges of fulfillment designed to maximize individual and organizational gains. According to Burns (1978), the marketplace urges adaptability, flexibility, reciprocity and real-time cost-benefit evaluation. Transactional leadership entails directing and motivating followers primarily via an appeal to their self-interest. Transactional leaders draw their powers from their formal responsibility and authority within the position held in the organization (Liu et al, 2011). The important goal of subordinate is to obey the leadership instructions where motivating is via a method of rewards and punishment.
Transformational leadership (TL)
The concept of Transformational Leadership was conceptualized by James MacGregor Burns (1978). According to Burns (1978), transforming leadership depicts “a relationship that entails mutual elevation and stimulation that transforms followers into leaders and could transform leaders into agents. Essentially, transforming leadership happens when an individual or individuals engage in a manner that followers and leaders raise one another morality and motivation levels (Diaz-Saenz, 2011). At the core is an emphasis on a leaders’ capacity to empower and motivate followers and equally the moral element of leadership. The transformational leadership goal is mainly to ‘transform’ organizations and its people to change them in heart and mind in order to; broaden understanding, insight, and vision; make behaviour compatible with principles, beliefs, or values; clarify purposes; and inject changes that build momentum, is self-perpetuating, and permanent/sustainable (Bass & Avolio, 1994).
According to Burns (1978), a transformational leader raises followers’ consciousness level regarding the value and importance of preferred outcomes and ways of attaining the outcomes. The TL convinces followers to surpass their self-interest in order to achieve interests of the firm, while uplifting “followers’ level of need as per Maslow’s hierarchy (1954) needs to achievement and self-actualization from concerns for security and safety (Bass, 2008). Northouse (2001) consider TL as a process that transforms and changes individuals (get people to improve, embrace change, and to be led). Examples of TL include John F. Kennedy, Margret Thatcher, Mahatma Gandhi, Howard Schultz (former CEO of Starbucks), Bill Gates of Microsoft, and Sam Walton of Wal-Mart.
Autocratic leadership is where a leader possesses complete and domineering command over his/her followers or employees (Robbins et al., 2010). Autocratic leadership is considered predictable and also associated with high productivity, however often linked to low creativity, morale, and motivation (Marquis & Huston 2008). Autocratic leadership entails a style where the leader controls all decisions with minimal inputs from followers or other members (Marquis & Huston 2008). Autocratic leaders make decisions and choices based on own beliefs. However, this method can be valuable and appropriate in crisis situations, where changes are occurring fast or in start-up businesses where the entrepreneur is pushing to have his/her idea implemented (Rycroft-Malone et al, 2012). An autocratic leadership style can be appropriate and effective in work settings where quick decisions are necessary, Close Oversight is required and where processes need to be streamlined. This leadership can be linked to the Roman Empire under Julius Caesar, Henry Ford in the early times of Ford motors, and Napoleon Bonaparte era. This form of leadership is common in the police and military sectors.
The primary feature of democratic leadership is that democratic leaders encourage their subordinates to participate and engage in the decision making the process. A real democratic leader, rather than imposing his ideas, he argues with his subordinates before making any important decision. Hence, it favors dual way communication. In a democratic leadership style, subordinates are delegated authorities, involved in the overall decision-making process and almost have the freedom to perform the work in their own way.
A democratic leader always strives to create and maintain a climate of trust. He provides moral support and promotes teamwork. Furthermore, subordinates also get the chance of personal development under democratic leadership which motivates them in performing their best.
A Democratic leader is as much interested in the human aspect as the task at hand and strives to create a climate of trust. He promotes teamwork, promotes the personal development of his subordinates and provides moral support. The democratic style is at the origin of altruistic leadership. It is based on the principle that the best way to encourage people to do their best is to take an interest in them. To be effective, the altruistic manager must be able to listen, adopt an empathic participatory approach, offer help and assistance to subordinates, and consider the person as a whole (Zahra Malik et al., 2016). Although (Zahra Malik et al., 2016) criticized this leadership style by stating that, “democratic leadership does not have the characteristics more fundamental, and that democracy is not a style but a system, in which power ultimately belongs to the people”. This criticism tends to highlight that this leadership, is an abusive appellation that covers the coercive nature of power.
Laissez-faire leadership refers to a style where the leader facilitates an environment or setting where the subordinates are accorded numerous opportunities to make decisions (Roussel 2006). The leader himself relinquishes or delegates responsibilities to others who are often skilled and need less supervision. Laissez-Faire leadership can be frustrating and non-directional because leaders who embrace it tend to let their subordinates take control (Roussel 2006). This style works well where team members are self-directed and highly motivated, and can, therefore, result in greater motivation, creativity, and autonomy compared to democratic and autocratic leaderships (Richens, 2004). The democratic leadership, as mentioned earlier in the table, is a type of leadership style in which members of the group participate actively in the decision-making process.
(Amanchukwu RN, Nwachukwu, Ololube, Gloria Jones Stanley). However, Laissez-faire leadership necessitates multiple change agents and resistance from group members is often experienced in this style of leadership (Delmas &Toffel, 2008).
Difference between the leadership of the private and public sector
There is quite a vast difference between the leadership of the private and public sectors. The most accentuated differences between public and private leaderships are mainly of structure, talent, culture, and environment. (Tolboom, 2016) by using the Business Attitudes Questionnaire compared and analyzed the personalities of 1200 senior private and public sector leaders in Europe. He then compared the results with those of 65000 people in the global population. Consequently, his study revealed new findings which helped the organizations to determine the best business attitudes for the leaders of today and tomorrow. The primary result which he gained through this study was:
Private sector leaders mainly focus on short term and rapid results. Whereas public sector leaders primarily focus on developing a long term strategies, instead of winning in the short term. Furthermore, Private sector leaders are more ‘trusting’ and ‘believing’ but the public sector leaders tend to ‘control’ more and are less optimistic about the results. In addition to it, young managers receive more opportunities and more space for their self-development in the private sector. Whereas, women leaders have a robust profile in the public sector.
Trait, behavioral and contingency models of leadership
The essence of leadership is the proper functioning of management (planning, organization, leadership, and control) Along with having the ability to positively influence others. The leader can accept his obedience to perform a specific task for a group of people, and the authority of the leader comes directly from the organization, which is obliged to set specific tasks for team members. A good leader cannot rely solely on the coercive power of his position: he must also demonstrate leadership. Even if a leader can come from all levels of the organization.
Trait model
The main factors that influence leadership style are strength and personality traits. Strength can come from the organization (the ability to reward or coerce, the legitimacy of the position) or from the individual (charisma, gender, emotional intelligence, traits, expertise). Organizational strength can force subordinates to carry out tasks, even if they do not necessarily respect the authority of their leaders. The personal strength of a person can strengthen the interaction of the working group, but this does not explain why the leadership style is effective in a particular situation and does not work in another.
Behavioral model
To better understand these relationships, Ohio University’s researchers in 1941 decided to focus on the nature of behavior between leaders and subordinates working under him. According to their observations, an exceptional leader can always support their subordinates in accomplishing the specific task in dual ways:
- Consider the organization and structure of the tasks to be performed;
- Focus on team considerations, personal accomplishments, and satisfaction.
- Fundamentally, when the work is not routine and subordinates complete the work, the structure of the task will be more efficient, otherwise, it will be studied by more efficient employees. However, this behavioral model helps in understanding the directing relationships, the main drawback is that it does not take into account the context of the situation in which the relationship arises.
Contingency Model
The background may affect leadership style. Therefore, the contingency model refers to observation variables that interact in certain situations and influence the choice of leadership style. There are three main types of contingency models:
- Federer Contingency Theory;
- Theory of the critical path of House;
- The Jago Model
Fiedler contingency model
According to Fiedler, the effectiveness of a team depends not only on the leader’s behavior but also on his ability to control and influence random variables. The context variables of the Fiedler model are team emotions (bad or good), task structure (organized or not), and the strength of the position of the leader (weak or strong). Based on a combination of these variables, the situation will strengthen the interpersonal-oriented or task-oriented leadership. Although many critics attribute Fiedler’s model to their mono-dimensional characteristics (leaders cannot be both person-oriented and task-oriented).
Model of the critical path of House
According to the objective path of the house (critical path) model, leaders must remove barriers that stop subordinates from attaining their goals. Compared to Fiedler, House believes that leadership style must change depending on the situation and can use more than one style at the same time to improve secondary productivity, job satisfaction, and performance of subordinates. Leaders must evaluate variables that are contingent, such as subordinate’s personal characteristics (need for or hierarchical, autonomy level or recognition) and the characteristics of their tasks (organized, repetitive, complex actions, etc.), in order to determine the appropriate style and leadership. These patterns can be positive behavior (tailored) and instructive (task building)
Vroom-Jago Decision Model
The Vroom-Jago model emphasizes that leadership style effectiveness depends on the nature of decisions made. Some decisions must be made directly by subordinates, some decisions must be made dictatorially, and others by subordinates.
The above three models of contingency highlighted above use different standards for measuring leadership effectiveness. Fiedler focused on performance whereas House focused on job satisfaction and accomplishment for subordinates. Although, Vroom and Jago focused on the effectuality of the decision and its positive effects on the organization.
Leadership in the Public Sector
Public sector organizations are considered to be more structured as compared to private organizations and therefore, the requirement of strong leadership in this sector is usually ignored. These weak leaders are viewed as having little influence on followers. (Kerr 1978).
There is a difference between leadership in the public and private sectors. Public sector leaders offer ideas about novel procedures; motivate their followers for growth; start new projects; try out new methods; suggest future plans (Arvonen 1999, 245).On the other hand, a private-sector leader is friendly and shows compassion for his followers and trusts them and involves them in making decisions (Arvonen 1999, 245).
Another difference in the leadership of the two sectors is in terms of motivation profile. The public sector leader wants , do something exceptional to outperform someone or some predetermined standards (McClelland1972, 34) while a private-sector leader focuses to have impact; make an impression on others; make powerful action; exert strong positive or negative feelings in others ; have concern for own reputation or positions (McClelland 1972, 34).
The leaders in this region of the world mainly follow the teachings of the Quran in their lives including their dealings and business. They have high regard for their culture, values, and traditions and cultivate trust. Professor Peterson conducted interviews that revealed some of the leadership traits followed in Arab countries. They are described below:
- The Arab leadership is mostly characterized by unequal power distribution whereby the followers have to comply with the decision taken by the leader. However, a leader must discuss with the followers before finalizing a decision.
- The Arab leaders cultivate trust in their followers who follow the golden principles of sincerity as laid by Islam.
- It was also revealed during an interview that in Arab countries that the whole team is considered as one and the weaknesses of one party are covered by the strengths of others. Trust and clearly defined goals encourage followers to give their best.
- Arab leaders usually establish open-door policies.
- Leaders in the Middle East are bound to consult their followers before exercising power. Decisions are taken for the good of the organization as well as the followers. (Saudi Gazette)
Leadership and change management
The behavior, values, and traits of a leader have the capability of influencing the reaction of followers or employees regarding the change brought about within the organization (Leadership, 2009). The FIVE different attributes of a leader that can lead the process of change management towards failure or success were identified by Prosci’s benchmarking research (Berman and Marshall, 2014). These are as follows:
- Communicating about the change
- Supporting the change
- Training the workers through the change process
- Participating with the project team
- Detecting and managing resistance
Although, change management may fail due to inappropriate leadership (Tolboom, 2016). Dr. Linda Ackerman Anderson states that supportive leadership is imperative for Organizational change as it communicates the advantages of change to all the stakeholders. This change may involve digital transformation. Furthermore, (Tolboom, 2016) published in his study that good leadership brings about the success of the organizational change.
Kotter’s model
Effective leadership plays a pivotal role in the proper functioning of organizations and ensures that digital transformations are carried out in the most effective manner. Leaders initiate the process of change management while undertaking any kind of digital transformation. The leader’s involvement is extremely vital as his traits, values, and attitude have an enormous impact on the manner in which customers and employees perceive the change within the organization (Hess et al., 2016). In order to have an effective digital transformation, organizations can try to implement the Kotter’s eight-step model. However, a change that is not lead efficiently may even result in the collapse of the organization.
There are several techniques applicable to change management in maintaining the different entities associated with digital transformation (Oswald and Kleinemeier, 2016). One of the change management models known as Kotter’s model was introduced by a world-renowned change expert, Kotter in his 1995 book, “Leading Change.” This model was developed after conducting researches on 100 organizations that were subjected to change management. The eight steps of this model can be useful for organizations to transform digitally. The organization alone is not involved in the process of change due to which it can face many challenges and issues if appropriate measures are not adopted for catering to the needs and requirements of each entity. Employees are one of the major components of an organization and their actions can determine the success or failure of digital transformation. The organization may face resistance from the employees during the initial stage of digital transformation. The eight steps identified by Kotter include developing a sense of urgency, building a powerful team for guidance, developing strategies and vision, communicating and sharing the vision with involved individuals, empowering employees and mitigating obstacles, developing short term goals, enhancing gains, and ensuring the permanency of changes. Before implementing or adopting any of the steps it is necessary to ensure the employees learn the issues the organization might face if does not implement change or transform digitally.
John Kotter, a professor of leadership and change management at Harvard University, introduced eight important change models in his 1995 book on leadership change. Based on the careful design of Kurt Levin, the model lists eight key stages in the process of change, arguing that if ignoring any of these steps will lead to the failure of the whole initiative.
Stage one: creating a sense of urgency
The ability to change the organization becomes really necessary for its success. This change can be useful if an area is developed in which people understand the current problem and see what they can imagine. A discussion of what is happening and what the organization can do will achieve this goal. One way to achieve this goal is to hold a meeting to discuss possible problems and understandings. This progress is linked to the overall preparation. Kotter estimates that 75% of an organization’s management usually supports change in order to be productive.
Stage two: Building a Strong Alliance
It will be difficult to lead the entire process of change alone, so a person needs to create alliances that allow him to coordinate with others. The alliance that he is developing should consist of a number of opportunities, areas of expertise and specialists from different areas of the business to expand this change process. An alliance can truly help in spreading messages across the organization, delegate missions, and provide support for change leadership. Colleagues who work together complement each other and are more interested in working hard will definitely make their life easier, and change will be effective and successful.
Stage 3: Creating a Vision of Change
Changing steps can be confusing and often difficult to understand, especially for workers employed at a lower hierarchy. Therefore, developing a clear vision and a common perspective is a useful way to enlist the support of the entire organization. Although this vision should be simple and reasonable, it is equally persuasive to have the greatest impact.
Stage 4: a vision of communication
Developing a vision is not enough to enlist its support, and then this needs to be taught through an entire organization. This is a great opportunity to use the alliances a person is developing that can be organized in all areas of activity. When considering all issues, this information should be transmitted sequentially, and competitive information is still disseminated.
The first four stages are the structural basis for the beginning of change, but another step in the search for factors that can reduce the chances of progress. Whether it’s people, practices, rules, or practical obstacles, there may be barriers preventing a person from changing course. In order to make the change successful, the is a great need to identify these obstacles as early as possible along with relying on the available resources so that these obstacles can be broke down without disrupting any other areas of the organization.
It takes a long time to change an entire leadership in order to gain benefits, and if people think that their efforts are lost, this can lead to failure. Thus, the benefits of the new changing process should be demonstrated by achieving some short-term success. Short-term goals are another useful tool for inspiration and progress. Using these successes to legitimize speculation and effort can help persuade employees to continue to support change.
Stage 7: Structuring on the change
Many of the change initiatives failed due to a lack of interest in penetration to the end, and the task was not completed correctly. According to these ideas, Kotter believes that change should be supported and implemented in the long run after accomplishment. Continue to analyze detailed goals and objectives that could be implemented in order to progress better.
Stage 8: Consolidating Change in Corporate Culture
Simply changing the habits and processes of employees is not always enough to instill a culture change across the organization.
Fundamental changes in the process of operations are not enough to instill cultural changes to an entire organization. These changes should be a part of the center of all the areas of the organization in order to have a lasting impact. Keeping senior associates on board, encouraging new employees to accept the changes and praising those who accept the changes will greatly improve the changes in the organization.
The main reason Kotter propounded these methods is to emphasize that this change is certainly not a basic and flexible process. Different mechanisms are needed, and despite the changes, much work remains to be done to ensure the success of this model. Kotter believed that 70% of the initiatives for change failed which are related to the fact that most organizations are not in the necessary state of readiness or do not fulfill every step. Using this model ensures that change initiative is a long-term achievement.
Levin model
In 1939, Kurt Levin led a group of researchers who studied leadership. Although he later expanded the number of well-known methods, Levin and his team initially identified three leadership styles: authoritarian, conniving and democratic. As part of the research, students were distributed into three groups, each of which was headed by an individual who identifies one of the main leadership styles.
Authoritarian leadership style (directive in nature)
Authoritarian leaders always explicitly explain what to do, when to complete a task, and how to complete it. When making a decision, they don’t tend to take into account the opinions of other members of the group, therefore, there are often differences in opinions between them and those who fulfill the order.
Levin identified that with this leadership style, people have little room for creativity in the decision-making process. If a leader abuses power, he or she is someone who likes to command and control it as a dictatorship.
Authoritarian leaders are most appropriate when the leader is the most qualified member of the team or when the team does not have time to develop a solution. Moreover, it has become more difficult to move from authoritarian to democratic leadership than from democratic to authoritarian leadership.
Democratic leadership style
The findings of the Levin team showed that this is the most effective democratic leadership style. Democratic leaders are actively involved in the activities of the group, which allows other members to express their views and provide assistance and recommendations.
Levin found that in these groups, children are not as effective at defining work as teams led by authoritarian leaders, but they contribute more.
The final decision was left to the democratic leaders, but all the members of the group participated in the decision-making, which made them feel involved and motivated, which greatly contributed to their creativity.
Conniving Leadership style (liberal)
Leaders with this approach will show a negative attitude and pass on all decisions to the shoulders of team members.
Levin found this type of leadership to be the worst. Researchers noted that in this group, children asked leaders to give orders and make decisions that they could not make independently and that they were very reluctant and ineffective. However, this model may be useful if all members of the group are highly qualified in a narrow field, but in most cases, this can lead to a decrease in enthusiasm for team members and unclear role assignments.
Summary
Various change management models are available but we can consider Kotter’s eight steps model which can be used by organizations while transforming digitally. In an organization, the employees are an essential part as their performance determines the success or failure of the process of digital transformation. Before adopting any steps, it is essential that the employees are made aware of the issues and challenges that the company may experience if it is unable to transform digitally and implement effective changes (Viaene, 2017). We are considering Kotter’s model due to the following benefits offered by it
- It successfully brings about change by obtaining buy-in from main employees
- This model is appropriate for traditional organization structures (Expert Program Management, 2010-11)
We have already discussed the four leadership styles and here, we will be discussing the adoption of a transformational leadership style to bring a change in a conflicting business environment. The reason behind the choice of this style is that this style enables the leaders in organizations to involve all employees in the decision-making process and to consider their views and opinions. It gives an enormous amount of importance in teamwork and united efforts as this help in greater productivity and success of the procedure of the digital transformation. This motivates the employees to perform better as they feel themselves to be an active part of the organization and they take pride in its development and success and want to work hard for achieving it (Nuseir, 2018). Therefore, it can be stated that digital transformation is a necessity in today’s world and in order to control the risks associated with the process, the leaders of an organization must monitor the processes to ensure that everything is conducted in the most appropriate manner.
CHAPTER FOUR: THE CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Introduction
Alec Ross in his book “The industries of the future wrote that the industries of the future will never find a stable business model and market research will become a constant process to replace the existing methods of marketing. Check it out with the advertisements of various companies that are offering digital solutions to the existing businesses across the world. We can register two types of trends. First they are presenting a conceptual side of the software and other solutions and second they are offering change management from a holistic viewpoint.
While fixing the role of a leader in the process of the digitization or the digital transformation of the various departments of the UAE public sector a leader has to acquire a different approach altogether.
On the level of the development of a conceptual framework, this approach will be dependent on the amalgamation of the past knowledge and projections of the future.
Constant changes faced by the organizations due to improvements on technological fronts have made it difficult for the organizations to maintain a stable work and business environment. The moment we add this word “constant changes,” a new set of theories related to the behavior of the leaders starts rolling in, Leaders are one of the most essential entities during the process of digital transformation. The holistic vision of the leaders can guide various teams to attain a singular goal quite easily (Hoberg et al., 2017).
The conceptual framework of the change designed for the public sector organizations of the UAE can be compared with the theories associated with agile project management. The theory of agile project management divides the process of change into multiple factorials. The planning team along with the leader decides the flow of the actions and resources in a certain direction to meet out the needs related to various factorials.
Image 6: Factorial chart for a single unit of the Public sector in UAE during the course of a Digital transformation.
In the previous chapters of this proposal, we emphasize on the needs of the fragmentation of the change management process in various parts. Image 6 represents the set of activities and the flow of the processes in a singular part or the singular section of an organization. For instance, we can take the example of the “ mutual obligation department for the waged work” working under the social welfare ministry of UAE. This department works on two different ideologies, the first ideology forces the government to ensure minimum wages and adequate support for the people that are living under the status of being an underprivileged person. The second responsibility of this department is to scrutinize the offenders that are taking this aide unduly.
Digital transformation can introduce a mapping of the individuals and unify them in a list where software can take charge of fixing the entitlement. In image 6 the headings of Dynamic requirements and iterative planning can support this system. On the right side of the diagram, we can see the presence of the monitoring department of UAE officials to check the progress and performance of various changes. This is a cyclic process, in general terms many experts will write off this model on the basis of conventional theories because it does not seems like a streamlined and organized procedure of the working.
While considering the study to decide the behavior of a leader in the changing business environment it is important for us to understand the case of UAE from a different perspective. This perspective is related to the fact that a big chunk of the population living in UAE can be considered as neo-Luddite, they are highly educated and learned in their individual stream of learning, however, when it comes to digital technology, they need a special interface to unlearn their previous education and move ahead with the new technology.
Image 7: The types of the change and the role of the leader, a note from the side “Dunphy and Stace Contingency model of the change” and its implementation on a factorial unit of UAE public sector
Image 6 presents a model of the change that works in accordance with the response of the individuals towards the change. As a model this arrangement allows a leader to look at the process of the change from the perspective of the agent of the change and the respondent of the change. The contingency model of change management and leadership allows a leader to understand the variable nature of the change and the application of various types of strategies to make some plans to counter all the four quadrants of the problem and decision making as they are described in the image 6. Dunphy & Stace Contingency model of the change describes the matrix of leadership styles in correspondence with the style of the change as it is described in image 6.
In this image, we can see the separation of various stakeholders in different quadrants in accordance with their role and behavior during the process of the change. This model of change is specifically developed for the UAE Public sector and it is dependent on the hierarchy of the reporting, working culture of the individuals and their attitudes towards the change. A change in the US public sector is always different from a change taking place in UAE because of the digital awareness levels of the individuals.
For instance, we can take the example of digital payments, teenagers of USA embraced the culture of digital wallets and later on the government of USA came up with the concept of Digital fortress where an individual can not only keep his money but he can also keep his necessary documents in a secured form. It was an easy transition for USA because of their cultural affinity towards the digital mediums. A respondent in UAE will definitely look at it from a different perspective.
It also means that if we check the exercise of digital transformation in the field of digital payments from the US perspective, we will find that it is easier and it can be done with the help of a straight line change management model. The demographic details of the USA give us an idea that most of the citizens are mapped, they have steady E-mail accounts and digital identities, their banks have already achieved the target of a “largely cashless economy.” In the case of UAE, this is a distant dream, this is why we need a complex model like “Dunphy & Stace Contingency model of Change.”
While considering Dunphy & Stace’s contingency model of change as tool to address the exercise of digital transformation of the public sector of the UAE then we can always consider another fact related to the fact that digital transformation can be considered as large and critical changes within the organization that may require implementing the various aspects of change management. In other words, digital advancements must be supported by a strategy for change management (Daniel Painter, 2019). In the case of UAE, this change can be further studied on a social level because a big chunk of the population is not fully ready and equipped to entertain the change.
At an internal level, it is imperative to mention Daniel Painter’s observations that identified 6 aspects as crucial for managing change brought about by digitalization. These aspects include flexibility, in the case of UAE the scope of the flexibility increases to a social level where an organization has to first set up a culture and then go for beta testing of the culture to figure out the gaps and finally they have to figure out a middle path, it can be achieved with the help of a process which is mentioned in the image 6 where we mentioned about the factorial chart of a single process.
The second step is related to the formation of various teams. The factorial model depicted in image 6 gives us an idea about three stationary teams, first we have a team that is monitoring the progress, second, we have a team looking after feedback and the third team is the reiteration team. The first team is the team which is encouraging and balancing a change, the second team in the process is giving it a tangible form by collecting feedback and the third team is the team that reiterates the demand curve and coming up with new solutions (Piccinini et al., 2015), as a leader it is the job of an individual to have a holistic view on all the sections of the operations and align their acts in accordance. The involvement of a leader through this process is extremely critical and important for achieving success through change management.
Before moving on further, it is imperative to understand what a leader actually is. A leader is a person who influences others for the accomplishment of an objective. According to John C. Maxwell, the Real leader is the person that is willingly followed by others. “On the basis of these definitions, leadership can be defined as the act of influencing others for achieving an objective.
In the case of change management of UAE public sector under the contingency model we can also say that every leader has this additional responsibility to manage and direct various aspects of the change management exercise, it is true that we are applying the theories of change management, however in the case of the digital transformation of the UAE public sector, we are dealing with a transformation exercise and we need leaders to transform, managers can manage processes on a beaten track. Leaders, on the other hand, inspires others to manage themselves and become a part of the transformation or the exercise of the goal achievement.
Leadership is defined as the process of influencing the activities of an organized group toward goal achievement (Rauch & Behling.) The image seven associated with the contingency model gives us a chart of stakeholders participating in the process of the digital transformation of the UAE public sector. The contingency model can support a leader in converting the masses into an organized group. Their reaction and adaptability towards the change can be considered as a parameter to fix a group for them and later on this group can be treated as an organized group by implementing the right set of strategies.
The conceptual framework associated with digital transformative can be seen from a different perspective altogether, for instance, image 6 can describe a variable problem area, under the heading of “uncertainty of the human nature” towards the nature of the change. leadership traits defined by various management experts can be treated as an alternative approach to deal with the tangential problems attached to a mainstream operation that can bring a major change.
The contingency model here serves as a constantly changing path of the change management, with the help of a contingency model a leader can prepare plan A and plan B or many other alternatives to meet out the probable challenges. At the turn of the previous century, Microsoft Inc also faced the same challenge when the introduced MS office suite and Windows as the harbinger of the digital transformation. At that point of time, they were catering entire world population as their target area, their search for universal solutions decided the course of the future for the basic design of MS Office and Windows, Microsoft appointed many contingency agents to fill the gap of information and came up with some rewards to promote the digital culture.
Under the present circumstances, a leader has to adopt the same technique of approaching a problem under various parts. Dunphy and Stace’s contingency model of change can help a leader in developing a basic understanding of the various leadership styles in accordance with the need of the hour.
Hypotheses Development
The implementation of the leadership model in a change that is required to carry forward on such a large scale, it is important to explore some statements that can serve as universal statements and have relevance in various complex situations that may occur during the course of the implementation of a mammoth goal. In order to facilitate this complex situation, it was important for us to come up with some hypotheses that can also play the role of the simplifier in the task. During the development of these hypotheses, we took an account of many previous works done in the same direction.
The hypotheses formulated for this particular research have been defined below:
H0: Adoption of different leadership styles and preferences on digital transformation is variable in nature, it is dependent on situations. A standardized format can be developed in accordance with the nature of the situation and effectiveness of the leadership style that can be adopted by a leader.
H1: Technological leadership changes are dependent on the demographic variables of the end users. Contingency model can support the insertion of supplementary actions to fill the gap.
H2: The key problems associated with the digital transformation of the UAE public sector can be addressed with the help of contingency model of the leadership while switching between transformational and transactional style of leaderships.
H3: Contingency style of leadership has this power to fill the gaps in ideologies and frameworks of technology leadership and Conventional methods of leadership in the public sector of UAE.
Research novelty and contribution
The research novelty of this research paper can be determined through the ability of inclusion of practical insights and necessary variables related to the difference in the demographic details and the conditions of the other countries where the process of the digital transformation took place. In the same chapter we discussed the case of the digital transformation in USA and compared some of its component with the digital transformation which is taking place in UAE. This is an example to elaborate on the novelty factor associated with the results of this research. Under this research program we will compare and contrast the conceptual frameworks of the leadership techniques adopted in those countries with a hypothetical model developed for the digital transformation of the UAE.
With the help of adequate and systematic literature review, this research program will counter the literature gaps identified in the different papers referred for understanding the available literature regarding digital transformation and changing leadership approaches in public organizations, with a purview of UAE and the rest of the world.
Relationship between leadership and Digital Transformation
This area is under development and indeed this is one area that needs constant evolution of the facts and the changing circumstances. Prima-facie a researcher can draw a straight line relationship between two phenomenons; a technology leader has to look at the area of change from the point of view of the feasibility. At the same time, he is required to check the entire equations from a different perspective. For instance, we can take the example of cybersecurity. The means to strengthen cybersecurity often create roadblocks for the end-users; however, they are mandatory, as a leader it is a complex situation to handle. This area is a variable area and during the course of the research many facts and statements may come in our way that can serve as a universal guideline for the leaders handling digital transformation. “Security comes first” is a tagline given by Cybersecurity experts can be served as an example in this regard.
Dependent variables: Public organization’s technological preferences
The dependent variable (DV) is the one that is affected by the independent variable (ID). This is the effect, of what is measured. For example, measuring the number of digital help centers in ratio of the population density is a dependent variable. Where the values are stationary in accordance with the demographic data of the UAE, at the same time measuring the same data on the merit of the digital information level is an independent variable because we cannot fix the value in the absence of a quantifiable measurement.
This is the focus of the study in general in which the experimenter focuses his observations and measurements to see how his behavior responds to controlled changes. In other words, it is the so-called “effect” of the relationship studied. Depending on the type of study, it can also be called an experimental variable, a measurement variable or a response variable.
This study will identify the role of leadership in the areas where a change can be carried out in a controlled setup. However, the impact of these changes in an uncontrolled environment will be a different value; this study will try to measure the role of the contingency model-driven leadership approach to resolve this problem. It is apt in the case of UAE because the gap of information level between the experts, middle layers and end users is significantly high.
The existence of public organizations is aligned with the requirements of various kinds of services for the common people. They, however, do not aim at profit maximization. The technological preferences are the preferred medium of the users and this is usually based on a number of technological preferences. The different public organizations take huge measures to be aware of the technological advancements that exist today and their benefits (Choi and Chandler, 2015). Digital transformation of the public sector in UAE can also add a profit maximization in the final outputs of the departments by cutting the costs of the operations and consume the slacks into useful other activities. The framework of the contingency models can be utilized to identify this slack area, the present research will also explore this area of the operations and try to come up with a framework dependent on the other models, this framework will be accommodated in the recommendation part of the research.
Dante Ricci of SAP’s Global Public Services team asserted that the current technological preferences among the majority of the public organizations are IoT, blockchain, and analytics. However, their adoption is based on the services offered by the organization. Adopting these technologies make dependence on labor significantly less. It also enables utilizing sensors, which regulate traffic flow efficiently. This also makes it easier to gather information and data and maintain the security of business transactions. It also makes it easier to analyze the information that has been gathered through different levels, which help them in their decision-making processes. These organizations are benefitted from blockchain as it helps to offer huge possibilities for functions that enable fund transfer and record storing with enhanced security and protection (Palm and Lilja, 2017).
The common society of the UAE is not adapted to these changes, an inclusion of these technologies under the process of the digital transformation may bring in some negative ripple effects. This is where the role of the leader can become important and this study will try to ascertain certain preventive methods with the support of other models that we will address during the course of the systematic literature review.
Apart from these, artificial intelligence has helped organizations in the process of automation of business operations in a way that reduces the need for manual labor. Implementing these digital technologies help organizations to reach out to their customers in an enhanced manner and retain their unique presence in the hugely competitive and massively growing business environment today. It is increasingly important for organizations today to adapt and develop itself with the evolving aspects of the market for maintaining effective stability and efficiency of their productivity and its current market presence.
Technology in public organizations may also be categorized as cost-reducing and service-augmenting technology. Usually, the service-augmenting technologies are preferred by public sector organizations since they enhance the number of customers of the organization due to its budget expansion which consequently reduces the cost of the organization. ( Irwin Feller,1980).
Independent variables: Leadership changes
An independent variable can be defined as the variable which changes in research or experiment in order to test its effects on the dependent variable. Whereas, a dependent variable is a variable which is measured and tested in research or experiment. This variable has a dependence on the independent variable. As the changes are noted in the independent variable, the effects on the dependent variable can be recorded and observed.
Figure 1: Research Framework including the independent and dependent variables along with their internal relationship
(Source: Created by Learner)
A scientific explanation of the association between the framework elements
The concept of a research framework supports understanding the exact structural contents included in any paper or article, based on which readers can easily understand the exact direction of the study. As per the statement of Bongiorno et al. (2018), the research framework is developed according to the investigation made during the analysis of previous scholarly articles relevant to the topic. Besides this, evidence suggests that research framework also provides an in-depth view of the research progress along with highlighting the significance of relevant dependent and independent variables. In this thesis, the dependent and independent variables are already highlighted in the above portion, which is public organizations’ technological preference and digital transformation along with leadership changes. Through considering the designed research framework, it can be assessed that the dependent variable is directly proportional to the independent variable, as it is required to change the leadership strategies and approaches along with the changing preferences of different public organizations.
The framework depicts that the independent variable can be categorized into two different concepts, which are the concept of digital transformation and technology-related leadership approaches. Matter al. (2015) stated that the concept of digital transformation is not a new one, as it was started along with the time of globalization. Almost all of the organizations currently operating in this modernized, globalized, and transformed world follow the principles of digital transformation, for connecting with the outside world. Besides this, it becomes one of the most significant contributory tools in case of maintaining a competitive industrial position. However, Kane et al. (2015) argued that concept of digital transformation automatically brings the ideation of leadership changes, as it would not be possible for the organizations to manage the drastic digitalized changes without proper guidance and support. Therefore, it becomes necessary to understand the inter-dependent nature of the two categorized concepts. The framework represents that the digital transformation is proportional to the technology-based leadership approaches.
On the other hand, as influenced from the viewpoints of El Sawyer al. (2016), technology-oriented leadership approaches include different sub-elements, which are mentioned in the framework with direct arrows, such as leadership approaches, leadership skills, and leadership strategies. Technology-oriented leadership approaches have a direct effect on leadership approaches, leadership skills, and leadership strategies. When the technology-oriented leadership approaches are implemented, they boost the performance of leaders by easing the workload and enhancing the pace of the work. Moreover, leaders can influence their employees, motivate their sales teams, build customer loyalty and connect with peers through the use of technology-oriented leadership approaches. They are also able to monitor their followers more efficiently (Holger Arians) this consequently enables the leader to focus more on his skills, approaches, and strategies which is beneficial for both the leader and the organization. The success factor of leadership changes is dependent on the above-mentioned points. At this viewpoint, it can be stated that inter-dependent or highly complex nature of the leadership approaches might face several challenges while performing the digital transformation process. Contingency model of the leadership has this capacity to handle this complex nature of the leadership especially when someone is dealing with the complex task of the digital transformation of a society which has strong values and a well-developed stream of learning’s to conduct day to day affairs. It can become a mechanical intervention in many processes that are designed for the society. Contingency model can prescribe certain leadership injunctions to remove these barricades in the process of an effective and smooth digital transformation of the public sector of the UAE.
The utilization and interaction of the dependent and independent variables can be elaborated in the table which goes as follows.
| Variable | Theoretical Definition | Operational Definition | Measurement Scale |
| Dependent Variable 1 Contingency Model | Contingency driven leadership model allows a leader to change the leadership style in accordance with the situations. The style of leadership can be ascertained in accordance with the situation which is arising. | While going for a digital transformation of the UAE public sector, two types of leadership styles are apt. First we have transformational leadership style where a leader can act as a motivator, at the same time a leader has to set some goals in accordance with a transactional leadership style, which will be feedback-driven. This style will also support a leader in bringing the conventional practices of the public sector at par with the technology-driven changes. | A satisfaction survey based on the Likert scale can be commissioned for some sample departments. The X-axis of the form will be consisting of various situations or problems. On the Y-axis the respondents have to pick from transactional style of the leadership or the transformational style of the leadership. |
| Dependent Variable 2Conventional methods of leadership versus Technology-Driven leadership | Set of practices and leadership models prescribed by the conventional reporting methods and the methods of calculating the outputs are stationary. | The amalgamation of the technology solutions will add new values and methods to measure the output, the role of contingency driven leadership model will be decided on the merits of the satisfaction levels of the conventional leaders and the methods of the transformation. | Measurement of the satisfaction levels of the conventional leaders with the help of Likert scale based question sheets. Where each fragment of the technology-driven solution will be posted as a separate heading. |
| Independent Variable 1 Readiness levels of the stakeholders and identification of the gaps from the perspective of a leader. | The readiness level of the stakeholders is the most crucial element of the change management style. Stakeholders can find certain parts as easier parts. As a leader one can figure out the exact nature of the leadership intervention with the help of “readiness quotient.” | Demographic details and the computer literacy levels of the area can be taken into an account to take care of the readiness levels of the end-users. Apart from the leadership style, this type of study can also fix a need for certain other interjections in the process of change management. | Semi-structured survey forms can be utilized to collect the feedbacks of the recipients. Apart from it they can also share their problems associated with technology driven difficulties. The results of this survey can be further distilled to come up with key result areas of the leadership-driven intervention. |
| Independent Variable 2 Problems related to the standardization of the data and inclusion of supporting interfaces or mechanisms. | In order to fulfill the gaps caused by the information gaps of various segments of the society, sometimes technology-driven solutions can be introduced in the systems to bring in a parity, as a leader working under a contingency model it is important for a leader to identify these areas. | In the case of the UAE public sector, the gap between the information levels of various segments of society can be very high. For instance we can take the example of the “cybersecurity” related practices. One layer of the population sample may need additional services to practice involved in the system and it can cause additional cost into the process. The same case is applicable to the block-chains, where equal participation of all the segments is required but there is a huge gap in the information levels of various fractions of the society of UAE. | Cost analysis survey dependent on the inclusion of the additional processes. As a contingency driven leader, a leader has to go for an optimized path. Information level surveys can help a leader to identify |
| Independent Variable 3Search for the customization areas and areas where technology developers can contribute | As a leader working under the contingency model, it is very important for understanding the power of the technology and how it can change the process for better results. There are times when a leader can acquire an autocratic approach while undertaking a transformation, someone has to pay for the creation of a greater good for the society is the mantra behind this change. | As a democratic setup, the public sector of UAE is accountable for the betterment of each section of the stakeholders. This is why it is important for a contingency model-driven leader to take care of certain legal aspects related to the fundamental rights of the individuals. The “right to privacy” can be one such example, for instance many individuals can say no to digital transactions because it is an invasion of their privacy. | The measurement of this section will take place under two steps, in the first step, with the help of a Likert scale drove information form, a leader can collect the information related to the displeasures of the fractions of the society and the cases of the violation of the fundamental laws. Further they can request the authorities to change certain policies in an optimum way to facilitate a digital transformation. The output of this survey will also help a leader to signify the fact that whether it can be done with the help of awareness campaigns or stringent measures are required. |
In addition, the challenges are also directly linked with the concept of digital transformation. For example, one of the critical challenges faced by public organizations might be the absence of determining suitable transformation processes according to the organizational aim and objectives. As per the statement of Schwarzmülleret al. (2018), leaders need to apply proficient strategies along with appropriate skills for effective implementation of the transformation process. However, absence in such skills or understanding the applicability of the implementation process might create barriers in front of the public service organizations. In the case of the digital transformation of the public sector of the UAE we can always mention that a transformation of the public sector in a country like UAE also carries forward many social determinants. It is more of a social transformation at various levels and this is why when we compare it with other models, we find that introduction of certain social determinants is also required. The participation of the females in the process of the transformation can be one such issue. Digital technologies identify each and every individual on the merit of his or her unique identity. The active participation of the females in the process of mapping and the creation of unique digital identity can serve as a poignant question.
Apart from the above-mentioned independent variable, it has been assumed that the dependent variable is influenced by different internal and external characteristics. Kreutzer et al. (2017) stated that such internal and external characteristics could influence the other operations of the organizations. The internal and external factors are directly proportional to the technological preference standards of different organizations, as it can be interpreted that changing internal and external factors might change the technological preferences of the companies. For instance, organizations generally choose their preferable technology according to the organizational objectives and the services are given to their customers. In addition, the internal workflow design and external world connection might also influence the technical preferences of public service organizations (Karmakar, 2015). Like the organizations, operating retail businesses could incorporate online buying platforms whereas the organizations working for societal benefits might incorporate the network security platforms. All of these preferences are according to their choice and service types.
There are many other internal and external factors that might affect the organizations while choosing their digital platforms, such as types of business, resource purchasing capabilities, size of the business, and so on (Khan, 2016). All of these could modify the technological preferences. For example, most of the organization incorporates digital security technology; however, most of them do not include inventory management platforms. The research framework represents that the challenges developed in case of the independent variable are also related to the factors involved Ain the dependent variable. The proportional relationship reflects the fact that challenges occurred from the leadership approaches might affect the technology preference also. On the other hand, internal or external barriers often create problems before the technical leaders. Therefore, challenges are a common element in the entire research framework. Through expanding the background of the study, it can be stated that public organizations operating in UAE require investigating about the challenges regarding the digital transformation, leadership changes, and technological preferences, for mitigating the future impacts of these variables on the operational productivity level.
Summary
There are different kinds of organizational leadership styles that are applicable to digital transformation (Nadeem et al., 2018). An organization must select a leadership style depending on its nature. In the current scenario, there are different kinds of organizational leadership suitable for different kinds of situations. All leadership styles are not suitable for every kind of situation (Nadeem et al., 2018).
In earlier times, there were four basic leadership styles (explained later in section 2.2.1 of this thesis) that have been mixed and bred to offer more than 10 to 12 styles of leadership such as autocratic leadership, democratic leadership, strategic style of leadership, transformational leadership, team leadership, and cross-cultural leadership. The other kinds include facilitative leadership, Laissez-faire leadership, transactional leadership, coaching leadership, charismatic leadership, visionary leadership, situational leadership, and such other styles of leadership (Henriette et al., 2015). The table below gives a brief account of each of the leadership styles mentioned earlier.
The contingency model allows a leader to change the leadership styles in accordance with the situations and the profiles of the stakeholders. One of the primary motifs of this research is to formulate the impact of the profiles of the stakeholders on the development of the situation and their culminations with the help of right leadership styles procured from the conceptual framework of the contingency driven leadership model.
| Type of leadership style | Description |
| autocratic leadership | Autocratic leadership is a leadership style characterized by individual control over all decisions and little input from group members(Kendra Cherry, 2019) |
| democratic leadership | It is a type of leadership style in which members of the group participate actively in the decision-making process.(Amanchukwu RN, Nwachukwu, Ololube, Gloria Jones Stanley). |
| strategic leadership | Strategic leadership can be defined as employing a strategy for the management of employees.(Prachi Juneja) |
| transformational leadership | Transformational leadership is a leadership style in which leaders motivate their followers to innovate and bring change for the success of the organization. (Sarah K. White, 2018) |
| Laissez-faire leadership | Laissez-faire leadership refers to a style where the leader facilitates an environment or setting where the subordinates are accorded numerous opportunities to make decisions (Roussel, 2006). |
| transactional leadership | According to Burns (1978), Transactional leadership theory suggested the relationship between followers and leaders as a sequence of exchanges of fulfillment designed to maximize individual and organizational gains. |
On a primary level when we check all the leadership styles that are applicable in the present case from the point of view of the contingency-based models, we cannot negate any particular style or adapt any particular style, they all have their own set of virtues and demerits under different circumstances.
Some leadership styles are suitable for mitigating issues with employees such as Democratic Leadership, Laissez-Faire Leadership and Transactional Leadership (Meffert and Swaminathan, 2018). Whereas some other leadership styles may be useful for changing the operational style of the business running within the organization such as autocratic and transformational leadership (Alos-Simo et al., 2017).
Technological and transformational leadership are some of the most suitable styles of leadership due to several reasons (Paracha et al., 2012). Transformational leadership considers all the involved individuals in the decision making processes and believes in teamwork that can produce enhanced ideas and vision for the process of digital transformation (Uhl and Gollenia, 2016). The transformational leaders believe in inspiration and motivation for executing the necessary change within the organization. Transformational leadership emphasizes longer-term and vision-based motivational processes (Bass & Avolio, 1997). The style of leadership greatly influences the technological preferences of organizations (Shap. Digit. Enterp., 2017). Digital transformation requires the maximum number of consciousness and minds to achieve the set goals and objectives (Shap. Digit. Enterp., 2017). Transformational leadership enables employees to authorize decisions according to their job roles within the organization. (Hofmann, Sara & Ogonek, Nadine 2018) studied that, digital transformation is essential for meeting the requirements of the ever-growing business environment for both public and private sectors.
CHAPTER FIVE: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Introduction
The research methodology is used as a framework to systematically conduct the research. This saves time and money for the researcher as he will have information and knowledge about the necessary steps that should be taken while conducting the research. A research philosophy refers to the different beliefs about the methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation for research. Different researches require different research philosophies that are chosen on the basis of the research topic. There are various types of research philosophies- positivism, interpretivism, realism, pragmatism, objectivism, subjectivism, functionalist, radical humanist, interpretive and radical structuralism. Positivism research philosophy is chosen in this research by the student/researcher based on the research topic and literature review. Positivism research philosophy states only facts and data which is gained through observation. In this type of research philosophy, the researcher will only be able to collect and interpret the data in an objective manner. The findings based on this research topic are quantifiable and observable (research-methodology.net, 2019).
In the case of present research program the methodology will focus more on the exploratory nature of the research, the calculation of the key results areas determined in accordance with the dependent and independent variables will be collected with an intention to identify the problems. After this identification, a standard chart related to the leadership approach will be furnished. After a discussion on the various aspects of the data collected from different areas, generalization of the findings will be done with an intention to come up with findings, discussions and conclusions.
While dealing with a leadership model drive by the contingency model, it is advisable to go for action research, instead of regular research. The interdependence of the variables works as a major problem in this case. This interdependence creates a matrix of the requirement and the scope diagram associated with the contingency model identifies various problem areas where research is required. This is why a research program consisting of power and dynamic model like contingency model can adopt multiple approaches by fragmenting the research questions. It can also assimilate all the findings in the final draft with the help of a vision document.
A research approach is defined as the way the research should be conducted. The three main types of research approaches are the deductive approach, the inductive approach, an abductive approach. The research approach used in this research will be a deductive approach as it will be beneficial for the research topic. In this approach, hypotheses are developed based on the existing theory and then the research is conducted to prove the hypotheses as true or false. The deductive approach uses reasoning to analyze and interpret the data. It helps in gaining causal relationships between the variables and the concepts. It measures the data in a quantifiable manner. The data collected will be tested based on this approach so that the reliability and validity of the hypotheses can be proved (research-methodology.net, 2019).
A research design is used to carry out a research study. It refers to the different arrangement of conditions for collecting, analyzing and interpreting the data. The different types of research design are- exploratory research design, explanatory research design, descriptive research design, and conclusive research. The researcher has chosen the exploratory research design as it will be more useful for the research topic since this area has not been explored much. The exploratory research design does not seek to provide concrete and final solutions and outcomes to the research topic. The researcher will be able to explore various depths of the research topic and identify the impact. In this research design, the data collection methods and its interpretation are flexible and dynamic. However, the results and outcomes based on the exploratory researches are not complete and further research can be conducted (libguides.usc.edu, 2019). In the present case, we can see that the researches related to the adaptation of the big data facilities in the public sector of the UAE are inconclusive, the success of this endeavor can only be judged after its success in delivering the goods. For instance, for effective inventory management in a hotel or airport, it is important for a company to collect data for a stipulated time. After this collection the developers can come up with the fields of the comparison and draw conclusions. The present status of this data collection management is in a state of trial, authorities are collecting data, they are making projections, and still the formidable conclusions are out of sight. We can compare this scenario with the automobile industry of USA. Almost a decade ago this industry collected consumer data at war footage, after the collection of sufficient amount of data, the companies implemented the recommendations, during the first few years the projections were correct. However, after a point of time their system became a victim of the oversaturation of the data, this is important for the public enterprises of the UAE to learn from these examples. However, the present status clarifies that most of the organizations are still in the phase of data collection. As a leader it is important for a person to analyze the situational variables and project about the success or the failures of the model with the help of beta testing of the results.
When we compare the same scenario with the IoT devices, we find that during the initial run of the installment they met with the success, however, on the scale of the leader situation, it denotes that this situation demands moderate leadership, the moderate leadership is the need of the hour because of the fact that security concerns related to the IoT devices are still untested, unforeseen events or perils may occur because even now we cannot trust machines blindly. A situational analysis with moderate intervention is the need of the hour.
A research strategy will enable the researcher to determine the ways and methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation. The different types of research strategies include surveys, experiments, action research, case studies, grounded theory, ethnography, and archival research. The research strategy used in this particular research is surveys and interviews as it will help the researcher in gaining a deep insight into the research topic from the respondents. It will provide the researcher with a new perspective based on real-life responses. Primary data will be collected thus using surveys and interviews will be beneficial for analyzing and interpreting the collected data (web.wlu.ca, 2019). Most of the digital technologies promote the culture of operational research, this research can be equated to the quality management mechanism where they check a given product or service on certain parameters.
The research choices refer to the methods through which data is collected. It is of three different types- mono method, multi-method and mixed-method. In the mono method, only one type of data is collected that is either quantitative or qualitative data. In mixed method, both quantitative and qualitative data is collected. In this research, the researcher has opted for mixed methods as it is beneficial for analyzing the outcomes of the research topic. It will also help in answering the research questions efficiently. The quantitative data is gained from the survey while the interviews contribute to the qualitative data. However, the qualitative data can sometimes be biased as they are subjective whereas there are fewer chances of the quantitative data to be biased as they are objective. Primary research uses mixed methods for collecting the data and interpreting the results (resourcecentre.foodrisc.org, 2019).
The era of digital transformation promotes the culture of the digital footprints, the conventional methods of the data collection become redundant here, and however, a leader can utilize this data by segregating it for the purpose of the processing. While thinking about it one has to keep an eye on cybersecurity as well, for instance the data collected through EVM can be misused by certain parties; it can be misused to break the oath of the secrecy associated with the process of the voting. As a researcher it was important for us to table down all the perils associated with the technologies because it is also an important question that needs an answer at all the possible levels.
The sampling technique used in this research study is random probability sampling. Sampling is necessary for a research topic as it helps in choosing the respondents for the survey. The two kinds of sampling are probability sampling and non-probability sampling. The respondents are chosen from various public organizations in UAE as they will be able to provide first-hand authentic information about the research topic. It will help in answering the research questions. For qualitative data, 4 managers from various public organizations in UAE will be chosen who have experience in the field of digital transformation and the role of leadership in that. The topic is vast, this is why it was important for us to kill the monotony of the respondents, in order to maintain this variable nature of the answers, we choose our samples from all walks of the life that were connected with the operations.
The implementation of the operational research is very common with the digital technologies because most of the technologies are enabled with adequate mechanisms to conduct regular surveys with an intention to keep a check on the levels of the quality of the service levels. While adopting a contingency model for the leadership, a leader can take advantage of these mechanisms in the form of the beta testing of various tools and the satisfaction levels of the users.
Out of the two data collection techniques, namely primary and secondary, the researcher has opted for the primary data collection method as it will enable him to gain first-hand information about the research topic. Primary data collection consists of quantitative and qualitative data which are both used by the researcher in this particular research. It will provide both quantifiable and non-quantifiable data and help in analyzing and evaluating the data. The quantitative data will be analyzed using graphs and pie charts as they are based on statistics and numbers. The qualitative data will be analyzed using the transcripts which will be gained from the interviews. The researcher has followed the research onion for conducting this research methodically.
In developing the research methodology for the proposed study, a number of issues must be taken into consideration such as the type of data needed, the sample size, the design among others. The research onion can be a good pathway to implement the methodology framework for the study. Nonetheless, the sections cited in each part have been linked to the research onion meaning when fully developed are going to provide a lean process that shall enable the researcher to succeed to realize a well-founded research methodology application.
On a summarized note following salient points can be jotted down related to the methodology of the research.
- The research program follows a mixed structure in terms of the methodology. Where deductive methods are employed with an intention to accommodate the inductive flow of the information.
- The data collection sources are primary sources, the questionnaires are designed for the research follows a semi-structured nature.
- The semi-structured nature of the questionnaires allows the researchers to deduct the desired information to examine the hypothesis. The other part of the questionnaire is aimed to generate leads towards new issues and tangent areas that can become important.
- This research program largely follows random sampling methods, however in order to mitigate the impact of the variables geographical and demographical variety is introduced.
- The identification of the core problems follows a layered structure; the researchers identified the core problems with the help of a systematic literature review where they compared the models of digital transformation. The second layer of the exercise accomplished with the help of the primary data collection where respondents from the segments of various stakeholders expressed their views on the difficulties that they are facing.
From the objectives, the action plan shows a need to have scrutiny on the effects of leadership outcomes on digital transformation. The two mark the key-dependent and independent variables to be operationalized come the main dissertation. The action intended in the objectives can be a hint on the most suitable methodology for the proposed study.
While conducting this research the dimension of interpretivism ruled the proceedings mainly, under this philosophy research prefers to collect random data on its face value and put it in a table form to bring out interpretations related to various fields that are associated with it. Under the present theories, this approach has become an effective tool to facilitate knowledge management. Considering the nature of the research that we are undertaking, it was important for us to collect the data in such a fashion so that it can become an effective technology-based tool (McNabb, 2008). Here we need to understand two more factors associated with the research, the output of this research is dependent on the correlation between these two factors. The first factor was associated with the identification of the problems associated with the digital transformation. The second factor was related to the contingency-based leadership model. This research was attempted to explore the problems and the dynamic solutions that contingency-based models can offer in relation to various processes and other aspects. This research follows the ideology propagated by Burrell and Morgan (1979), they noted, “it does not matter whether the researcher is cognizant or not since every stage of his research involves making assumptions”. For instance, the assumptions could be about human knowledge i.e. epistemological assumptions or realities encounter at the time of research i.e. ontological assumptions and the degree to which personal values influence a selected research process i.e. axiological assumptions. It is these assumptions that in turn shape a research’s understanding of the research questions set out, the methods selected and the manner of interpretation of the findings (Crotty, 2008).
The current research also presented many occasions where we made assumptions and most importantly we followed the nature of action research in order to facilitate those assumptions with an intention to enrich the contemporary nature of the research.
This is why we can say that we successfully developed a coherent research project whereby all the research elements fit together. Persuaded by Johnson and Clark (2006) it is important for management researchers to have awareness over the philosophical commitment they make through their choice of research strategy. The reason is that such would have a significant impact on the undertakings they make and how they comprehend what it is they are investigating.
The variable nature of the exploration area was another challenge that we faced. The satisfaction levels of the respondents with the technology were changing because it is an interaction that was taking place between them and technology. They were constantly thinking and rethinking the technology from various points of view. Social reality and personal comfort level were constantly at change this is why striking a coherence that can be considered as a controlled environment was difficult to achieve. However, the quotient of this coherence also forms the USP of this research. The consistent operational researches conducted by mechanical means often fails in registering this coherence because of their limited fields, however, semi-structured research with a human standing at the receiving end has this potential to capture certain useful details with great ease. Hence, affirming that social reality derives from the perceptions as well as consequent actions linked to social actors i.e. people.
It is pertinent to mention certain other elements that have the potential to stereotype the results, for instance, as Gill and Johnson (2010) noted a positivist would seek to establish causal relationships in the data to arrive at “law-like generalizations”. Similarly, the generalizations can be used as universal standards to explain or predict trends and events in organizations. These generalizations are useful when the variables of the research are slow-moving or stationary, however, the same generalization can force a stagnancy in the results when we see them from the perspective of a mechanism like contingency-based research.
We rely on the data generated from the feedback of the participants at UAE Public Organization to make generalizations that shall, in turn, be used to explain and predict behavior in this firm as far as leadership processes influence digital transformation. And persuaded by Gill and Johnson the researcher will seek to establish possible causal relationships between leadership and digital transformation. Due to this, means the research philosophy to be sought shall be positivism. How then does this contrast with interpretivism philosophy?
Interpretivism holds that humans and physical phenomena are in different positions. Thus, human beings cannot be studied in the same context with physical phenomena; for interpretivists, social sciences are not the same as natural sciences. Further, different individuals given their varying cultural backgrounds and circumstances, end up giving different meanings hence create unique social realities. It is held that unlike positivists, interpretivists are hesitant towards the formulation of universal laws that are applicable to everybody. In other words, interpretivism school of thought does not advocate for generalization or law-like premises. Thus, the focus of interpretive research is to come up with new, richer comprehension as well as interpretations of social realities and contexts. For instance, in the context of business or management research, a researcher would look at the organizations from the purview of different groups of individuals. The arguments are that for an interpretivism a CEO or board of governors or employees et cetera perceive or experience their company in different ways; thus have varying and separate workplace realities (Kelemen and Rumens 2008). The researcher is looking at interpretivism was persuaded by its assertions but given that it talks of multiple experiences and realities was seen as not the suitable philosophical paradigm for the present study. There will be a need to have law-based affirmations on the effects of leadership towards digital transformation making positivism philosophy the better research philosophy for the present research.
In research approach, there exist two paradigms namely: (a) deductive approach and (b) inductive approach. For instance, a deductive approach involves a movement from theory to hypothesis to observation and then confirmation. On the other hand, the inductive approach is a movement of research starting from observation then pattern then hypothesis and culminates in theory (Wilson, 2010). Better still, if a researcher commences from theory that is developed from the readings such as academic literature and then designs a research strategy with the view to confirm/test the theory then such points to deductive approach (Anderson, 2004). Evidently, for the present research it can be affirmed that there are quite substantial readings that will be required to understand what past scholars have said regarding leadership processes and models and their effects on digital transformation. On the same note, the researcher is keen to engage as much literature and theory as possible to understand how the two variables relate to testing the hypothesis. Due to this, the proposed study depicts that it shall rely on a deductive approach. On the converse, an inductive approach is whereby the researcher starts by data collection to explore the phenomena in the end process building theory through a conceptual framework (Wilson, 2010). In the proposed study, it can be seen that the researcher upon reading the literature review at the bottom has developed a conceptual model that links aspects of leadership to digital transformation. However, along with inductive approach, this topic also leads to the analysis of an abductive approach which is a logical inference that considers an observation or set of observations to find the simplest and most probable explanation for the observations (Wikipedia). In abductive approach, data is gathered to explore a phenomenon, capture themes and explain patterns; and also generate new ideas to existing theory by eventually testing through data collection (Anderson, 2004).
Research design can be considered, as the plan required determining the activities and tasks of the overall research project.. Under this research we are dealing with certain activities that are out of the locus of control, they are out of the locus of the control of the administrators as well. This nature of the activities forced us to adopt the path where the findings of exploratory research can pave the way for some recommendations that can facilitate a leader to adopt the contingency model of leadership and increase his locus of control over the activities with an intention to cultivate desired outcomes.
The explanatory research will be more beneficial for this particular research since the purpose of this research is to comprehend find the general impact on UAE public organizations. The Explanatory research design will be used in this research study as we already have enough knowledge and insight into the research topic. The impact of leadership on digital transformation in the public organizations in UAE is a relatively new topic and this is why we don’t have many accredited sources that can support us on the path of this journey.
Explanatory research design enhances the understanding of a researcher on a particular topic. Especially when we don’t have data fields that can be compared that easily. A lack of data can in any given field gives rise to an inductive approach and exploratory research becomes essential to leverage the research program.
It does not provide conclusive results because of the lack of its statistical strength, but it makes the researcher determine how and why things happen. Data for explanatory research may be obtained from Secondary sources such as published literature or data one of the drawbacks of this kind of research is the small sample size. Some commonly used methods of explanatory research design include literature searches, depth interviews, focus groups, and case analysis (Muhammad Yousaf). We studied the models of digital transformation models of the other countries along with the notes prepared by various change management agencies. We also rummaged through the dailies of many such programs to jot down some standard problems. For instance, affinity with digital devices can be one such area that can emerge as a big handicap for many people during the course of a digital transformation.
Analytical Techniques
Since the research is explanatory research, the research strategy will constitute a case study which etymologically means “an instance of”; it is usually an investigation carried out of either one or a number of specific “instances of” something that relates to the case in question (Yin, 2009). While writing the findings and recommendations we will follow a micro to macro approach, under this approach we will establish our case study and the findings as a specimen of the probable events and allow the readers to compare the case facts and the findings with the other cases to draw parallels.
A case involves something concrete such as a group or individual or an organization; also, something that is much abstract such as a management decision, an event or a change program (Gomm et al, 2000). It is worth noting that cases occur in a natural way hence cannot be manipulated as would be the case with an experiment. Also, a case study may be developed within multiple sources of data such as questionnaires, interviews, archival documents or observations as a way to facilitate triangulation in the findings (Yin, 2009). In fact, it is on the basis of this statement the researcher in the research methods will set to use mixed methods so as to facilitate the triangulation of the same case study. The other issue worth noting is that case studies have widely featured in vast management research as well as strategy, innovation, organizational change, information systems all this depicting the versatility of the design. Also, the capacity to undertake investigation on cases in-depth and to apply multiple sources in terms of evidence renders such a strategy (case study) useful tool for research studies that are descriptive (Gomm et al, 2000). According to Yin (1998) case study research facilitates theory building as well as theory testing. For instance, in explanatory research, case studies provide avenues to investigate causal mechanisms as well as the specific situations at which they are activated (George and Bennet, 2005).
In the current research, we opted for a hypothesis consisting of three fields. In case our hypothesis fails then it can be considered as a theory of failure if it succeeds then it will become a theory of success, and in case of a variable result or a result where a change can make the hypothesis work, then it will become a derived theory. The contingency model of the leadership is a data-hungry model, as a leader working to facilitate a contingency-based model, it is very important to consider every find either as a stepping stone or an experience that can save him some time in the future.
The case studies are 2 public sector organizations in UAE both belonging to the oil and gas sector. The organizations are Abu Dhabi National Oil Company and Emirates National Oil Company. Both these organizations are observed for a period of 6 months to find out the influence of different leadership approaches on the digital transformation in these companies. The transformational leadership approach was applied to Abu Dhabi National Oil Company and transactional leadership approach to Emirates National Oil Company. The results revealed that changing the leadership styles increased the efficiency of these organizations. It was observed that transformational and transactional leadership were successful in promoting an environment where change in digitalization was managed more appropriately by the followers. However, the Abu Dhabi National Oil Company showed more digital transformation than the Emirates National Oil Company. Hence, it was concluded that appropriate leadership approaches have a positive impact on the public sector in UAE. The oil and gas companies were selected for the case study due to the fact that oil and gas are the main sources of income for UAE and these organizations are vital to the country’s economy.
The preferred research method for the proposed explanatory study shall be mixed methods. Generally, mixed methods research is whereby an investigation involves, gathering (collecting), analyzing and interpreting either quantitative or qualitative data compiled in a single study or series of studies (Leech and Onwuegbuzie 2008). Mixed methods are a design characterized by both philosophical assumptions and methods of inquiry. Methodologically, it incorporates philosophical assumptions that guide the process of collection and evaluation of data in a study(ies); the assumption with mixed methods is that the combination of both quantitative and qualitative criteria gives a better comprehension of cited research problems (Creswell and Plano Clark, 2007). Below is a summary construct of the mixed methods approaches.
Table 3.1: Mixed methods techniques
| Qualitative (Postpositivist) | Quantitative (Positivist) |
| Meanings | Causal |
| Subjective reality | Objective reality |
| Human intentions | Separated or detached |
| Personal involvement | Samples/populations |
| Natural settings for the actors | Variables |
| Verbal information | Numerical/statistical |
| Generalises findings in the cases | Impersonal |
Source: (Cameron, 2010)
The proposed study, therefore, shall rely on the combined use of qualitative and quantitative research to capitalize on their advantages. It involves collection of data relying on both qualitative and quantitative data where the former may be operationalized using instruments, checklists or records, and the latter interviews, documents, observations, audial-visuals or archival documents. Quantitative analysis involves statistical analysis to perform group’s comparisons, variables linkages and description of occurring incidences; on the other hand, qualitative analysis relies on texts as well as images to code, develop and relate themes (Leech and Onwuegbuzie 2008). For the proposed research, the implementation of mixed methods shall be in the fact that there will be statistical analysis of variables upon data generated from the closed-ended questionnaire; then follow up interviews to be initiated using interviews shall form the basis for the qualitative research data in the project.
There exists two study time horizon namely cross-sectional and longitudinal. A cross-sectional study is whereby gathering of data is administered to a whole study population within a single point in time usually to investigate the nexus between variables (Wilson, 2010). Longitudinal research involves the study of individuals at varying stages of their lives; for instance, one group can be studied for a long period of time e.g. many years (Anderson, 2004). Just from the description of the two study time horizons, it will be ruled out that longitudinal study is not going to be suitable for the proposed research because following up the sampled group for a period of many years would not be necessary. However, the data collection administered to the sample shall only require to be administered at one single point in time and from there proceed to analyze data. This is the reason why this proposed study shall constitute a cross-sectional study time horizon.
In contemplating about types of data, it refers to the fact that the researcher will settle for mixed methods and also most of the data for this purpose will be gathered by going through the content already available on this subject. In that case, there shall be both primary data and secondary data. Secondary data shall be developed upon review of the content of documents i.e. journals, books, peer-articles, management, and digital transformation reports to furnish the study with insights related to the main variables. Primary data shall draw from the primary sources to be used in the study such as questionnaires and interviews. Due to primary research there shall be both qualitative data and qualitative data that shall be generated from the surveys as well as individual depth interviews.
Normally, a sample serves as a subset of the population; in summary, it is the group of individuals that take part in the study while a population been the broader group of individuals to whom the results apply (Yin, 2009). Let us consider an example to comprehend the difference between a sample and the population. Suppose the employee base of a public organization in UAE is 7500. In such a case if the research only considers the employees in this organization (suppose oil and gas company), then this number will represent the population of the research but in case, the research considers the employees of all the oil and gas companies then this number (7500) will represent the sample of the research. For instance, earlier it was indicated that UAE Public Organisation has an employee base of over 7,500 (Berman, 2012). Hence this would constitute the population in as far as the investigation is about digital transformation in UAE public organizations.
Questionnaire Development
After selecting the sample, the questionnaire is developed and then distributed among the participants. As the mixed research method is used, both qualitative and quantitative questions would be included in the questionnaire. The quantitative approach may be used to answer queries such as:
- What are the technological leadership approaches adopted by the public organizations in UAE?
- What is the impact of technological leadership approaches on the preference of digital transformation in UAE public organizations?
- How has the adoption of the technological leadership approach affected the technological preferences of the public organization in UAE?
- What challenges are associated with the technologies preferred by the public organizations in UAE?
And qualitative approach may be used for obtaining answers to the following queries:
- How can the identified challenges related to technological preferences and changing leadership be prevented or mitigated?
- Which technologies are preferred by the public organizations in UAE?
The responses from the participants are noted to collect data. The questionnaire is designed keeping in view all the dependable and independent factors mentioned earlier. The questionnaire was printed on a paper and responses were obtained in writing. The questions were designed keeping in view the explanatory nature of the research. The fonts in the questionnaire were kept bigger so as to facilitate ease of reading. The questionnaire was thoroughly read before distributing it to respondents.
Measurements
Operational variables refer to how you will define and measure a specific variable as it is used in your study. Our research takes into account two variables; dependent (technological preference of public organizations) and independent (digital transformation and change in leadership). Here, we can estimate the change in the dependent variable created by making some changes in the independent variable only through operationalization. In our research, we will observe the changes in the technological preference of public organizations by switching to transformational leadership and introducing the use of new digital tools.
The Sample
In terms of sampling, the researcher shall rely on the probabilistic approach mainly random sampling. In simple random sampling such involves the case where each member in a sampled population has equal chances of being selected or chosen (McNabb, 2009). For instance, the proposed study will require to enroll X employees from the approximated 7,500 employees forming the employee base for UAE Public Organisations. The actual sample size details have been illustrated next.
Sample Size and Population
The actual sample size was calculated using Slovin’s formula as shown below.
In the proposed research, a margin of error at 10% will be allowed because there shall be needed a 90% confidence interval to show and justify the relationship between leadership processes and digital transformation at UAE Public Organization. The actual implementation of the formula is as shown below:
7,500 ÷ (1 + 7,500*0.1)2 = 99
The sample size to give a 90% confidence interval of the results shall be 99.
However, assuming the researcher will see to have a margin of error at 5% then the sample size will be:
7,500 ÷ (1 + 7,500*0.05)2 = 380
Thus, the two remain possible sample size comes the main dissertation depending on the ability to run a survey of up to 400 employees in the digital transformation organizations in UAE.
No doubt that bias exists in all research designs. However, while conducting this study, the researcher had a critical focus on the biasness level. The researcher tried his best in minimizing bias during the study. Outlining the potential sources of bias enabled the researcher in the critical evaluation of the research outcomes and conclusion. The researcher explicitly articulated the rationale for and chose an appropriate research design to meet the research aims and as a result general pitfalls in relation to bias were reduced.
Validity and Reliability Analysis
The researcher, while conducting this study carefully addressed the issues of validity and reliability. The term ‘reliability’ refers to the degree to which the same answers can be gathered using the same instruments one time. Therefore, the data gathered for conducting current research was associated with the high levels of reliability which can be further used by other researchers using the same research methods under similar conditions.
Whereas, the term ‘Validity’ can be described as an extent at which requirements of study method have been crucially followed during an entire process of generating research outcomes. The researcher while conducting this research carefully considered validity as a compulsory requirement of the research. Some of the major forms of validity which the researcher followed were criterion-related validity, internal and external validity, construct validity, face validity, and concurrent validity.
Ethical Considerations
Non-maleficence and beneficence
In the process of data collection, the researcher shall ensure not to put harm to the participants whatsoever. It means to ensure there shall be permission granted by the management to survey the employees hence indulge them in a process that would not harm their careers i.e. crisis with the management. Ultimately, the completed research shall, in turn, be shared with the management of the UAE Public Organization to give them insights on how they could leverage their leadership processes with digital transformation.
All the participants shall be treated with dignity and their personal information such as names shall not be disclosed whatsoever. The same applies to the fact that the departments they work for shall remain confidential.
All the participants retain the right to determine whether to participate in the research or withdraw at any time. A consent form shall be sent to every participant to ensure they sign on it as a way to show their consent to participate in the study.
All research participants will be treated with all fairness and attention; all gender, for instance: shall be presented with similar survey questions and their opinion not likened to their gender et cetera.
The anti-discrimination act will be considered before conducting surveys and interviews.
The boundaries of this research project are set around the UAE public organizations and all kinds of employees of these organizations will not be involved in the data collection and analysis process.
Summary
A research agenda is created for this research project that revolves around the impact of leadership on digital transformation in UAE public organizations. The research agenda defined for this particular research is a plan that focuses on the ideas and issues of leadership and digital transformation. The researcher will focus on the important and necessary fields for carrying out this research project. The research agenda is not concrete and they keep changing from time to time due to the increase in the knowledge base and new research topics and questions. For instance, the research may start off with the study of transactional leadership on the various aspects of digital transformation. However, the researchers may come across different styles of leadership through further review of literature that may prove other styles of leadership to be more beneficial for digital transformation such as situational leadership. The present structure of the research is promoting the concept of contingency based leadership model to handle various types of variables that can force the enablers and receivers to look at the process from a different view point.
For developing an adequate research agenda the researcher will seek responses from faculty members regarding their views on the chosen topic or subject area. The faculty can be used as a resource to understand the concept of leadership and digital transformation, which requires an in-depth explanation and study. This will help the student to understand their area of research and interests. If the interests are overlapping and similar for the students, then the perspectives of everyone should be considered (Mahler, 2017). It is necessary to have a great deal of knowledge related to the research topic. It will be beneficial for the student to study materials related to digital transformation and leadership in order to create the most appropriate and suitable research agenda for the overall research project. New topics can also be read in order to widen the scope of interests. The students/researcher can take the help of the faculty to gather various reading lists for enhancing their knowledge. The information should be read and understood thoroughly and the key authors and scholars should be identified. Their work in the related research topic must be understood properly to conduct the current research efficiently (de Reuveret al., 2018).
For understanding this research agenda, the student has to identify the different courses of leadership and digital transformation that will help them to advance their research agenda in terms of relevant methods and specific knowledge about the issues. The faculty can be contacted to understand the title and course of a particular class as only the title will not shed much knowledge about the content of the class. They can take the help of various departments instead of sticking to one department. For instance, for this particular research two departments need to be consulted that is management and other departments of digital background. This will enhance their knowledge about the different courses and help them in choosing courses according to their interests. By understanding the research questions, the student/researcher will also be able to find ways to answer them.
After getting a grasp of it, the courses can be selected which will help them in achieving the goals and objectives. Furthermore, to advance the research agenda, class assignments can be used to understand a specific part such as the literature review or proposal for a research study (www.tau.ac.il, 2019). For instance, a literature review of digital measures in the current business environment and the requirement of change in leadership can be studied and reviewed to gather a better understanding of the chosen topic for the research project. The research agenda may include surveying different kinds of public organizations in UAE and their response towards transforming digitally. Furthermore, it is necessary to understand the previous trends of digital transformation in order to develop an authentic research agenda that can fulfill the criteria of novelty. It is necessary to test the research agenda against reliability and authenticity of original research. Similar researches on the subject area have been conducted before that requires consideration before adopting this particular research agenda.
The research agenda will also enable the student to go out of their comfort zone and explore diverse interests and topics. For instance, the researchers can study the process of digital transformation for public organizations of other countries in order to understand the styles of transformation and leadership in different countries. Comparisons provide a better understanding of the overall topic that enhances the final outcome of the overall research project. The students/researcher can take the help of the faculty members to provide them with research projects in which they can participate. The faculty members can belong to different departments. This will help in gaining different perspectives and enhance the interests of the students/researchers regarding digital transformation and leadership. Additionally, to enhance the research agenda, students/researchers can attend different conferences of different leaders of various public organizations to understand different ideas and gain feedback on their research topic.
The research agenda for this project plays a significant part in helping the students/researchers and faculty design scholarly activities related to different aspects of this particular research. It can help in enhancing the areas of research and the methodologies that will be used for answering the research questions. A meeting with the faculty and other senior students will help the students/researchers gain clarity about their research and help them in designing their research activities (Abbasi et al., 2016). A well-formulated research agenda will provide boundaries in the research and help the students/researchers in conducting the research in a methodical manner. To develop the research agenda, the students/researchers should first be able to understand the concept of leadership and digital transformation and then identify the sources which are used for conducting the literature review.
The research topic of this research is to identify the impact of Leadership in digital transformation in UAE public organizations. Digital technology plays a huge role in our daily activities and has helped in simplifying our lives. Digital technology is used in businesses to transform business operations and positively influencing society. The aim of the public sector organizations is to provide maximum benefits to the people in the society by offering better facilities and services. Thus, the public sector enterprises in the UAE use digital technology to digitally transform their business. Leadership also plays a part in the digital transformation of organizations. The business environment is constantly changing and thus it is necessary to engage leaders so that the digital transformation can be implemented successfully. Leaders are responsible for influencing the employees and followers so that there is effectiveness and efficiency while achieving the digital transformation for business. This topic is chosen by the student/researcher as this topic is intriguing and the student/researcher wants to explore more about the topic in the future. They want to become a leader in an established public sector organization. Thus, having considerable knowledge about the field will enable the student/researcher to efficiently work in the future. The literature review was collected from various journals, books and previous researches related to the current research topic. The students/researchers have gained interest in this topic as he has seen many leaders leading a group of people for a particular cause (teachingcommons.cdl.edu, 2019). Leadership is necessary for every field and the faculty of the university also serves as a leader in the classroom. Thus, the students/researchers have found it interesting and hence chose this topic to carry out the research. Several research questions are developed which are divided into primary and secondary research questions. The primary question will seek to answer the impact of technological leadership approaches on digital transformation among the public sector organizations. The secondary questions will mainly seek to answer the different types of technologies used by the public enterprises in the UAE and the challenges faced by them. The research objectives are formulated with the help of the research questions. This will help the researcher to conduct the research in a methodical manner as he/she knows which path to follow for the research (cse.unl.edu, 2019).
Abbasi, A., Sarker, S. and Chiang, R.H., 2016. Big data research in information systems: Toward an inclusive research agenda. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 17(2), p.I.
Ahmed, A. and Abdalla Alfaki, I.M., 2013. Transforming the United Arab Emirates into a knowledge-based economy: The role of science, technology, and innovation. World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, 10(2), pp.84-102.
AlaaEldin Ragab, 2014. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20141022083516-52718218-the-impact-of-poor-leaders-on-employees/
Al Athmay, A.A.A.R., 2013. E-governance in Arab countries: status and challenges. Global Journal of Business Research, 7(5), pp.79-98.
Al Qubaisi, J.M.L.F., Badri, M.A., Ajmal, M. and Elanain, H.M.A., 2015. Leadership, culture and team communication: analysis of project success causality–a UAE case.
Alameri, M., 2013. Assessing resistance to technological change for improved job performance in the UAE (public sectors) (Doctoral dissertation, University of Salford).
Al-Jenaibi, B., 2014. Comparing the roles of PR practitioners in the public and private sectors in the UAE. International Journal of Information Systems and Social Change (IJISSC), 5(3), pp.64-76.
Al-Jenaibi, B., 2015. Current issues about public relations professionals: challenges and potentials of PR in UAE organisations. Middle East Journal of Management, 2(4), pp.330-351.
Al-Khouri, A.M., 2014. Digital identity: Transforming GCC economies. Innovation, 16(2), pp.184-194.
AlMazrouei, H. and Pech, R.J., 2015. Working in the UAE: expatriate management experiences. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, 6(1), pp.73-93.
Alos-Simo, L., Verdu-Jover, A.J. and Gomez-Gras, J.M., 2017. How transformational leadership facilitates e-business adoption. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 117(2), pp.382-397.
AlShamsi, O. and Ajmal, M., 2018. Critical factors for knowledge sharing in technology-intensive organizations: evidence from UAE service sector. Journal of Knowledge Management, 22(2), pp.384-412.
Amanchukwu RN, Nwachukwu, Ololube, Gloria Jones Stanley
(Ameer Rosic,2019) https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-blockchain-technology/
(Amish Gupta) https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/blockchain-technology-introduction/
Arvonen 1999, 245
Awofeso, N., Hassan, M. and Hamidi, S., 2016. Individual and collaborative technology-mediated learning using question & answer online discussion forums–perceptions of Public Health learners in Dubai, UAE. Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and e-Learning, 31(1), pp.54-63.
Azmeh, S. and Foster, C., 2016. New trade conflicts and the race for technological leadership in the digital economy. International Development.
Bason, C., 2018. Leading public sector innovation: Co-creating for a better society. Policy Press.
Bass & Avolio, 1997
Bealer, D. and Bhanugopan, R., 2014. Transactional and transformational leadership behaviour of expatriate and national managers in the UAE: a cross-cultural comparative analysis. The international journal of human resource management, 25(2), pp.293-316.
Bin Taher, N.A., Krotov, V. and Silva, L., 2015. A framework for leading change in the UAE public sector. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 23(3), pp.348-363
Bodolica, V. and Spraggon, M., 2014. Managing organizations in the United Arab Emirates: Dynamic characteristics and key economic developments. Springer.
Bongiorno, G., Rizzo, D. and Vaia, G., 2018. CIOs and the digital transformation: a new leadership role. In CIOs and the Digital Transformation (pp. 1-9). Springer, Cham.
Broadbent, M. and Lelliott, M., 2016. Leadership transformation underpins digital transformation. Government News, 36(2), p.10.
Burns (1978
(Chen et al. 2012; Loebbecke and Picot 2015).
Choi, T. and Chandler, S.M., 2015. Exploration, exploitation, and public sector innovation: an organizational learning perspective for the public sector. Human Service Organizations: Management, Leadership & Governance, 39(2), pp.139-151.
Cse.unl.edu. (2019). [online] Available at: http://cse.unl.edu/~grother/nsefs/03/research.pdf [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Dahlström, P., Desmet, D. and Singer, M., 2017. The seven decisions that matter in a digital transformation: a CEO’s guide to reinvention. Digital McKinsey article (Feb 2017).
Daniel Painter,2019. https://www.itproportal.com/features/six-change-management-essentials-for-digital-transformation-success/
Dr. Chakib Bouhdary https://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-economy/2018/05/01/comparing-two-approaches-to-digital-transformation-06144132
Dr. Linda Ackerman https://blog.beingfirst.com/5-reasons-why-organizational-change-fails
de Reuver, M., Sørensen, C. and Basole, R.C., 2018. The digital platform: a research agenda. Journal of Information Technology, 33(2), pp.124-135.
Demirkan, H., Spohrer, J.C. and Welser, J.J., 2016. Digital innovation and strategic transformation. IT Professional, 18(6), pp.14-18.
Doherty, E., Holmes, J. and Chatterjee, D., 2018. Leadership: Insights in the digital context.
Dutot, V. and Van Horne, C., 2015. Digital entrepreneurship intention in a developed vs. emerging country: An exploratory study in France and the UAE. Transnational Corporations Review, 7(1), pp.79-96.
Dwight D. Eisenhower https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/3269-how-to-be-a-leader.html
(Ecoggins, 2016) https://toughnickel.com/business/The-History-of-Leadership-Studies-and-Evolution-of-Leadership-Theories
El Sawy, O.A., Kræmmergaard, P., Amsinck, H. and Vinther, A.L., 2016. How LEGO Built the Foundations and Enterprise Capabilities for Digital Leadership. MIS Quarterly Executive, 15(2).
Elmasry, T., Benni, E., Patel, J. and Moore, J.P., 2016. Digital Middle East: Transforming the region into a leading digital economy. McKinsey.
Enginess https://enginess.io/insights/what-is-digital-transformation
(Expert Program Management ,2010-11) https://expertprogrammanagement.com/2010/11/kotter-change-how-to-lead-change/
Flick, U., 2015. Introducing research methodology: A beginner’s guide to doing a research project. Sage.
Forbes magazine (25 july 2017 edition)
(Graetz and Michaelis, 2015; Bonin, Gregory, and Zierhahn, 2015, p. 21; Arntz, Gregory, and Zierahn, 2016, p. 25).
Henriette, E., Feki, M. and Boughzala, I., 2016, September. Digital Transformation Challenges. In MCIS (p. 33).
Hess, T., Matt, C., Benlian, A. and Wiesböck, F., 2016. Options for formulating a digital transformation strategy. MIS Quarterly Executive, 15(2).
Hessa Buhumaid, Margaux Constantin, andJörg Schuber https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-sector/our-insights/how-the-uae-government-modernized-citizen-services
Hicks, 2017
Hoberg, P., Krcmar, H. and Welz, B., 2017. Skills for digital transformation. IDT survey.
Hofmann, Sara & Ogonek, Nadine. (2018).
(Holger Arians) https://peopledevelopmentmagazine.com/2017/09/10/technology-leadership/
Irwin Feller Vol. 26, No. 10 (oct,1980) pp. 1021-1030) https://www.jstor.org/stable/2631312?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
John C. Maxwell https://www.inc.com/peter-economy/44-inspiring-john-c-maxwell-quotes-that-will-take-you-to-leadership-success.html
Kamali, A., Jayashree, P. and Lindsay, V., 2015. Leadership Development Programs: Investigating the impact of contextual and cultural factors on LDP effectiveness in United Arab Emirates. International journal of management and applied research, 2(4), pp.172-186.
Kane, G.C., Palmer, D., Phillips, A.N., Kiron, D. and Buckley, N., 2015. Strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation. MIT Sloan Management Review and Deloitte University Press, 14, pp.1-25.
Kane, G.C., Palmer, D., Phillips, A.N., Kiron, D. and Buckley, N., 2015. Strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation. MIT Sloan Management Review and Deloitte University Press, 14, pp.1-25.
Karmakar, A., 2015. E-governance and its role in infrastructure services of UAE, case study—Dubai. In E-Governance for Smart Cities (pp. 81-97). Springer, Singapore.
Kendra Cherry, 2019) https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-autocratic-leadership-2795314
Khan, H.U., Artail, H.A., Malik, Z. and Niazi, M., 2014, August. Information technology adoption, possible challenges, and framework of supply chain management: a case study of a leading gulf economy. In 2014 4th International Conference on Engineering Technology and Technopreneuship (ICE2T) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
Khan, S., 2016. Leadership in the digital age: A study on the effects of digitalisation on top management leadership.
Khan, S., 2016. Leadership in the digital age: A study on the effects of digitalisation on top management leadership.
Kotter,1995 .Leading change https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_82.htm.
Kreutzer, R.T., Neugebauer, T. and Pattloch, A., 2017. Digital business leadership. In Digitale Transformation-Geschäftsmodell-Innovation-Agile Organisation-Change Management, 1. Auflage. Springer Gabler.
Kumar, R., 2019. Research methodology: A step-by-step guide for beginners. Sage Publications Limited.
Lévy, P. and Bononno, R., 1998. Becoming virtual: Reality in the digital age. Da Capo Press, Incorporated.
Libguides.usc.edu. (2019). Research Guides: Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Types of Research Designs. [online] Available at: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/researchdesigns [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Lindsay, 2017)
Ltd, W. (2019). Mixed methods research. [online] Resourcecentre.foodrisc.org. Available at: http://resourcecentre.foodrisc.org/mixed-methods-research_185.html [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Mackey, A. and Gass, S.M., 2015. Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Madichie, N.O. and Al Athmay, A.A., 2013. An initial assessment of e-governance and public sector marketing in the UAE. International Journal of Business and Emerging Markets, 5(3), pp.234-253.
Mahler, S.J., 2017. Theoretical and Empirical Contributions Toward a Research Agenda for Transnationalism 1. In Transnationalism from below (pp. 64-100). Routledge.
Matt, C., Hess, T. and Benlian, A., 2015. Digital transformation strategies. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 57(5), pp.339-343.
Matt, C., Hess, T. and Benlian, A., 2015. Digital transformation strategies. Business & Information Systems Engineering, 57(5), pp.339-343.
McClelland 1972, 34
Mok, 2017
Neuman, W.L. and Robson, K., 2014. Basics of social research. Toronto: Pearson Canada.
(Ng 2018)
Nuseir, M.T., 2018. DIGITAL MEDIA IMPACT ON SMEs PERFORMANCE IN THE UAE. Academy of Entrepreneurship Journal, 24(2).
ONS https://www.bbc.com/news/business-47691078
Oswald, G. and Kleinemeier, M., 2017. Shaping the Digital Enterprise. Springer International Publishing, Cham.
Palm, K. and Lilja, J., 2017. Key enabling factors for organizational ambidexterity in the public sector. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences, 9(1), pp.2-20.
Pavlik, J.V., 2015. Transformation: examining the implications of emerging technology for journalism, media and society. Athens J Mass Media Commun, 1(1), pp.9-24.
Pera, 2015a, b; 2014. https://www.questia.com/library/journal/1P3-4065432191/the-critical-role-of-social-media-in-crisis-communication
(Prachi Juneja) https://www.managementstudyguide.com/strategic-leadership.htm
Prosci’s benchmarking research https://www.prosci.com/resources/articles/manager-change-management-role
Qasim, A., 2018. Audit committee effectiveness: reflections from the UAE. International Journal of Economics and Business Research, 15(1), pp.87-107.
Rauch & Behling https://managementhelp.org/leadership/index.htm
(Reed and Dongarra 2015).
Research-Methodology. (2019). Research Approach – Research-Methodology. [online] Available at: https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/research-approach/ [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Research-Methodology. (2019). Research Philosophy – Research Methodology. [online] Available at: https://research-methodology.net/research-philosophy/ [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Roussel , 2006
Salem, F., 2016. A Smart City for Public Value: Digital Transformation Through Agile Governance-The Case of’Smart Dubai’.
(Sarah K. White, 2018)
(SaudiGazette) http://saudigazette.com.sa/article/513858
Schiliro, D., 2013. Diversification and development of the UAE’s economy.
Schmidt, E. and Cohen, J., 2014. The new digital age: Transforming nations, businesses, and our lives. Vintage.
Schwarzmüller, T., Brosi, P., Duman, D. and Welpe, I.M., 2018. How does the digital transformation affect organizations? Key themes of change in work design and leadership. mrev management revue, 29(2), pp.114-138.
Silverman, D. ed., 2016. Qualitative research. Sage.
Sisk, Annie, 2019 https://bizfluent.com/about-6744256-importance-information-technology-business-sector.html. 17 July 2019
Steve Ranger,2018 https://www.zdnet.com/article/what-is-the-internet-of-things-everything-you-need-to-know-about-the-iot-right-now/
Tau.ac.il. (2019). [online] Available at: https://www.tau.ac.il/medicine/cme/pituach/240210/8.pdf [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Taylor, S.J., Bogdan, R. and DeVault, M., 2015. Introduction to qualitative research methods: A guidebook and resource. John Wiley & Sons.
Teachingcommons.cdl.edu. (2019). Developing a research agenda. [online] Available at: http://teachingcommons.cdl.edu/cdip/facultyresearch/Developingaresearchagenda.html [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
The Royal Literary Fund. (2019). What is a literature review?. [online] Available at: https://www.rlf.org.uk/resources/what-is-a-literature-review/ [Accessed 29 Mar. 2019].
Uhl, A. and Gollenia, L.A., 2016. Digital enterprise transformation: A business-driven approach to leveraging innovative IT. Routledge.
Viaene, S., 2017. What digital leadership does.
Web.wlu.ca. (2019). [online] Available at: https://web.wlu.ca/learning_resources/pdfs/Research_Strategies.pdf [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Revolution
World Economic Forum. (2019). How digital technology is transforming Dubai. [online] Available at: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/05/how-digital-technology-is-transforming-dubai/ [Accessed 1 Apr. 2019].
Anderson, V. 2004. Research Methods in Human Resource Management. Reprint. CIPD Publishing
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall
Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership: Good, better, best. Organizational Dynamics, 13(3), 26-40.
Bass, B. M. (2000). The future of leadership in learning organizations. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 7(3), 18-40.
Bass, B. M. (2008). The Bass handbook of leadership: Theory, research, & managerial applications (4th ed.). New York, NY: Free Press.
Bass, B. M., & Riggio, R. E. (2006). Transformational leadership (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Psychology Press
Bass, B.M. (1985) Leadership and Performance Beyond Expectations. New York: Free Press.
Burns, J. M. (1978). Leadership. New York, NY: HarperCollins
Burrell, G. and Morgan, G. (1979) Sociological Paradigms and Organisational Analysis. London: Heinemann.
Cameron, R, (2010). ‘Mixed Methods in VET Research: Usage and quality’. International Journal of Training Research, Vol. 8, No. 1, April, pp. 25-39.
Crotty, M. (2008) The Foundations of Social Research. London: Sage
Delmas M, Toffel M (2008) Orgarnzational– responses to environmental demands: opening the black box. Strategic Management Journal. 29, 10, 1027-1055.
Diaz-Saenz, H. R. (2011). Transformational leadership. In A. Bryman, D. Collinson, K. Grint, B. Jackson & M. Uhl-Bien (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of leadership (pp. 299-310). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Eid, J., Johnsen, B. H., Bartone, P. T., &Nissestad, O. A. (2008). Growing transformational leaders: Exploring the role of personality hardiness. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 29(1), 4-23
George, A. L. and Bennet, A. (2005). Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Gill, J. and Johnson, P. (2010). Research Methods for Managers (4th edn). London: Sage.
Gomm, R., Hammersley, M. and Foster, P., (eds.) (2000). Case study method. London: Sage.
Hambley, L. A., O’Neill, T. A., & Kline, T. J. B. (2007). Virtual team leadership: The effects of leadership style and communication medium on team interaction styles and outcomes. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 103(1), 1-20
Hautala, T.M. (2006). The relationship between personality and transformational leadership. Journal of Management Development, 25(8), 777-794
Johnson, P. and Clark, M. (2006) ‘Editors’ introduction: Mapping the terrain: An overview of business and management research methodologies’, in P. Johnson and M. Clark (eds) Business and Management Research Methodologies. London: Sage, pp. xxv–lv.
Jung, D., Wu, A., & Chow, C. W. (2008). Towards understanding the direct and indirect effects of CEOs’ transformational leadership on firm innovation. The Leadership Quarterly, 19(5), 582-594
Kelemen, M. and Rumens, N. (2008). An Introduction to Critical Management Research. London: Sage
Kirkman, B. L., Chen, G., Farh, J.-L., Chen, Z., & Lowe, K. B. (2009). Individual power distance orientation and follower reactions to transformational leaders: A cross-level, cross-cultural examination. Academy of Management Journal, 52(4), 744-764
Leech N, and Onwuegbuzie, A, (2008). A typology of mixed methods research designs, Quality and Quantity, 43(2), March, pp. 265-275.
Liu, J., Liu, X., & Zeng, X. (2011). Does transactional leadership count for team innovativeness? Journal of Organizational Change Management, 24(3), 282-298.
(Muhammad Yousaf )https://scholarshipfellow.com/explanatory-research-definition-types-comparison-advantages-disadvantages/
Northouse, P.G. (2004) Leadership: Theory and Practice (3rd Edition). London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Northouse, Peter G. (2001). Leadership Theory and Practice, second edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc.
Robbins. (2003). Organizational Behavior: Concepts, Controversies, and Applications. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Engelwood Cliffs.
Sadeghi, A., &Pihie, Z. A. L. (2012). Transformational leadership and its predictive effects on leadership effectiveness. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(7), 186- 197.
Veil (2011)
Wilson, J. 2010. Essentials of Business Research: A Guide to Doing Research Project. Annotated Edition. SAGE Publishers
Yin, R. K. (1998). The abridged version of case study research: Design and method. In: Bickman, L. and Rog, D. J. (eds.) Handbook of applied social research methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Doing case study research. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Al-Fuqaha, A., Guizani, M., Mohammadi, M., Aledhari, M., Ayyash, M., 2015. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials.
Berman, S., Marshall, A., 2014. The next digital transformation: From an individual-centered to an everyone-to-everyone economy. Strateg. Leadersh.
Berman, S.J., 2012. Digital transformation: Opportunities to create new business models. Strateg. Leadersh.
Christidis, K., Devetsikiotis, M., 2016. Blockchains and Smart Contracts for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access.
Dery, K., Sebastian, I.M., van der Meulen, N., 2017. The digital workplace is key to digital innovation. MIS Q. Exec.
Henriette, E., Feki, M., Boughzala, I., 2015. The Shape of Digital Transformation: A Systematic Literature Review. Mediterr. Conf. Inf. Syst. Proc.
Khan, S., 2016. Leadership in the digital age – A study on the effects of digitalisation on top management leadership. Stock. Univ.
Kreutzer, R.T., Neugebauer, T., Pattloch, A., 2017. Digital Business Leadership.
Leadership, V., 2009. Iste standards for administrators. Int. Soc. Technol. Educ.
Meffert, J., Swaminathan, A., 2018. LEADERSHIP AND THE URGENCY FOR DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION. Lead. to Lead.
Nadeem, A., Abedin, B., Cerpa, N., Chew, E., 2018. Editorial: Digital transformation & digital business strategy in electronic commerce – The role of organizational capabilities. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res.
Oswald, G., Kleinemeier, M., 2016. Shaping the digital enterprise: Trends and use cases in digital innovation and transformation, Shaping the Digital Enterprise: Trends and Use Cases in Digital Innovation and Transformation.
Paracha, M.U., Qamar, A., Mirza, A., Waqas, I.-U.-H., 2012. “Impact of Leadership Style (Transformational & Transactional Leadership) On Employee Performance & Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction” Study of Private School (Educator) In Pakistan. Glob. J. Manag. Bus. Res.
Piccinini, E., Hanelt, A., Gregory, R.W., Kolbe, L.M., 2015. Transforming industrial business: The impact of digital transformation on automotive organizations. In: 2015 International Conference on Information Systems: Exploring the Information Frontier, ICIS 2015.
Rosenbloom, R.S., 2000. Leadership, capabilities, and technological change: The transformation of NCR in the electronic era. Strateg. Manag. J.
Schwarzmüller, T., Brosi, P., Duman, D., Welpe, I.M., 2018. How does the digital transformation affect organizations? Key themes of change in work design and leadership. Manag. Rev.
Shaping the Digital Enterprise, 2017. , Shaping the Digital Enterprise.
Shaughnessy, H., 2018. Creating digital transformation: Strategies and steps. Strateg. Leadersh.
Sow, M., Aborbie, S., 2018. Impact of Leadership on Digital Transformation. Bus. Econ. Res.
Tolboom, I., 2016. The impact of digital transformation. Delft Univ. Technol.
Westerman, G., Tannou, M., Bonnet, D., Ferraris, P., McAfee, A., 2012. The Digital Advantage: How Digital Leaders Outperform their Peers in Every Industry. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev.
World Economic Forum, 2016. Digital Transformation of Industries : Digital Enterprise. World Econ. Forum.
Zahra Malik, S., Saleem, M., Naeem, R., 2016. Effect of Leadership Styles on Organizational Citizenship Behaviour in Employees of Telecom Sector in Pakistan. Pak. Econ. Soc. Rev.
Zimmermann, A., Schmidt, R., Sandkuhl, K., Wißotzki, M., Jugel, D., Möhring, M., 2015. Digital enterprise architecture-transformation for the internet of things. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 19th International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference Workshops and Demonstrations, EDOCW 2015.