Introduction
Stakeholder engagement is an integral part of the organisation`s operations. Stakeholders are those members of the business that support the organisation in its operations in some or the other way. Stakeholders affect the business either directly or indirectly. The report analysis the impact of stakeholder`s interest and their level of power that has been exerting on the organisation while making the decisions. This report elaborated the role of internal and external stakeholders in 7-eleven, which is a chain of convenience stores that operates at international level. Stakeholder interests often become conflicting in some situation where one party has to compromise to benefit the other. A last, a stakeholder matrix has been constructed to evaluate the level of power, influence, threat of competence, and cooperative potential on the company (Henisz, 2017).
Background of 7-eleven
7-eleven is a Japan-owned American chain that operates internationally with convenience stores. 7-Eleven is a retailer who operates in more than 60000 convenience stores existing in Asia and North America. This outlet operates at small scale with limited stock, turnover products, and drinks. It is a subsidiary of Tokyo based 7-Eleven, which is headquartered in Dallas. Currently, the organisation operates franchisees and licensees in 12 countries with 67480 stores. The company earns a gross profit of 59% from the franchise.
Identification of functional areas
Merchandising
Marketing
Sakes and supply chain management
Supervision of convenient stores
Loss prevention (physical safety) and cash handling
Operations
Standard documentation and training
Human resources management
Identify internal and external stakeholders and their roles
After the establishment of the company, it always attempted to remain sincere company towards its stakeholders, which includes catering of local communities, employees, shareholders, customers and other business partners. The company strives to understand the expectations of the stakeholders so that it can respond (Henisz, 2017).
Internal stakeholders
Employees- the company aims to provide a considerable workplace where the employees can participate and get the satisfaction of their work. The company creates an environment with fair and considering the human rights. It undertakes the protection of employees by considering privacy and safety (Howse, Hankey, Farinelli, Bauman, & Freeman, 2018).
Directors and owners- the organisation`s operations are underpinned by the investors when they fund the organisation. In order to respond to the trust of the shareholders, the company emphasizes management system that is highly transparent so that it can communicate and fulfil the duty towards its accountability with the help of disclosures. The company attempts to conduct the general meetings of the shareholders and inform them with the help of organisational newsletter. The owners choose to opt for innovation strategy in order to embed high level of competent with lost costing so that it can create its market share (Hutt, & Ferrell, 2016).
External stakeholders
Customers- customers play an important role in the organisation. The main vision of the organisation is to fulfil the wants of the customers by maintaining the retention and loyalty. 7-eleven focuses on providing the excellent services to the customers. The company aims to provide quality products with variety of the offerings. The company offered variety of promotional events. Apart from this, PSC undertook CLIQQ messenger. Customers can further register their phone numbers under the organisation for getting discounts (Hutt, & Ferrell, 2016).
Business partners- The company`s operation cannot be conducted without the cooperation of the business partners. The company undertakes the laws and regulations and check whether its internal rules are relating to the fair trade with establishing the relations of trust with its business partners in order to ensure maintaining the safety, accounting, and security for the rights of the business partners (Hutt, & Ferrell, 2016).
Community- the company aims to play an indispensable role in the communities. The company to provide products and services that could match the lifestyle of the local community. It encourages local production, and consumption among the co-existing so that it can provide and promote the activities so that they can contribute to the development of the community.
Identify the nature and degree of main stakeholders’ interests, and implications of conflicting interests
Suppliers- the degree of the interest is low in terms of interrupting in the making of the business strategy. Their nature of interest only lie the increase in the production of the organisation that will increase the sales of the supplier. On the other hand, the supplier has huge interest in looking at the financial position of the company especially the liquidity conditions.
Customers- The level of interest of the customers is low as they do not engage in any of the operational or strategically action of the organisations. The main interest of the customer lies greater quality at low prices, fulfilment of the needs, and convenient needs. Customers like to see improvement in their offerings in regards to product portfolio and quality so that they can get the better value for the money paid.
Business partners- the level of interest in the organisation is very high as the nature of interest is in the form of increase in the business activities and product line. Increase in business partners will happen only if the company starts diversifying in different countries to great extent.
Community- the degree of community is high due to its impact on employment and its social contribution.
Senior management and investors- senior management have their interest in providing great products and services to the customers. They have huge level of interest while constructing the strategy, formulating and executing the plans in order to achieve the objectives and greater profitability (Gross, 2018).
Governmental agencies- the interest of the government agencies is too high as it is interested how the organisations works in order to ensure that it is not working unethically. It ensures that the organisation works according to rules and regulations regarding the legislations compliance made by the organisation (Gross, 2018).
Employees- The workforce have considerable interest from the organisation. As they are always concerned with the level of salary increment, growth, development, job appraisal, and training sessions. It includes the lower level and middle level employees so that they can be guided through business level strategy according to the senior manager (Nelson, Smith, Ly, Gustavsson, Sudlow, & Bexelius, 2018).
Conflicting interests
Stakeholder’s interest differs from their role and impact in the decision making of the company. Due to difference in the interest, disputes occur. Conflicts in the stakeholders is common in internal stakeholders such as top-level management, owners, shareholders, and employees analyses such decisions so that they can support and create organisational decisions (Zhuang, & Jiang, 2016). For example- when the organisation decides to cut down the jobs due to its suffering from country`s recession and this decision will be supported by the business owners and shareholders but at the same time, employees and community will be suffered (Zhuang, & Jiang, 2016). Another illustration can be that it lead to addition in order to create the extra shift so that they can increase its productivity and top-level management, supplier, customer and investors will support this decision because the organisation will need more raw material increasing the profits of suppliers. The employees and the local community will oppose this decision especially if it is without any incentive. This means exploitation of the employees (Zhuang, & Jiang, 2016).
Introduction of new machinery with an aim to replace the current employees in order to reduce the cost of the company. The customers will support this decision because they will be benefited through the low costing production of the company (Xue et al., 2017). Shareholders will enjoy greater profits on the other hand; employees will suffer from huge unemployment. Increasing the sales in order to generate greater profits by lowering the quality of the products, which will benefit the shareholders whereas, it will not be supported by the customers (Xue, Cheng, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Qu, & Wang, 2017).
Interest conflicts will occur when the aims and objective of the stakeholder differs and does not match with the beneficial thinking of the stakeholder. For instance- project manager may hard schedules in peak seasons, which may be liked by the employees. It is important to comply with the interest of maximum stakeholders but it is not possible to great extent because paying attention to the concerns of the shareholders and the customers is most important to benefit the organisation as well (Wang, Lin, & Tsai, 2018).
In current era where the employees are also empowered, if the interest of the customers are considered by the organisation by exploiting the employees and neglecting the employees interest. It will lead to increased turnover with greater employee dissatisfaction (Wang, Lin, & Tsai, 2018). The impact of conflicting interest of the top-level management and shareholders will lead to decreasing profit margins. The clear reason is that senior management is concerned with the customer satisfaction who fulfil the interest of the wants of the customers whereas; shareholders are interested in making profits (Voinov et al., 2016).
Identify the level of main stakeholders’ influence
Some of the crucial stakeholders of the 7-eleven exerts huge pressure on the company especially some business activities. This enforcement will lead to conducting the business as per their will. This pressure will be clearly identified in the stakeholder` matrix (Tseng, Barnoya, Kruger, Lachat, Vandevijvere, & Villamor, 2018).
The stakeholders are identified according to the competitiveness as a threat and their potential according to the potential to cooperate. For instance- customers, regulators, government agencies, local communities, senior level management, senior executives, and the shareholders exert high pressure due to huge power and greater interest in the operations that affect the organisational performance and its profitability. On the other hand, supplier, receptionist, developer, trainers, testers, auditors, and employees exerts lower pressure as they does not create competitive threat (Thanh, & Phuong, 2018).
Create a stakeholder matrix
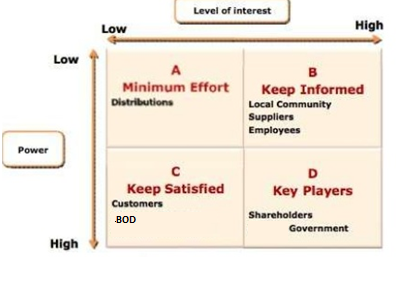
Stakeholder are different in nature in the company and it is followed while considering the cooperative potential and competitive threat in 7-eleven. It affects the business organisation in different manners. This depends on the level of interest and power with every stakeholder in the organisation (Šimek et al., 2018). The main stakeholders for the 7-Eleven who have different interest and degree of influence according to the power they have-
Suppliers, employees, and local community- these stakeholders have high degree of interest but they are not much empowered that can reflect that influence is low in the organisation`s decision. The company informs them in regarding to diversification, increasing the product portfolio, it has offered, business strategy, and decision made. As elaborated in the conflicting interest section, conflicts arise among the employees and other stakeholders as they have the interest in business organisations but do not have the power to exert which further creates dissatisfaction (Serôdio, McKee, & Stuckler, 2018).
Customers and board of directors- The consumer do not seem as very much interested in strategic business decisions of the company but the customers have huge power to influence the business decision especially the quality of the customers and marketing decisions for which the manager has to do something unique so that it can attain a situation of competitive advantage. Board of directors have greater power to influence the aspects of the business but they do not have any interest in the daily operations. The conflicting situations between shareholders and senior management is because of high power to both the parties (Sadeghirad et al., 2016).
Government agencies and shareholders- the level of interest and degree of power is high for both shareholders and the government agencies of the company. As it reflects huge influence over organisation and its operations. However, it is considered priority list according to stakeholder` interest and they are main players in the organisation (Rodrigues, Nikhil, & Jacob, 2016).
Distributors- these are the associated business partners that helps to provide goods to the customers to other convenient stores. These stakeholders have minimal interest in the business operations where they do not have any power in making the decisions. The impact of the distributors is nearly low in the organisation where the makes minimum efforts for the distributors (Hueske, & Guenther, 2015).
Compare the Industry your business operates in with their industry
When comparing the convenient stores and supermarket industry with the construction industry. The above discussion is concerned with the key stakeholders for the retail departmental company by undertaking the example of 7-Eleven as the illustration. On the other hand, the main stakeholders for the construction of the organisation that further includes project sponsors, contractors, lenders, suppliers of raw materials, technological advancement, architects, chemical dealers, and sub-contractors (Ramus, & Vaccaro, 2017). On the other hand, external main stakeholders in the construction industry includes labour unions, licensing organisations, debentures, long-term lenders, and interest groups. After differentiating the stakeholders for both the industries, it is seen that there are different internal and external stakeholders that affect the operations of the organisation in different industry. For instance- organisations who have the potential of earning very high and are existing in the market since a very long time. The organisation has to comply with the CSR activities that affect the preferences of the stakeholders such as shareholders and customers. Body shop is an organisation who greatly serves a particular percentage of its profits for the social cause and higher quality. This is the reason of customer’s loyalty (Kearns, Apollonio, & Glantz, 2017).
Conclusion
Stakeholders
of the organisation can be either affected or affect the company by its actions,
objectives, and policies of the organisation. From the above discussion, it can
be seen that a comparative analysis has been conducted on how the 7-eleven
stakeholders affect its operations and how it differs from the construction
industry. After analysing the stakeholder`s competitive power and its
cooperative potential, it has been analysed through the stakeholder`s matrix. customers
and investors are threat to the company`s strategy. Stakeholders with
empowerment can impose higher power in affecting the staff such as in the retail
sector. After considering people with huge potential and high competitiveness. The
main three suggestions to deal with the stakeholders is to comply with the
rules and regulations, change the laws according to the laws, and implementing
the policies according to the services. One of the key business partnership is
with the WWF (world wildlife fund) so that it can improve the hygiene of water
as communities suffer from clean water and other sanitation issues. Government
agencies and SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), these stakeholders will
impose penalties on the organisation as they do not have potential in
profitability but affect the organisation to great extent.
References
Gross, D. (2018). 1609e Stakeholder perspectives of return-to-work success. bmj journals, 75(2).
Henisz, W. J. (2017). Corporate diplomacy: Building reputations and relationships with external stakeholders. Routledge.
Howse, E., Hankey, C., Allman-Farinelli, M., Bauman, A., & Freeman, B. (2018). ‘Buying Salad Is a Lot More Expensive than Going to McDonalds’: Young Adults’ Views about What Influences Their Food Choices. Nutrients, 10(8), 996.
Hueske, A. K., & Guenther, E. (2015). What hampers innovation? External stakeholders, the organization, groups and individuals: a systematic review of empirical barrier research. Management Review Quarterly, 65(2), 113-148.
Hutt, G., & Ferrell, O. (2016). A stakeholder marketing approach to sustainable business. In Marketing in and for a Sustainable Society, 13(1), 61-101.
Kearns, C. E., Apollonio, D., & Glantz, S. A. (2017). Sugar industry sponsorship of germ-free rodent studies linking sucrose to hyperlipidemia and cancer: An historical analysis of internal documents. PLoS biology, 15(11), e2003460.
Nelson, M., Smith, M., Ly, A., Gustavsson, A., Sudlow, C., & Bexelius, C. (2018). D2. 3 Stakeholder generated lists of priority RWE relevant outcomes and D2. 4 Disease progression and outcomes classification matrix.
Ramus, T., & Vaccaro, A. (2017). Stakeholders matter: How social enterprises address mission drift. Journal of Business Ethics, 143(2), 307-322.
Rodrigues, J., Nikhil, S., & Jacob, S. (2016). Promotional Strategies of McDonalds and Market Effects. Journal of Management Research and Analysis, 3(1), 53-55.
Sadeghirad, B., Duhaney, T., Motaghipisheh, S., Campbell, N. R. C., & Johnston, B. C. (2016). Influence of unhealthy food and beverage marketing on children’s dietary intake and preference: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Obesity Reviews, 17(10), 945-959.
Serôdio, P. M., McKee, M., & Stuckler, D. (2018). Coca-Cola–a model of transparency in research partnerships? A network analysis of Coca-Cola’s research funding (2008–2016). Public health nutrition, 21(9), 1594-1607.
Šimek, K., Grujčić, V., Hahn, M. W., Horňák, K., Jezberová, J., Kasalický, V., … & Shabarova, T. (2018). Bacterial prey food characteristics modulate community growth response of freshwater bacterivorous flagellates. Limnology and Oceanography, 63(1), 484-502.
Thanh, N. T. H., & Phuong, N. N. D. (2018, October). Exploring Customer Satisfaction in Fast Food Industry: A Descriptive Analysis. In Global Conference on Business, Hospitality, and Tourism Research (GLOSEARCH 2018).
Tseng, M., Barnoya, J., Kruger, S., Lachat, C., Vandevijvere, S., & Villamor, E. (2018). Disclosures of Coca-Cola funding: transparent or opaque?. Public health nutrition, 21(9), 1591-1593.
Voinov, A., Kolagani, N., McCall, M. K., Glynn, P. D., Kragt, M. E., Ostermann, F. O., … & Ramu, P. (2016). Modelling with stakeholders–next generation. Environmental Modelling & Software, 77, 196-220.
Wang, C. H., Lin, I. H., & Tsai, J. Y. (2018). Combining fuzzy integral and GRA method for evaluating the service quality of fast-food restaurants. Journal of Interdisciplinary Mathematics, 21(2), 447-456.
Xue, H., Cheng, X., Zhang, Q., Wang, H., Zhang, B., Qu, W., & Wang, Y. (2017). Temporal growth and spatial distribution of the fast food industry and its relationship with economic development in China—2005–2012. Preventive medicine, 102, 79-85.
Zhuang, K., & Jiang, Y. (2016). An analysis of the development of the Chinese fast food industry. Journal of Asian Business Strategy, 6(5), 85.