Overview Department of Human service
The business capability model involves a comprehensive integrated set of service delivery by the government through the provision of social welfare. The focus is to support different groups of people under specific conditions that might require government interventions. In Australia, the Department of Human Services (DHS) is mandated to make sure people can get the required help efficiently. The government of Australia has developed mechanisms to the integrated framework to support its critical business operations by creating a bridge between Information Technology (IT) and the required basis to transform service delivery. To facilitate effective service delivery, various agencies have been integrated under the department of human service. It consists of agencies that are responsible for the delivery of social human welfare such as Medicare, Child support, and Centrelink. The department of human service requires a capability model to provide an overview of the service delivery and the core business operations. The goal of the model is to provide an abstraction of departmental functional processes and the flow of service delivery to vulnerable citizens. The department of human service capability model should bring together all functionalities that are outlined in the department charter in service delivery to present its functions and what can do. Notably, the Department of Human Services (DHS) should have a value stream of achieving the set objectives. Value streams are meant to outline both series and operational variations that DHS uses to manage its operations. In this case, one value stream would be used to analyze two capability models that explain the functionality and operations of DHS.
DHS business capability models
The government of Australia through DHS’s mandate is to integrate service delivery for ease of access by its citizens. The goal is to improve service delivery efficiency despite an upsurge in the number of customers requesting for the service and processing steps involved. The capability model for service delivery management focuses on essential services that are required by customers. The business service delivery operations serve to provide customers with required service access to facilitate user registration, payment services, choose the services they are eligible, and management of services after deployment. Payment reforms are services that involve several activities including; design of the services, planning, and implementation of DHS required services. The services required by DHS should originate from this section for use in daily business operations. Services should be guided by Australia needs to serve its vulnerable citizens more effectively. Once users’ data has been collected, it should be stored and used selectively by the authorized parties. It should be secured from the use by fraudulent users, conform to Australian rules and regulations n cybersecurity. Service delivery remains effective only if used by customers and with substantive benefits. To offer quality service, corporate and financial management is required. These services should range from human resource management that supports the IT system and customers of the organization. Organizational finances should also be managed for quality service delivery. In this case, DHS finances should be managed to make sure vulnerable and deserving Australian citizens do not suffer without government intervention.
The model also focuses on product management through the procurement and management of services that are meant to support and change the lives of the target groups. Human resource management is quite an essential service in the DHS capability model. It offers service consumers’ ability to get quality services from designated DHS staff with required qualifications. For quality service provision to Australia citizens, DHS should be able to have comprehensive human resource management. The process should be outlined from corporate to staff qualification and screening of prospective candidates as outlined in the capability model. The recruitment service can either be the outsourcing of services, acquisition of other agencies, or staff hiring. The last aspect that DHS should consider is the management of vendors, which include service delivery partners and service providers support teams.

Figure 1: Capability map level 1
Similarly, customer management remains a core operation in any service delivery. DHS being not an exception requires specialized and effective customer management procedures. Customer management involves several processes and operations that require customer interaction with the various application to access the subjected service. Online transactions support users of the welfare services from various integrated portals websites. For any user to access DHS services, records should be maintained across all the respective platforms. The next aspect is staff assisted interactions, at instances that complains and claims cannot be completed from within available platforms online. In such cases, customers require DHS staff interaction to help complete their requests over the phone call or visit the service center. To get staff support, customers are should provide detailed updates about their conditions concerning available services and payments. Claim processing is the third customer management process, which is done over the management system by observing rules and staff help. For any claim to be processed, validations and checks should be done to determine the eligibility of the requested service. Notably, access to service by the customer is subjected to the time of claim and collection of the approved claim. In cases where the customer status change from the time of application, it should be reported and updated immediately to the DHS to avoid losing the clam.

Figure 2: Capability map to level 2
Value streams are developed by integrating high-level business processes that capture series business operational variation for DHS. It focuses on the end-to-end value of the subjected service delivery to citizens by the Australian government. With the help of the value chain, it is possible to determine information flow from capturing customer data to the processing of payments. There is increased efficiency in service delivery as outlined in the DHS value stream. DHS value stream emphasis data collection from eligible customers and the management of the data to facilitate quality and effective service delivery to vulnerable citizens. The focus is only on the processes that make DHS service delivery outline clear and integrated substantively with capability models.
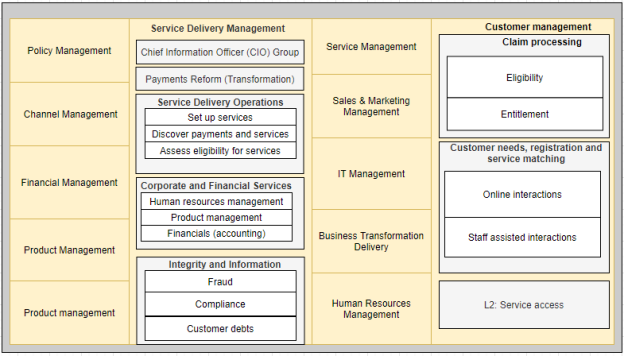
Figure 3: Capability map to level 2

Figure 4: service delivery value chain

Figure 5: Customer management value chain

Figure 6: Integrated capability model and value
Assumptions
In the development of the DHS capability model, some concerns were assumed to make it possible to deliver a compressive service delivery to citizens. Some of the assumptions include;
All services and processes within the department of human service (DHS) are automated and management over the e-system.
DHS agencies and stakeholders have the required access to the system without any operational challenge.
Service delivery operations related to DHS are managed by IT personnel recruited and managed by the department itself.
DHS can offer the required technical support to the users of the system for effective service delivery.
TASK II
ArchiMate model involves a representation of business processes graphically with aim of supporting a complete organizational architecture. The ArchiMate model is done using DHS structure like actors, roles, and hierarchy. The model also focuses on both external and internal collaborations with subjected Australian government agencies under the DHS department and other stakeholders. The other consideration would be on the key DHS functionalities and its associated information flow.
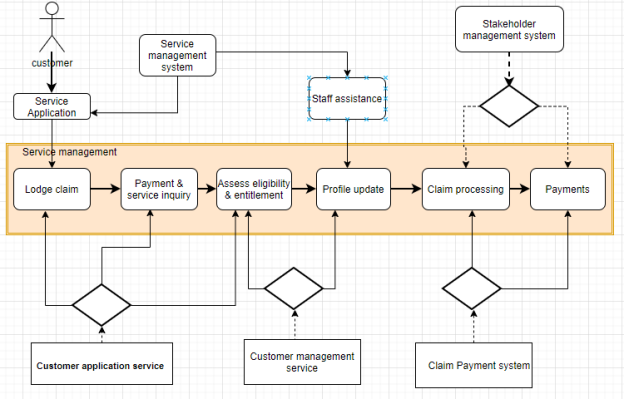
Figure 7: ArchiMate model
The discussion of the DHS service delivery to vulnerable Australian citizens is based on actors within and outside the department. The actors are people who actively facilitate the daily operations to change the living conditions of the target group. The model consists of high-level departmental agencies and stakeholders. The two groups of actors have employees and experts with the capability to handle all the requests from various customers. The human resource management entity should be responsible to deliver high-quality customer service and coordinate other internal operations within and outside the DHS. The operations within the department are classified as permanent with long term status to facilitate customer acquisition of services. The delivery of services can only be made successful by bringing all entities together through correspondents as either group or individuals. The value stream represents the end-points in the service delivery process that make it possible for DHS to execute its mandate. Business roles are quite essential as they define DHS functionalities and its operational capabilities. Essentially, business actors are meant to take required actions on the business operational roles and procedures. Business actors have correlated assigns that show the existing relationship between entities. In this case, the DHS business assign is the core business values that involve service delivery and customer management. All processes and operations should be assigned to specific DHS staff for effective management and delivery of services. Operational assigns are meant to facilitate planning without having to reference DHS departmental structure, change of procedures, and actors involved. Business roles are quite essential in facilitating business service and any role used in the operational process should be executed over business service. In business operations, there should be a close correlation between actors and roles that are performed with the subjected organization. For example, customer support staff from DHS should be able to support customer requests at all times without any technical challenge.
DHS business services are based on citizen welfare management, which is delivered through services that are supported by the department. The department service delivery can be from within the department or outsource in case it unable to run required operations. Some of the services from the DHS are payment of the claims. Once claims have been lodged by the customer and processing goes through, payment should be supported through various payment gateways. To execute internal roles substantively, it is important to realize the existing assigns and relationships that should be coordinated to make service delivery success. Processes are performed by triggering events that in turn executes a process. When a customer registers through customer management, the goal is to have payments processed. For payment to be processed, eligibility and need assessment should be done. The customer has to validate all the information and DHS should analyze and offer a response on the status of the application. Organizational information processed through the execution of business operations is helping in the grouping of DHS functions through capabilities.
Business operations are executed successfully through the collaboration of various entities and stakeholders. To execute business processes, each entity should play its role and collaborate with others to avoid conflict of interest. Interaction should be supported by various channels from within and outside the DSH. Business functionalities are grouped at the organizational level, which is broken down into roles, and processes that should be executed. DHS functionalities can be grouped in service delivery, management of customers, IT management, and business transformation. Once a grouping is done, roles are formulated from each functionality. The idea is to break down functionalities to basic operations that make service delivery possible. Software application and software application components are used to describe the existing interaction between the DHS system. Various applications have been integrated to make service delivery possible. These applications and related components play an essential role that cannot be exempted from departmental operations. In the delivery of welfare services by the Australian government through DHS, both system and service coupling remains an essential aspect that should be managed effectively. Failure of one application or sub-system can make service delivery through online mode a nightmare.
Assumptions
In the development of the DSH ArchMate model, some assumptions were put in place. Some of the assumptions in the ArchiMate model are;
Communication between integrated applications is dynamic and scalable for future use.
The integrated system does not experience frequent breakdown considering the number of applications lodged.
Australian citizens understand conditions that should be met for the successful application of welfare service support.