Question:-
Investigate 4G based Cellular IOT wireless networks such as NB-IoT, LTE-M, and LTE-CAT. Compare them and discuss the differences between them?
Answer:-
At this moment, fourth Generation technology is the most popular technical term. 4G is the very much faster network which is mainly connecting to the several wireless standards. Narrowband IoT is the one type of LPWAN network which is developed by the third generation partnership project. The bandwidth limits of the narrowband signal are 180 to 220 kilo Hz [4]. It is a very much new network, and it is mainly using for IoT applications. Related to mobile networks, NB-IoT deals with the energy-saving abilities that increase the battery life of IoT applications. Their connectivity is functional, but the difference depends on the latency and speed [2]. LTE also the standard of 4G networks and it is also developed by the 3GPP. LTE is very much faster standards and low latency level networks [6]. LTE play a vital role in the smart recovery of IoT applications that produce on-time information like data trafficking systems.
The downlink speed of LTE is 1 Mbps and bandwidth 20 MHz, but the downlink speed and bandwidth of LTE Cat is the greater than 1 Mbps and 1.4 MHz respectively. NB-IoT downlink speed is only 170kbps and bandwidth is 180 kHz. The main job of fourth-generation LTE is to enhance the capabilities of the third-generation network. The 4G LTE mainly increases the network speed [1]. Two basic standards of IoT is the Narrowband-IoT and LTE-M. LTE mainly upgraded the mobile software and tried to modify the network security. Another gateway of network structure is LTE cat1 and LTE cat 4. This standard helps to coverage in the whole world. Their speed is very much standard which supported the internet protocol security. But the NB-IoT mainly specified the 3GPP structure. NB-IoT is extensively using a broad range of mobile devices [5]. Narrowband is securely maintaining to the limited functional bandwidth, but this technology cannot communicate between the two different information streams.
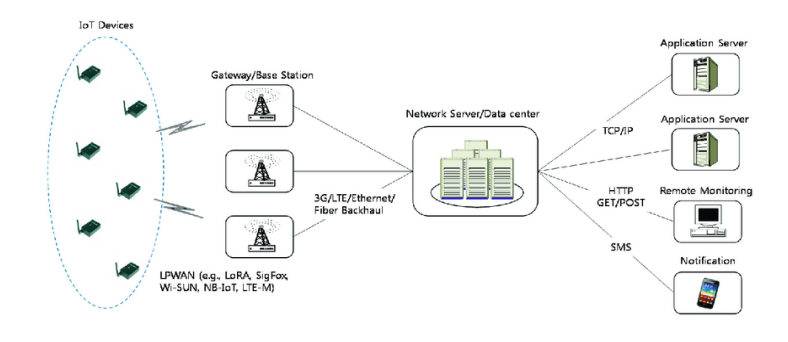
So the fundamental difference between LTE-M, LTE-CAT and NB-IoT are depended on some essential category like latency level, peak data rate, network and system bandwidth, cost, penetration etc. Three types of standards are very much appropriate for the fourth generation wireless network systems [3]. If the operator operates this mobile network very safely, then the battery longevity is very much more extended (more than seven years). All types of network server are works for the remote monitoring, application server and system server. All servers are creating the system gateway.Sigfox, LTE, narrowband IoT both are the medium which is linking between the network stations to an application server.
| Category | Long term evolution for machine (LTE-M) | Narrowband -IoT | Long term evolution for category (LTE-CAT) |
| BANDWIDTH(network) | 1.5 MHz | 170 – 180 kHz | 40 MHz |
| ANTENNAS | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| COST | Low but not less than Narrowband IoT | Low price | Higher than NB-IoT and LTE-M |
| UPLINK | 1Mbit/s | 200kbit/s | 50mbit/s |
| DUPLEX | Half-duplex | Half-duplex | Full duplex |
| VOICE | VOLTE | NO voice | VOLTE |
| PEAK DATA RATE | 380-390 kbps | Less 100 kbps | 25 – 50 Mbps |
| TRANSMITPOWER | 20 dBm | 23dBm | 23dBm |
| BANDWIDTH (system) | 1.4 MHz | 200 kHz | 20 MHz |
| INDOOR PENETRATION | Good | Excellent | Better than LTE-M |
| LATENCY | 60-100 Ms | 1.5-10.5 sec | 10- 15 Ms |
| POWER CONSUMPTION | Medium | Low | Higher Than NB-IoT |
References:-
[1] M. Knight, B. Seeber, “Decoding LoRa: Realizing a modern LPWAN with SDR”, In Proceedings of the GNU Radio Conference (Vol. 1, No. 1), 2016.
[2] M. Lauridsen, I.Z. Kovács, P. Mogensen, M.Sorensen and S. Holst, “Coverage and capacity analysis of LTE-M and NB-IoT in a rural area”, In 2016 IEEE 84th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), 2016, (pp. 1-5) IEEE.
[3] N. Mangalvedhe, R. Ratasuk and A. Ghosh, “NB-IoT deployment study for low power wide area cellular IoT”, In 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC) 2016, (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
[4] V. Petrov, A. Samuylov, V. Begishev, D. Moltchanov, S. Andreev, K. Samouylov and Y. Koucheryavy, “Vehicle-based relay assistance for opportunistic crowdsensing over narrowband IoT (NB-IoT)” IEEE Internet of Things journal, 5(5),2016, pp.3710-3723.
[5] Y. Song, J. Lin, M. Tang and S. Dong, “An Internet of energy things based on wireless LPWAN”, Engineering, 3(4), 2016, pp.460-466.
[6] Y.P.E. Wang, X. Lin, A. Adhikary, A. Grove, Y. Sui, Y. Blankenship, J. Bergman and H.S. Razaghi, “A primer on the 3GPP narrowband Internet of Things”, IEEE communications magazine, 55(3), 2017, pp.117-123.