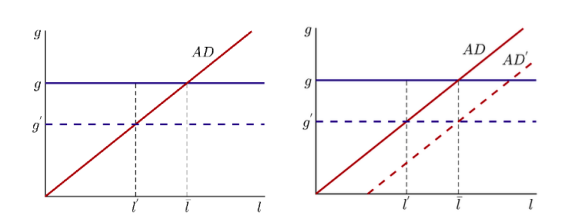
We take as our beginning stage a stripped-down form of the standard New Keynesian model (Gali 2009). As in the Keynesian convention, employment and output are controlled by aggregate demand. Thus, aggregate demand relies emphatically upon efficiency development. This impact offers to ascend to a positive connection between efficiency development (g) and employment (l), delineated by the AD bend in Figure 1.
Short-run equilibrium Coronavirus
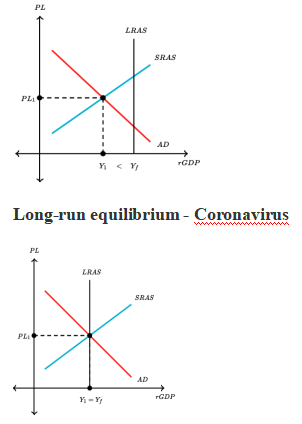
L
Corona virus has acted a demand shock
Impermanent negative supply shocks, for example, those brought about by a pandemic, lessen output and employment. As desperate as they might be, supply stun downturns are somewhat a productive reaction, since output and employment ought to surely fall.
The viewpoint we offer here is unique and dependent on the idea that supply and demand powers are interlaced: demand is endogenous and influenced by the supply stun and different highlights of the economy. Our examination reveals highlights of the economy that issue and the instruments by which powers following up on the supply side wind up influencing the demand side also. The fundamental instinct is basic: when labourers lose their salary, because of the stun, they diminish their spending, causing a withdrawal in demand. In any case, the inquiry is whether this system is sufficiently able to cause a general deficit in demand. (Jordà et al.)
The economy now in a recessionary gap or an inflationary gap
Conventional recessions can be handled by free fiscal and monetary policy. These won’t work when dread drives the log jam. In numerous nations, financing costs are as of now near zero, so national banks have lost their capacity to stimulate through huge rate cuts. Soma banks could cut loan fees by as much as 2%, however, will that restore loaning when recession and dread are slaughtering organizations? The doomed money related framework will dull all fiscal and monetary activities. This is fundamentally a recessionary gap and can’t act naturally amended. It needs the assistance of the government and the budgetary organizations.
The proposed stimulus package
The activity of any transient improvement must be to assist genuine people with genuine issues: defending wellbeing and enduring the financial crunch. Bailouts to supported enterprises are a weak and insufficient approach to accomplish these objectives. The best thoughts would most likely be to send unhindered assets to state and nearby governments to help settle the expense of coronavirus, toss everything conceivable at expanding zero-carbon power age, and briefly decrease manager side finance assessments to dishearten organizations from laying individuals off. (Jordà et al.) The right arrangement is to consent to fiscal upgrade however expect it to appear as making newly programmed stabilizers.
This isn’t simply unrealistic reasoning concerning a pandemic. In 2009, during the Great Recession, President Barack Obama marked the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, a generally $800 billion improvement bundle. Be that as it may, this time because of the high swelling and the financial demand the infusion will be higher than that. An accurate sum can’t be resolved. (Makridis, and Hartley)
References
Jordà, Òscar et al. “Longer-Run Economic Consequences Of Pandemics”. Federal Reserve Bank Of San Francisco, Working Paper Series, 2020, pp. 01-16. Federal Reserve Bank Of San Francisco, doi:10.24148/wp2020-09.
Makridis, Christos, and Jonathan Hartley. “The Cost Of Covid-19: A Rough Estimate Of The 2020 US GDP Impact”. SSRN Electronic Journal, 2020. Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3570731.