Introduction
Brief background on regional trade blocs
In the present day, the fact that the regional trade blocs are among the most important features of the global economy can be put down to the fact that they assist in the effort of cooperating more economically with regions that are within a specific geographical area. Such agreements concentrate on the creation of free-trade areas, and the removal of the obstacles to transportation of the goods and services as well as investments, thus, may affect the economic growth in these countries. Union members have their competitive advantage via joint efforts in the global market through shared resources and bargaining in the group.
Introduce the East African Community (EAC)
The EAC which is a short form for the East African Community or the East African Community is one of the few regional trade blocs which have attracted attention and fame lately. Established in 2000, the EAC comprises six member states (Lwesya, 2022). These are the countries that were of concern to the United Nations (UN):
EAC endeavors to achieve this objective through the relaxation of non-trade barriers and their free movement, that is across the borders of all member countries.
Critically examine the trade barriers-related issues
The EAC is facing a range of trade barriers that are in the way of the EAC’s sustainable integration into a single customs union (Kijogi, 2021). On the other hand, the complications that have appeared here have been political, economic, social, cultural, legal, and regulatory barriers which have been in many ways the most challenging hurdles and have not allowed the improvement in trade flow and economic integration in this region. Scrutiny of these challenges that hinder attaining high-level integration that is the benchmark of the EU’s success as common market implementation cannot be overlooked.
Trade Barriers Affecting the EAC
Political barriers
Political obstacles are the root of the problem of the East African Community (EAC) because the unstable political environment in some member states as well as interstate disputes interrupt collection efforts and cooperation (Ntara, 2023). While the governments may share the same strategic objectives, the dissonance of the political agendas as well as the absence of a harmonized policy casts a cloud of the lack of policy alignment at the regional level and therefore the emergence of divergent regional strategies.
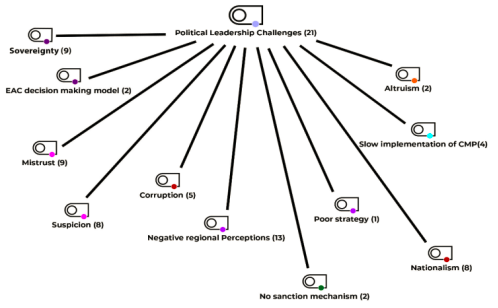
These problems get solved when individuals and countries meet to create sustainable peace, dialogue, and cooperation that will ensure the same goals for the political interests and economy of the countries. They are only short-term measures that can just take up the political problems and thus become the route for the bigger EAC union and prosperity in the region.
Economic barriers
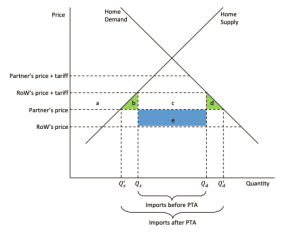
The economic elements have been another cause that has contributed to the integration process failure of the EAC. Even though both member countries, and among themselves, have disparities in the levels of economic development and income, it is the task to create an even suitability to establish a level of economic integration (Ng’imor, 2020). The other factors that are affecting the EAC are the poorly developed transportation networks, the unreliable energy supply, and few telecommunications connectivity, which have fallen behind the movement of goods, services, and people in the community.
Social and cultural barriers
The diversity of social and cultural norms about the Eastern African Community (EAC) is an obstacle to effective cross-cultural exchange and amity. The many ethnic groups, languages, and cultures can engender communication gaps, provoke misunderstandings, and provoke mistrust among the member countries (Njenga, 2020). The main cause of the refusal to adopt comprehensive integration policies entirely is these disagreements. Overcoming these obstacles requires joint efforts to let know people about the intercultural exchange, build up respect between people, and glorify the different cultures within the EAC. Through the growth of this common vision and goal, the area can overcome social and cultural hindrances, and move forward into more unison and teamwork.
Legal and regulatory barriers
The very existence of legal or regulatory barriers has hindered the smooth EAC’s process to the monthly market. Regulation disparities that often feature in the domains of taxation, labor, and intellectual property rights set forth the main problems among the member countries regarding the laws (Munezero Buzingo, 2021). Indeed, this is the case as doing business across borders has reached nightmarish proportions for businesses, being both uncertain and costly. However, a lack of simplification and the complex bureaucratic procedures at the customs desks has been the most significant barrier to the movement of goods and services within the region along with non-tariff barriers such as technical standards and licensing conditions.
Critically analyze why these barriers have prevented the EAC from achieving an EU-level common market
These complex barriers have altogether impeded the EAC from attaining a scope of economic integration that could have been as intensive as the EU. The EU has succeeded in building a common market due to its capacity to tackle the same kind of challenges through continued political participation, the harmonization of policies, and the establishment of strong institutional structures (Ong’oyi, 2021). The EAC, on the contrary, faced obstacles in removing said barriers, which in the end have slowed down the free flow of goods, services, labor, and capital within the region.
To reach an EU-like common market, the EAC requires the barrier to be addressed through joint efforts and policy interventions. This could be done by improving political stability and cooperation, closing the economic gaps by developing targeted programs, increasing social integration and understanding, and establishing legal and regulatory frameworks common among members, only through addressing the barriers straight on, can the EAC realize the whole potential of regional economic integration and harvest the fruits of the integrated common market.
Proposed Trade Policy Solutions
Strengthen political commitment and cooperation among member states
Closer political relations and political interaction of the EAC member states are the two primary aspects of overcoming conflict and integrating the states more into a single unity. Such a framework may be established via the establishment of high-level periodical dialogues, a common decision-making system, and the creation of a complete regional governance system (Kimutai et al., 2022). When the political objectives of those members are in harmony and the military conflicts undergo diplomacy the member states can create a peaceful and conducive environment that favors economic engagement.
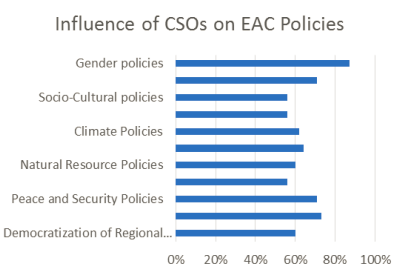
Harmonize economic policies, regulations, and legal frameworks
The alignment of economic policy, law, and regulation frameworks of the EAC member states is necessary given the problems of economic and regulatory barriers. The standardization may be done through the development of common tax arrangements, labor laws, and intellectual property rights regulations; investment policies could also be part of the standardization processes (Ekutu, 2021). Maintaining the standards for trading rules across the region will not only help to create a level playing field but also cut down on compliance costs and therefore encourage the movement of goods, services, and capital within the region.
Invest in regional infrastructure and connectivity
The proper control of infrastructural and connectivity projects within the region is a key tool for overcoming economic hindrances as well as improving intra-regional trade. It could be the designing and building of a reliable transport network (roads, railways, airports, ports), improved energy infrastructure (power generation, distribution), and telecommunication network enhancement. Through the efficiency of transport infrastructure, transportation costs will go down, and the movement of goods and people will increase, which in turn contributes to integration.
Promote socio-cultural integration and awareness
The challenge of social and cultural barriers shouldn’t be only met by programs that inaugurate the education process about cultural diversity. The main program is aimed at education (ABUBAKAR, 2020). It is intended to create a common understanding about different cultures, promote common languages or introduce multilingual policies, and of course, celebrate our common cultural heritage and tradition. The EAC is the link that enables community, social, and cultural barriers to fashion regions’ identity to disappear and integration to progress smoothly.
Align trade policies with GATT/WTO principles
Through the GATT and the WTO principles, the EAC can set its rules and make them harmonized and based on rules that are understood and respected by all. Those are among the principal things set on the agenda, such as the removal of tariff and non-tariff barriers, transparent trade regulations, and fulfillment of the commitment to international trade (Conjwa, 2020). The application of the GATT/WTO strategy can aid the EAC in expanding its global competitiveness and utility of foreign investment.
Justification and problem-solving strategies for each proposed solution:
Political commitment and cooperation: The setting of the stage for economic integration and the management of political barriers are some of the salient advantages of strong political states and mutual objectives.
Harmonization of policies and frameworks: The uniform laws and legal processes will balance the market, together with reducing the compliance costs, and further contribute to the free flow of products, services, and capital across borders consequently removing both the economic and the regulatory barriers.
Regional infrastructure investment: The optimized transport infrastructure will cut shipping costs, improve connectivity, and accelerate the flow of goods and people, which are an important factor for the growth of intra-regional trade.
Socio-cultural integration and awareness: Since EAC is based on cross-cultural understanding and a common heritage appreciation it can bring the bridging of social and cultural frontiers which will give a regional identity sense as well as enhance the ease of integration.
Aligning with GATT/WTO principles: As EAC is rule-based, trade liberalization, transparency, and international agreements are going to be the basic principles of its operations for the sake of its better competitiveness in the global market, reception of direct investment, and barrier-free trade.
Provide justification and problem-solving strategies for each proposed solution
Adoption of GATT/WTO principles in trade liberalization, transparency, as well as trade agreements for international trade will solve trade barriers through the reduction and removal of tariff barriers and the establishment of a predictable and open trading environment. This will certainly reinforce the EAC’s global image and lure more foreign investors, hence contributing to the stable movement of goods and services (Anami, 2023). Equity and fairness can also be achieved by compliance with the rules and principles that are universally recognized which will guarantee that the EAC is a part of the international trading framework and that it is integrated.
Benefits of a Fully Integrated EAC Common Market
Increased intra-regional trade and economic growth
Among the main advantages for EAC is building up an environment of an open and common market which will guarantee unrestricted trading of goods, services, labor, and capital. It would also be a tool for promoting international trade through the reduction of taxes, abolishing non-tariff barriers, and harmonizing the trading regulations among countries (Mmari et al., 2022). Trade flows consequently would be the motors, which in the end would cause economies of scale, specialization, and diversification that would, in turn, help to promote economic development and growth in this region.
Improved competitiveness and attraction for foreign investment
The EAC would become more appealing to foreign investors and multinationals who would want to explore the region’s market opportunities as a result of integrating and growing the market. A common market will complement the region by opening a consumer market of a greater range, a pool of skilled labor, and a business jurisdiction that is harmonized, making the region competitive. Therefore, exports would attract foreign direct investment, technology transfer, and job creation which along with economic growth and development would enhance the economy further.
Greater bargaining power in international trade negotiations
The EAC would be a single economic bloc that will be able to negotiate better trade deals both at the international level and at trade forums (Krapohl & Van Huut, 2020). Collectively, member states can be able to present a common voice and negotiate more favorable trade agreements, thereby securing better access to the global markets as a result of their combined market size. This can be a foundation for its presence in the international trade system and the security of its economic interests.
Socio-cultural integration and cooperation
Economic and political gains are the major results of a fully integrated EAC with the impact of molding socio-cultural unions and cooperation among the diverse communities in East Africa. The free movement of people would stimulate cultural exchange by seeing the worth of others and this would thereby promote the region’s personality and cooperation. In addition, joint work in fields, such as education, health, and tourism would be a great starting point towards more long-term, collaborative development and progress for both sides.
Conclusion
The aspirations of the East African Community are not different from those of the European Union, which is aimed at establishing a fully integrated common market. Nevertheless, surmounting the multifarious prerequisites of political instability, socio-economic inequalities, socio-cultural conflicts, and legal inconsistencies is inherently important. A strategic approach focusing on the issue of political will, policy coordination, infrastructural provision cultural integration, and GATT/WTO agreement could be a promising way. An EAC common market with a high degree of success promises that intra-regional trade will grow, as will economic development, investment prospects, increased negotiations, and enhanced socio-cultural cooperation. Through joint forces and a good policy framework, the EAC can unleash its full innovation as an integrated economic powerhouse.
Reference List
ABUBAKAR, A., 2020. Critical Appraisal Of The East African Community (EAC) (Doctoral dissertation). http://repository.riarauniversity.ac.ke/xmlui/bitstream/handle/123456789/1052/Mohamed%20Ammar.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Anami, A.K., 2023. Contribution of regional integration to economic development of member states, case study: East African community (EAC). World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 17(2), pp.758-769. https://wjarr.com/sites/default/files/WJARR-2023-0292.pdf
Conjwa, S., 2020. The African Continental Free Trade Agreement in Context. https://www.academia.edu/download/65375305/Final_Copy.pdf
Ekutu, B., 2021. The Prospect of Monetary and Financial Co-operation: a Legal Evaluation of Kenya’s Regional Economic Integration Endeavour in the East African Community (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi). http://erepository.uonbi.ac.ke/bitstream/handle/11295/160585/Ekutu_The%20Prospect%20of%20Monetary%20and%20Financial%20Co-operation%20-%20a%20Legal%20Evaluation%20of%20Kenya%E2%80%99s%20Regional%20Economic%20Integration%20Endeavour%20in%20the%20East%20African%20Community.pdf?sequence=1
Kijogi, M.M., 2021. The effect of Non-Tariff Barriers on Trade in the East Africa Community. https://ikesra.kra.go.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/1425/The%20effect%20of%20non-tarriff%20barriers%20on%20trade%20in%20the%20East%20Africa.pdf?sequence=1
Kimutai, G., Oluoch, K. and Opondo, P.A., 2022. The Influence Of Civil Society Organizations (CSOS) On East African Community (EAC) Policies. https://repository.maseno.ac.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/5426/paper_12.pdf?sequence=1
Krapohl, S. and Van Huut, S., 2020. A missed opportunity for regionalism: the disparate behaviour of African countries in the EPA-negotiations with the EU. Journal of European Integration, 42(4), pp.565-582. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/07036337.2019.1666117
Lwesya, F., 2022. Integration into regional or global value chains and economic upgrading prospects: an analysis of the East African Community (EAC) bloc. Future Business Journal, 8(1), p.33. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43093-022-00141-9.pdf
Mmari, D., Msami, J., Mwombela, S., Mpapalika, J., Demena, B.A. and van Bergeijk, P.A., 2022. EAC integration: evidence-based policy in difficult times. In Trade and Investment in East Africa: Prospects, Challenges and Pathways to Sustainability (pp. 21-39). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-19-4211-2_2
Munezero Buzingo, S., 2021. Challenges and opportunities in developing a common legal and regulatory framework on energy in East African Community. https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/handle/2263/82886/MunezeroBuzingo_Challenges_2021.pdf?sequence=1
Ng’imor, B., 2020. Economic integration of the East African community. http://stax.strath.ac.uk/downloads/h415pb06r
Njenga, L.N., 2020. Integration in Africa: International Legal Competence of the East African Community in the Economic, Social, and Cultural Sphere. Supporting Inclusive Growth and Sustainable Development in Africa-Volume II: Transforming Infrastructure Development, pp.169-182. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Adu-Nikez/publication/346444474_African_Union_Outer_Space_Program_Chances_and_Challenges/links/6061beaa458515e8347c39d7/African-Union-Outer-Space-Program-Chances-and-Challenges.pdf#page=183
Ntara, C., 2023. Political leadership and regional integration: A case of the East African community common market. Journal of Management and Training for Industries, 10(1), pp.1-20. https://search.informit.org/doi/pdf/10.3316/informit.171728742333013
Ong’oyi, M.K., 2021. The influence of national interest on regional integration: the case of Kenya in the East African community (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi). http://erepository.uonbi.ac.ke/bitstream/handle/11295/155987/Ongoyi%20_The%20influence%20of%20national%20interest%20on%20regional%20integration.pdf?sequence=3