1 Reflection and transmission at First Boundary:-
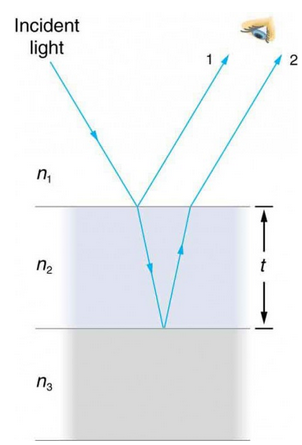
Figure 1:- Shows that reflection and boundary at first surface
When light strikes on the thin film then ray 1 is partially reflected and refracted partially at the top surface. The ray 2 is the refracted ray and partially reflected by the bottom surface. Interference of these rays depends upon the thickness of the soup film.
If the film in Figure 2 is soap bubbles which contains water and air both sides then ray 1 undergoes the phase shift of λ/2 and none for ray 2. If the film is very thin, the path length difference between the two rays is negligible, then these rays will exactly out of phase, and destructive interference will occur at all wavelengths and so the soap bubble will be appear dark here.
Figure 2:- Shows that Inverted or not inverted reflected wave
b) The frequency of transmitted wave in the film is equal to the frequency of incident wave in the boundary because the wave is not change on crossing a boundary,
c) Wavelength of more denser medium is always greater than less dense medium.
Figure3:- Shows that transmission of light denser to rare medium
Figure 4:- Shows the Reflection or refraction
d) When the ray at the first boundary then the reflection of the incident ray will be more like the fixed end. That is, a wave with an upward displacement will reflect off the end and return with an upward displacement. Pulse is not inverted. This behavior of non-inversion of the wave will always be measured at the end of the medium which is free to move.
e) When the reflection of light take place from a medium which reflective index is higher than the travelling medium refractive index then phase change of 180º or a phase shift λ / 2 shifts occurs.
Figure 5:- Shows the phenomenon of air, soup film and air
Reflection at the second boundary
2(a):-Reflection of light at second boundary from soup film to air.
Figure 6:- Shows the phase shift between incident and transmission light
2(b)
In this case reflection is approaches towards the free end because soup bubble is a medium of fixed end light after reflection goes towards the medium of free end or air.
(C) No reflected wave has not phase shift of 1800. It has a phase shift of 00.
3 Transmissions at the First Boundary:-
Figure 7:-Transmissions at the First Boundary
According to the snell’s law
n1sinθ1 = n2sinθ2
n1= 1
n2=1.35
sinθ2 = n1sinθ2/n2
sinθ2 =1 x sin 180 0 /1.35
sinθ2 = sin 180 0
θ2 =0 degree
n3sinθ3 = n4sinθ4
n4= 1
n3=1.35
1.35sin0 = 1sinθ4
θ4 = 180 degree
It shows that if ray is transmitted at the 180 degree angle then it is reflected at the angle 0 degree. Therefore, net phase shift is zero degree.
(b)Yes there is change in the phase. If the ray is transmitted back to the first boundary then there is phase change of the 1800.
D)
Figure 8:- Shows the phase change
Frequency= c/ λ
Frequency= 7.5 x 1014
C = 3 x 10^8
Frequency = 7.5 x 10-14/ 3 x 10^8
Wavelength of light wave= 2.5 x 106
Wavelength of soup film
λ = c/n x f
n- Refractive index of the air = 1.33
C = 3 x 10^8
λ = 3 x 10^8 / (1.33 x 2.5 x 106)
Wavelength of soup bubble-λ = 0.90 x 10^2
Frequency of soup film
Frequency= c/ λ
Frequency= 3 x 10^8/0.90 x 10^2
= 3.33 x 10^6 Hz
E) If the observer is located at the left side of the ray then incident ray after phase shift of 1800 reflected towards the observer. This ray is reflected from the one medium (air) to another (soup film) and reflection occurs. When light enter from higher refractive index to lesser refractive index then it will bent towards the normal.
Figure 9:- Shows the phase shift between incident and transmission light