General information
Purpose- the major aim of this integrated system manual provides a process and a risk-based approach which is meant to ensure that a positive achievement is attained at all the times. Each of the various procedures have own individual elements whereas others have common procedures (Ding ET AL., 2012). Having a detailed integrated management system makes it easier for the business to be panned, managed as well as strategies implemented across the various undertakings. It will provide an integrated system manual for warehousing management in a sub shore set up. The diagram below illustrates the action plan for the continual improvement
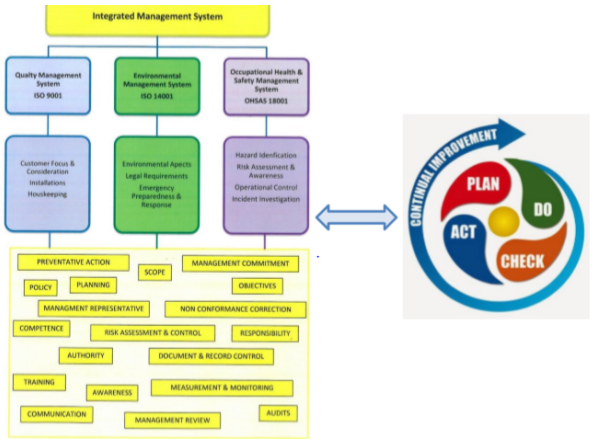
The manual
The manual provides a description of the area of the control and references which the construction applies in ensuring that all of the services and operational activities conducted are in reference to the contractual and in-house requirements. It offers detailed of the organizational chart, the management system policy, the authority, and accountability, the delegation of the responsibility, as well as the process of reference in compliance with the iso 9001 requirements, 2008, iso 14001:2004 and OHAS 18001:2007 international standard.
In order to assess the effectiveness of this integrated system management manual, the certification bodies, as well as the client companies, shall be granted access to the various procedures and systems that were possible as shall be permitted by the general manager. The policy of the organization has been attached herein by the general manager. It generally points out the general commitment of the towards the progress of the integrated system which is as well reflected in the various performance of the team members stipulated in the manual.
This IMS document is applicable in all the departments within the organization and every employee within the organization is entitled to achieving all the minimum requirements as stipulated in the manual (Domingues et al., 2011).
The scope
The scope of the organization is defined as design construction, infrastructure, installation, maintenance and commissioning of civil projects.
Exclusions
No exclusions
Applicable standards
: iso 14001:2004 iso 9001:2008, and ohsas 18001:2007
Preface
Xx organization was established in 2000 and since it has been among the leading contracting companies in the region. Over the years,the organization has successfully executed a variety of construction projects ranging from concrete rehabilitation, heavy industrial works, construction of stadiums among others. The major of the clients include the department of military works, the department of water and social services.
The company staff is composed of a group of qualified professionals, engineers, and skilled tradesmen (Elbeltagi & Meftahi, 2012). Most of the equipments is owned by the organization including the computerized systems.
Integrated management system
The construction company maintains a detailed and well documented and established system that is implemented through continual review. The documents are specifically designed to ensure fairness and satisfaction to the
- Customers
- The organization team members
- The authorization bodies
- As well as other interested parties.
The system has been established in a professional manner with proper implementation at the various stages which comprise of the below elements
Level 1: IMSM
In this document, the responsibilities, the structure, as well as the management system is documented. Majorly, its design ensures conformity to the iso 9001:2008, iso 14001:2004 and OHAS 18001:2007 standards. Its primary role is to offer a a detailed description of the compliance to the contractual elements. Additionally, it encompasses the company’s mission statement, the integrated policy, the commitment of the highest standards, as well as the cherished values. The document is referenced to the charts of the organization reporting which offers a clear reflection of the various relationships within the company (Hamidi et al., 2012).
Responsibility: the general manager/ manager
Level 2: the operating procedures of the integrated management system
The procedures of the organizations are the ones which helpin attaining the requirements of the iso operation standards iso 9001:2008, iso 14001:2004 and OHSAS 18001:2007. Other company activities are regulated by various documents, manuals, reports, procedures as well as forms that also comply with the iso standards iso 9001:2008, iso 14001:2004 and OSHAS 18001:2007 (Kauppila et al., 2015)
The responsibility: all team members
Level 3: the integrated management system forms
The forms play a crucial role in the organization. When they have been dully filled, the become part of the QHSE records. Most of these forms are aligned towards ensuring that the system is efficient and effective.
Responsibility: all of the team members
The management principles deployed
- Customer focus
The organization values the significance of satisfying customer needs and makes it a priority throughout the entire operations. In the past, the company did manage to fulfill the customers’ needs and preferences in various circumstances and is committed to achieving the same in the later years via the effective deployment of the principle of the integrated management system.
- Leadership
The company values team leadership, whereby all the members are involved and consulted on various activities. In the past, the company has established a corporate unity among the members and is committed to maintaining the relationship. In terms of the employee satisfaction, both externally and internally, the company has been outstanding (Kim et al., 2015).
- Involvement of people
All the team members are considered very important persons and they are regularly engaged through meetings as well as corporate cultural functions. They are significantly regarded as the organization’s human assets and are greatly taken care of their great contribution towards ensuring the company’s excellence.
- Process approach
All the activities which are conducted within the organization follow a certain intercalated process which are detailed in the operating procedure of the integrated management system. Special considerations are used in marking the process such as the inputs, interfaces, outputs, time factors among others (Klute-Wenig and Refflinghaus, 2015). There is an effective approach for monitoring and analyzing the process.
- System approach to management
A clear definition of the linked process interface is provided in the integrated management system. This ensures that the company is operating towards organizational excellence.
- Continual improvement
The company has a lot of faith and belief in its integrated management system continual improvement. To ensure that the improvements are reflected in the organizational members, a CAR process is employed in the organization. This process empowers the employees in the aspects of health and safety, quality, strategy, environment, and innovation.
- Factual approach to decision making
The process of division making follows a logical and factual analysis. A Critical decision is arrived at after thorough brainstorming by a selected team of employees (Mežinska et al., 2015).
- Hazard and environmental review
The organization adopts a variety of methods in assessing the quality of the materials being used as well as the products. In doing so, the organization has established potential hazards related to the operating conditions.
The processing module
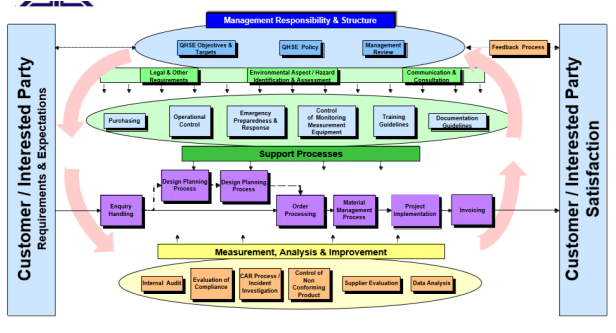
Management responsibility
The company is committed to offering the appropriate services which meet the demands of the clients. The company strongly believes in the the the continual improvement of the integrated management system as well as the empowerment of its employees. The corporate development basis for the company is its reputation of integrity, quality as well as dependability.
The construction policy
The construction company is committed totaining the quality oh & s, and environmental standards for its clients, shareholders, employees, as well as the entire environment. The documenteded policy is established and conveyed though the employees by way of issuance to help in meeting the demands of regulatory bodies, clients as well as the company values.
QHSE program authority
The entire responsibility of the integrated management system has been delegated to the management team headed by a management representative as well as the organization’s staff members. The management team is responsible for identifying problems, initiating actions as well as the implementation of the appropriate strategies. Further, they are in charge o ensuring compliance with the company policies (Nunhes et al., 2017). However, as the management team is the one responsible for ensuring compliance with various procedures, it is the prime duty of the employee to ensures that in their specific jurisdictions, there is compliance with the procedures.
Qhse objectives and target
The targets of the organization are in the denomination of revenues contribution, technological innovation, strategy as well as customer satisfaction. All the objectives are similar to the objectives of the company.
QHSE planning
The company shall make sure that the resources as well as equipment which are to be utilized for the execution of projects are identified in prior and planned for.
Most of the planning shall be documented, however, the daily routines shall be in the form of discussions and meetings.
In the planning process, the continual improvement of the process shall also be involved.
The planning process shall be detailed so that the integrity of the integrated management system is consistent deposit any significant revisions of the system parts
During the planning process, the management shall endeavor to identify the environmental factors which are significant during the operations (Olaru et al., 2014)
Further, the management shall ensure that the process of risk and hazard identification, as well as the respective assessment, is done and various control measures are detailed in the planning stage.
Further, the legal documents and requirements which are necessary for the performance criteria of the projects shall be identified and availed in the planning stage.
Environmental aspects and hazard identification, risk assessment and determining controls
The head of the project department shall be in charge of establishing the identification of safety and environmental aspects as well as the related impacts. The risk assessments shall also be conducted to ensure that all the people accessing the site are under the control and supervision of the organization.
The management of the risk shall be in accordance with the identification assessment as well as mitigation of the risk. It thus implies that all the employees shall be exposed to work health and safety training in order to avoid injuries during the conducting of the project.
A list of potential hazards and risks shall be availed to the employees so that they become aware and precautious while undertaking various activities (Ren et al., 2012).
All the risk which will be identified while executing the project shall be reported to the respective management representative who will offer a solution to the issues raised, or otherwise referenced on to the project departmental managers.
The legal documents
The legal requirements which the company subscribes to includes
A) industry codes of practice.
b) agreements with public authorities.
C) internal policy including subscribing to, e.g., international chamber of commerce business charter for sustainable development
D) corporate mandates (Safa et al., 2014)
Resources management
The company is fully committed to offering the necessary resources and manpower in a precise manner. The resources shall be offered in terms of physical resources, professional expertise, commitment, and infrastructure.
The resources provided in a timely manner shall also ensure compliance with the client’s requirements
In terms of human resources, the employees shall undergo thorough training before being deployed to undertake various project activities (Simon et al., 2014).
Measurement, analysis, and improvement
A corrective & preventive action request model has been provided by the construction company which is aimed at ensuring the effective and anticipated outcome. It will achieve the desired outcome through measurement, analysis as well as improvement of the methodology (Zhang ET AL., 2011). The CAR shall be responsible for offering the basic platform for defining, planning and implementing the framework’s activities necessary for attaining the conformity and improvement.
References
Ding, L.Y., Zhou, Y., Luo, H.B. and Wu, X.G., 2012. Using nD technology to develop an integrated construction management system for city rail transit construction. Automation in Construction, 21, pp.64-73.
Domingues, P., Sampaio, P. and Arezes, P., 2011. Beyond” audit” definition: a framework proposal for integrated management systems. In Institute of Industrial Engineers Annual Conference. Institute of Industrial Engineers.
Elbeltagi, E. and Dawood, M., 2011. Integrated visualized time control system for repetitive construction projects. Automation in Construction, 20(7), pp.940-953.
Hamidi, N., Omidvari, M. and Meftahi, M., 2012. The effect of integrated management system on safety and productivity indices: Case study; Iranian cement industries. Safety science, 50(5), pp.1180-1189.
Kauppila, O., Härkönen, J. and Väyrynen, S., 2015. INTEGRATED HSEQ MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS: DEVELOPMENTS AND TRENDS. International Journal for Quality Research, 9(2).
Kim, J., Koo, C., Kim, C.J., Hong, T. and Park, H.S., 2015. Integrated CO2, cost, and schedule management system for building construction projects using the earned value management theory. Journal of Cleaner Production, 103, pp.275-285.
Klute-Wenig, S. and Refflinghaus, R., 2015. Integrating sustainability aspects into an integrated management system. The TQM Journal, 27(3), pp.303-315.
Mežinska, I., Lapiņa, I. and Mazais, J., 2015. Integrated management systems towards sustainable and socially responsible organisation. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 26(5-6), pp.469-481.
Nunhes, T.V., Barbosa, L.C.F.M. and de Oliveira, O.J., 2017. Identification and analysis of the elements and functions integrable in integrated management systems. Journal of cleaner production, 142, pp.3225-3235.
Olaru, M., Maier, D., Nicoară, D. and Maier, A., 2014. Establishing the basis for development of an organization by adopting the integrated management systems: comparative study of various models and concepts of integration. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 109, pp.693-697.
Ren, Y., Skibniewski, M.J. and Jiang, S., 2012. Building information modeling integrated with electronic commerce material procurement and supplier performance management system. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management, 18(5), pp.642-654.
Safa, M., Shahi, A., Haas, C.T. and Hipel, K.W., 2014. Supplier selection process in an integrated construction materials management model. Automation in Construction, 48, pp.64-73.
Simon, A., Karapetrovic, S. and Casadesús, M., 2012. Difficulties and benefits of integrated management systems. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 112(5), pp.828-846.
Weng, T., Nwokafor, A. and Agarwal, Y., 2013, November. Buildingdepot 2.0: An integrated management system for building analysis and control. In Proceedings of the 5th ACM Workshop on Embedded Systems For Energy-Efficient Buildings (pp. 1-8). ACM.
Wu, W., Yang, H., Li, Q. and Chew, D., 2013. An integrated information management model for proactive prevention of struck-by-falling-object accidents on construction sites. Automation in Construction, 34, pp.67-74.
Zhang, J.P. and Hu, Z.Z., 2011. BIM-and 4D-based integrated solution of analysis and management for conflicts and structural safety problems during construction: 1. Principles and methodologies. Automation in construction, 20(2), pp.155-166.