Introduction
1.1 Background
The way of working has been changing since the past two centuries. The industrial age focussed on goods production but in the early 1930s it got transformed into service-based economy. After the service based economy, came the knowledge economy that emphasizes on the information process in the year 1960s and in the year 1990s, creative industries followed the previous ones and this focussed on producing original data (Xie et al., 2013). Thus with the changing patterns of work, the requirements for the workforce also changed thus affecting the workspace. As per the research done by McIntosh, Farwell & Arnold (2014), the evolvement of the information technologies in the year 1990s along with the rise of creative industries is the underlying cause that led to the formation of a new social group and was called the creative class. According to some researchers the creative work economy can be attributed to the knowledge workers. As per the research done by Liegl (2014), the factors are being analyzed that can contribute in a positive way towards the innovative work patterns. The present scenario however suggests that though the jobs based on knowledge can be done from any place aided by the advanced technologies still the knowledge workers prefer to work in an environment where others are also present. This can be conferred from the rapidly increasing co-working spaces.
1.2 Problem Statement
As per the research Methot, Melwani & Rothman (2014), some knowledge workers are of the opinion that working in these types of environments result in distractions and a person can focus better when alone. Contrary to this, the environment of co-working spaces serves a platform to share knowledge and develop team spirits. The concept of co-workspace refers to the physical setting where co-working takes place. It deals in physical configuration as well as considers the philosophy involved in the process of sharing. The term was coined by Bernie DeKoven in the year 1999 (Bockhorn 2013). He came up with this concept to provide descriptions about the style of the co-located and the equal but autonomous, work being made possible by the technological advancements in the mobile technology. Brad Neuberg opened the first official co-workforce based in San Francisco, Spiral Muse. Co-work space is conceptualized as being the micro clusters as these provide physical territories for dynamics to happen amongst the various local communities related to individual entrepreneurs, small initiatives such as start-ups and freelancers that are mainly active in fields such as new media and the creative industries. In such a workspace the individuals and the groups conducting separate businesses come under the same physical space along with the beneficial resources of the office (Wilhoit, 2018). This concept has many benefits for the small businesses and the freelancers owing to the reason that the total cost of lighting, renting, heating the workplace and furnishing are shared among the partners and still they enjoy the advantages of the environment of professional office.
1.3 Aim, Objectives and research Questions
1. Environmental dynamic and dimensions assessment of current workplace using academic literature
2. Environmental assessment of local cafe, allocated co-working space, and agent’s home guided by academic studies and literature.
3. Explanation of culture, dimensions of workplace in accordance to academic literature.
4. Analysis of organisation type, productions, service goals, structure in accordance to academic literature.
5. Evaluating and discussing various workplace environments and their features in accordance to academic literature and case studies.
1.4 Research Structure
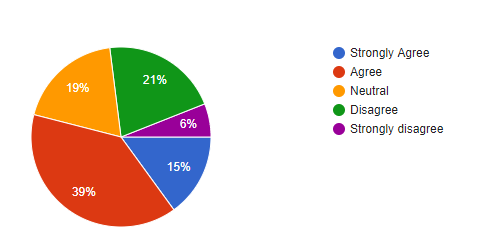
Figure 1: Research Structure
(Source: Created by author)
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Concept of Co-working spaces
As per the research done by Capdevila (2015), co-working is an embedded part of the rapidly growing movement which is known as sharing economy. Individuals prefer co-working environment for the associated intangible benefits that it offers such as socializing, sharing knowledge and collaborative activities along with the increasing economic benefits. The social aspects of the co-working environment is yet to be researched on as the researches that have been conducted as of now focus on the way these environments are inculcating and developing leadership qualities in the entrepreneurs community. As per the research done by Cummings & Worley (2014), the individual and the collaborative skills related to leadership are strengthening by the influence of co-working environments. The co-working spaces are providing an interesting way for the individuals to get adapted to work in an increasingly mobile culture. These environments also have the potential in them to benefit the communities where they are based. As per the research done by Segura et al. (2015), the workers coming together in a common workplace are enhancing their social skills, improvising their contacts and add strength to overall network related to the social capital in their respective communities. As per research done by Sollitto (2014), micro clusters help promote competition as well as cooperation. The practical application of the concept of co-working was done in the year 2000 and since then it has grown exponentially throughout the world. The concept is attracting people and they are eager to apply the same in their working styles. Gaining the popularity, the aspect that needs to be considered in case of the co-working spaces is how the developed work space can be designed effectively. The benefits that co-workspace provides to the business and the social capitals has a high level of potential. The initial insights regarding the various spatial factors of the co-workspaces that affect the perception of the users about the collaboration within the work space is to be considered. The physical design of the co-workspaces is linked with the innovative and creative work experiences and the new connections with the social networks that lead to increase in the social capital for the users along with the community they dwell in (Schulze et al. 2014). The concept stating that the co-working spaces are micro clusters specifically relate to certain cooperative dimensions of the clusters providing that the major philosophy supporting the co-working spaces concerns the basic collaborative approach that depends on certain sets of core values related to collaboration, accessibility, openness, sustainability and community. The collaborative approach of the concept requires emphasizing on the sharing of knowledge rather than on competitive practices as in this case complementarily is preferred to competition. The concept of co-working spaces deals in providing platforms for the urban based knowledge workers to meet and different skills of the individuals are combined together to put effort on a project. As per the research done by Gandini (2015), these type of environments help in promoting a specific type of configuration that can be referred to as open source approach with respect to work. This is an evolving and emerging trend in the domain of contemporary knowledge economy as the work in this case becomes more and more distributed.
2.2 Benefits of co-working spaces
In the co-working spaces, the entrepreneurs usually share a single big office and can be benefitted from a range of the services offered by the concept depending on espresso machines, membership and the available conference rooms. The concept is a boon for the entrepreneurs who do not want to burden themselves with the load of the office infrastructure and decoration or buying the furniture and even hiring assistants (Eigen & Schuster 2012). The concept of co-working spaces has proved to be beneficial as it requires rent a desk in any place that temporarily becomes to the person who has rented it. The flexibility regarding the time is an added advantage in this regard. Many of these co-working spaces provide a facility of drop-in that is people can stop by and do their work in a common place that is unreserved costing low or sometimes even free of cost. The co-working spaces are effective in offering plug and play collegiality. The spaces provided are different and are dependent on the person’s choice that needs to work in such type of a place. The co-working spaces can be related with the old ideas that of the shared artists’ studio (McQuoid & Dijst 2012). The atmosphere that these co-working spaces provide, go hand-in-hand with regard to the lifestyle of the startup that offers a new spot in order to build new projects and generating connections. As per the research done by (), the people operating in the co-working spaces define the process of their working as “movement”. Though these spaces are different regarding to the services and the culture, still they share four main common values that are sustainability, community, collaboration and openness. The main aim if the co-working spaces are creating a sense of community amidst the users thus benefitting all in upgrading their social skills. Generally each of these organizations has their own blog in order to share the ideas and to update the informations. Co-working spaces help inculcate the value of cooperation and socialism in the users thus making them actively participate in community life. Sharing ideas with each other gives rise to new creations and innovations and ignites the thirst to learn more. Charles Planck, CEO of Articulated Impact said: “You find that if you are at home too much, you lose your edge in dealing with people, this differs from a café like Starbucks where people generally don’t know each other and consumers don’t have their own reserved area.” The community serves as the primary competitive advantage of the co-working spaces where the collaborations and the participations are expected in a clear way (Alonzo et al. 2013). The other major advantage of the co-working spaces is that users can communicate face to face that enables them to come up with complex tacit knowledge. As per the research done by Schuermann (2014), these kind of interactions benefit the firms as they are liable to produce huge flows of informations that is referred to as buzz. Arguing that participating in buzz does not need investments to be done but certainly the clustered firms are continuously contributing and benefiting from news, rumours and information that is shared in the local communication networks simply by being present in that place. Furthermore these dynamics keep the potential to create new knowledge by the help of collaborations. Face-to-face interactions are important in the aspect of the creation of the knowledge within the clusters of the creative industry. The co-working space is dedicated to the lonely entrepreneurs those who are seeking socializing opportunities. “According to a 2007 CDW survey of over, 2000 workers showed that 79% of workers employed in the private sector and half of workers employed in the public sector were worried about feeling isolated and missing human interaction if they were to start a telecommuting” (Cornwell 2012). As per the research done by Sias et al., (2012), co-working does not deal with just the arrangement of space but rather includes the movement of lifestyle. With the new generations dominating the workforce, new ideas and effective approaches have been developed related to life and work. With the advancement of technology freeing people from the established work locations, involves a greater sense related to individualism amidst the workforce present today. As per the research done by Merkel (2015), the co-working spaces create greater autonomy and provide ideas and responsibilities related to ownership. Still there is a sense of belonging that is highly desirous thereby aiding the emergence of the co-working spaces that are an extension to the shared economical mentality. Being based on membership, the co-working spaces are capable of meeting both lifestyle needs that relate to the emerging workforce namely the community, flexibility and individuality. The environment of the co-working spaces provides the right surroundings in order to focus on the current and the future goals at the same time helping to become more productive. Co-working spaces are based on communities and thus is a perfect platform to make professional contacts that in turn can help expand the business. The people belonging to these different communities are interested in bringing people sharing same interests together. These communities help find clients and bring possible growth in income and talent. Surrounded by hard-working professionals in co-working spaces, individuals will be inspired to be focussed and work hard. The co-working spaces are an environment out of the comfort of home where work can be done in a clean and professional environment. As per the research done by Veeraraghavan & Gourdie (2016), co-working spaces also have a positive effect on health and lifestyle as for example people working from home generally suffer from insomnia as they cannot differentiate from the work and the home environment but adopting the co-working concept this state of mind can be changed. It is effective in cost cutting for the entrepreneurs as it can save the expense done on the utility bills. The co-working spaces do not burden its users with service providers and repairs and thus renting a co-working space is cheaper as compared to traditional offices.
2.3 Clusters and Relational Ties: Weak vs Strong, Local vs Global
As per the research done by Snyder & Miller (2012), the clusters comprises of weak relational ties that are considered to be the main plus point. The network theory proves that in case of relationships with the weak ties for example acquaintances require fewer investments in the form of establishing close relationships based on trust and can serve as primary source of information that is novel and job openings. Weak ties are being developed by the medium of daily interactions in between the clustered firms or in case of social gatherings for example events that help in making the relationships inherently local. The weak relational ties require fewer investments and maintenance, it has been a topic of argument that this permits for more to get established, the medium being networking activities that can be considered positive in the process of sourcing the complementary sources for creating knowledge because it provides the clustered firms with many options that can be chosen from. In the context of each weak tie relating to some other social circles, thereby providing the clustered firms with flexible, wider and diverse networks. As per the research done by Hristopulos & Mouslopoulou (2013), weak ties can help clustered firms to gain access to pools of knowledge that exist beyond the easily accessible local comfort zones that in turn is crucial for the competitiveness of the firm. It can be argued that the connections with the weak ties could possibly support and also strengthen the local interaction allowing scope for information and more knowledge that is residing from elsewhere required to pump into the internal networks resulting in the dynamic buzz that can be beneficial for the clustered firms. As per the research done by Owens et al. (2016), though weak ties have a support of various advantages, there is a need to focus on the available limited empirical evidence that is a support for the influence of these relationships based on the creation of local knowledge within the industries. As per the research done by Parrino (2015), there is a need for rethinking of the theory of the clusters as per its current implications of high level of the interactions that are local while empirical evidence suggest that hardly any facts are there in order that the above assumption that is “ the more localized interaction, the better” be considered. As per the research done by Komporozos-Athanasiou & Fotaki (2015), it has been found that the clustered firms usually prefer strong relational ties for the purpose of creating knowledge. The strong relational ties have a characteristic feature of high sense of reciprocity, mutual trust and emotionally closer relationships that are crucial in order to gain low-cost access to the essential resources, especially for those firms that are in their initial phase of development. The firms in their early- development phase are embedded with high level of uncertainty that they have to confront resulting in certain activities such as problem-solving and the exchange of fine-grained tacit knowledge and relevant informations. Although it has been assumed that there exists an inherent local component related to the creation of strong ties, recent studies have revealed that these types of relationships are now increasingly being developed by the medium of virtual communication in between spatially distanced agents. Consequently, the scholars argue that by merely sharing the same values and having a shared practice can be sufficient for creating strong ties in between the distanced actors. As per the research done by Demetry (2013), in order to gain optimal access to the available critical resources the network relationships in co-working firms needs to be developed in accordance to both strong as well as weak ties. Strong ties enable low-cost access to the fine-grained informations and tacit knowledge while the weak ties provide access to the novel informations. Although there are no such researches giving the ratio in between the two but has been considered that relying more on strong ties serves in reinforcing the existing knowledge, that can negatively affect the innovative capabilities of the firm and also provoke segmentation within the local actors. As per the research done by Dewyer, Argüelles & Zimmerman (2018), it can be argued that relying more on relationships with weak ties could make it difficult in identifying and filtering out the important informations. On the basis of the studies conducted on the co-working spaces it can be said that the above insights are relevant because they reveal that different strategies need to be considered in the process of knowledge creation that in turn would depend on the different types of the network relationships that is present in between the co-workers. As per the research done by Dashti, Grkovic & Quinn (2014), it can be assumed that the co-workers in the smaller environments will get the opportunity to interact more often thus strong ties will be developed within the co-working spaces. This will help to avoid the frequently organized networking events in order to foster the tie formations. Contrary to this, these initiatives could serve as a successful strategy confined in the large co-working spaces where the co-workers will presumably have less meaningful interactions in between them as a consequence of the size related to the space and the population. As per the research done by (), co-workers are mainly benefitted from each other owing to the interactions, feedback, partnerships, trust, referrals and learning while some other empirical studies are of the opinion that co-workers expect to make expansions in their network of the potential collaborations and customers by the medium of social interactions that are taking place in the premises of the co-working spaces (Matson et al. 2012). Initial studies on the so-working spaces emphasized on the fact that just providing spaces is not sufficient for dynamics as such to emerge among the co-workers. The strong ties or weak ties or being global or local, a co-working space needs to focus on the communication in between its users or co-workers as the interaction amongst the co-workers is considered vital in the process of knowledge creation. Treating the co-working space as drop-in offices will not benefit the co-workers as it can be considered as a wall between co-operation and interaction.
2.4 The Physical Environment of Co-working Spaces
As per the research done by Sengupta & Kundu (2012), the infrastructure of the buildings influence the exchange of knowledge by providing essential layouts that in turn offer interaction in between the workers. It has been debated for the potential of open-plan offices to foster collaboration and interaction between the workers. In comparison to the traditional office spaces, the open-plan offices have a characteristic feature of no wall premises that do not separate the workers from each other thus resulting in establishing layouts where the individuals can work together under one big roof. This characteristic of placing the individuals close to each other and removing the physical barriers with respect to communication and interaction between the workers as it facilitates the co-workers to share informations related to their task, create opportunities for friendship and promote feedback. The studies regarding behavioural impact of the open-plan offices indicate that these structures keep the potential to foster the informal interactions amongst the workers. As per the research done by Ross & Ressia (2015), while these structures were initially assessed to be a source of distraction and inefficiency from the real work, that stimulates informal interactions in between the workers that have become an important part of the management work in order to increase cooperation within the teams, and at the same time to influence the rate of the innovations being made in the organizations. Recognising the benefits of the informal informations, it has been a subject of interest among the researchers as well as the practitioners in order to understand the process of fostering the same. As per the research done by Roine et al. (2013), the informal interactions cannot be regulated or be planned but the probability of their happening can be affected by the medium of indirect means for example through the physical architecture. With respect to this Annamareddy & Eapen (2017), found that the new research buildings are excessively being developed in ways by the architects so that these significantly stimulate the informal interactions by the medium of open areas and the meeting spaces. As per the research done by Chandler, Gao & Waterhouse (2014), it has been claimed that these buildings should focus on providing the main there things in order to foster the interaction among the workers namely meeting areas, proximity and visual accessibility. The notion related to visual or aural accessibility is about holding the rules such as the buildings should desist from physical barriers in order to make it easy for the workers to communicate in that environment. On the other hand, proximity can be acquired by placing the workers closely in the open-plan offices. As per the research done by Tyner (2012), with regard to the relationship in between the informal interactions and the meeting areas, three main aspects have been mentioned namely the geography, physical architecture and function. Physical architecture means how enclosed or accessible a space is. Two of the main strands that are there with regard to the relationship in between the informal interaction and physical architecture regarding a space are theory of propinquity and privacy. Theories of privacy suggest that the enclosed spaces support and encourage informal interactions as they provide the workers the required comfort in order to control their conversational boundaries while the theories of propinquity suggest that the centrally located open spaces support informal interactions owing to the fact that they bring the co-workers closer to each other. The notions related to geography and functions are correlated as both of these refer to the dimensions of centrality. Considering the two concepts, physical centrality is a matter related to geography and functional centrality is a part of function of space. As per the research done by Tsao & Lo (2014), meeting places which are centralized and are easily accessible generate lot of traffic that is responsible to increase the chance of creating spontaneous encounters with one another. Functional centrality which concerns the function of the space relates to those reasons that people have for visiting certain places and the location of area with respect to the other functionally supreme locations in the premises of the office that the workers frequently visit throughout the day. As per the research done by (), in the process of interpreting the fact that how some settings are able to afford the informal interactions, the point that needs to be emphasized on is to include the social element in the theoretical reasoning. As stated by some of the studies some of the spaces that had certain ideal designs could not practice informal interaction until the social norms were established that in turn allowed the workers to do so. The scholars argue in this case that the workers get the mentality that they are allowed to socialize and that they are allowed to interact with each other in specific settings, or else no such real interactions can be desired. This social aspect of setting is called social designation by the scholars. As per the research done by Methot, Melwani & Rothman (2014), settings need to have correct propinquity, social designation and privacy in order to afford the informal interaction. On the basis of these insights, the assumption that can be made is that the co-working spaces that are desisted from the physical barriers to communication such as the stairs and the walls, those that include the open-plan offices and available meeting places, provide a chance for the dynamics of the knowledge that takes place in between the members resulting from informal interactions that is facilitated by these environments.
2.5 Co working Managers and Social Initiatives to Foster Knowledge Creation
As per the research done by Bockhorn (2013), studies focus on social strategies that the co-working managers can make use of in order to encourage dynamics for creation of knowledge and synergies amidst the co-workers and the external actors. It is argued that in order to achieve this, the managers can select co-workers in accordance to their compatibility with the other co-workers present. As per the research done by Wilhoit (2018), an increasing number of the co-working spaces are selecting the co-workers on the basis of their shared practice and their background of similar knowledge. There are various findings that state that there have been increases in the co-working spaces that are dedicated to sectors which are specific to a certain sphere such as design, high-tech and media. In addition to these studies on incubators have assumed that it can be considered a benefit if the members of the co-working space are selected on the basis of the degree that they tend to be engaged in with respect to a specific type of networking behaviour that is known as TIO. As per the research done by Capdevila (2015), these type of behaviours have a positive impact on the process of cross-fertilization amidst the incubated firms. TIO that is tertius iungens orientation deals with a specific form of altruistic networking conduct of people that usually have a tendency of facilitating the tie formation amidst the others in the network when they are of the opinion that these individuals can benefit each other. Some other studies argue that there is no such filtering done in the co-working spaces in regard to select the members. As per the research done by Cummings & Worley (2014), the managers of the co-working spaces can stimulate the process involved in the formation and enhancement of the relational ties in between the co-workers by the organizing events. The two types of events that can be distinguished from the scenario of literature are the social and the content events. Social events include after-work drinks that are considered effective in the mechanisms to harbour the local buzz and also enable the co-workers to find out opportunities and at the same time strengthening the relationships that are there with the weak ties. The content events for example seminars, organized talks and workshops by the members can cater to the needs of the co-workers and are seen to be enabling the co-located actors in order to study one another’s business practices (Sollitto, 2014). The events are open to public and thus they enable the co-workers to establish contact with the extrinsic sources of knowledge that can serve as valuable sources for the creation of new knowledge.
Research Methodology
3.1 Introduction
Research philosophy has been helping in giving suitable methodology that are required for achieving legitimate research conduction. The ideas created from research philosophies have been helping in keeping up a sharp methodology for conveying legitimate research consider. A definite philosophy should be pursued for getting legitimate results and results from the research. In this manner, for satisfying these prerequisites in the exploration, a legitimate philosophy should be followed in the research.
3.2 Research philosophy
Research thinking has been giving idea by which data and information ought to be assembled and separated. The research sanity has been a wellspring of data improvement that perceives framework for data assembling in the research. Research levelheadedness has been an import some bit of the exploration that urges scientist to pick about strategy ought to be picked to find answers to investigate questions. There have been three research hypothesis including positivism, Realism and interpretivism. These research speculations has been reached out from thought of epistemology. The term epistemology has been delineating palatable data for a particular domain. The positivism investigate theory tends to the exploration works that depend upon conspicuous social segment. In positivism examine methodology, the research strategy picked for the research is in a general sense set up on information gathering procedure and movement of theory tolerating any. A positivist researcher all things considered looks for after an altogether formed research framework for engaging the research question and the research speculation. Moreover, the utilization of positivism sensibility in an exploration wears out quantifiable perceptions and regularly administers quantifiable research of the aggregated information (Al 2013). Thusly, on picking positivism explore mental stability, the exploration her can no chance control any information amidst information social occasion process.
Authenticity is another research logic that depends upon philosophyal enquiry. The essential part of Realism believing is to discover and reveal truth of pith of objects of an research (Brown and Stowers 2013). Authenticity focuses reasonability is besides mentioned in another two portrayals which are speedy Realism and essential Realism.
Another research discernment that is considered for scholarly research wires interpretivism (Chandra and Sharma 2013). This bit of epistemology depends on checking on the distinctions among human and social on-screen characters. This procedure of research speculation is along these lines built up on open development and is, so to speak, subject to human science.
3.2.1. Legitimization for picking Positivism Philosophy
The scientist has discovered that positivism speculation will fit for reviewing the upsides of timber and stone work. The decision of positivism thinking has empowered the analyst to reveal the required information related with the utilization of timber in structure. The decision of positivism approach besides helped the analyst is endeavoring the gotten information against the apparent research questions (Leedy and Ormrod 2013). The research has not utilized Realism or interpretivism approach since the research is obliged to research and research of gathered information and does not want to pass on any new course of action of information or thought. Thusly the decision of positivism investigate reasonability supposedly is proper for this exploration.
3.3 Research Approach
To sort out the research as per the strategy, it is essential for the scientist to pick a specific procedure for the research. Research approach gives the subtleties of plan and frameworks that include certain wide suppositions adjacent unequivocal information social occasion process an research (Mitchell and Jolley 2013). There are on a very basic level three research approaches that can be utilized for instructive research. These are deductive research approach, inductive research approach and abductive research approach. The deductive research approach manages the gutting of a huge amount of speculations that are either should have been acknowledged or rejected in the arrangement. Thusly the decision of deductive research approach animates the scientist in arranging the research in a legitimate manner (Novikov and Novikov 2013). The recommendations that depend upon deductive methodology are essentially settled on theory, speculation, acknowledgment and affirmation or removal of a specific thought. Decision rather than the deductive method, the inductive research approach excludes the importance of theories. Thusly in deductive reasoning of research, a theory has as of late been set while the use of inductive research approach is fitting for concentrate that don’t utilize any research speculation (Salaberry and Comajoan 2013). Inductive research is fittingly utilized in research considers that are, figuratively speaking, subject to investigate objectives and the perceived research questions. All things considered the techniques attracted with inductive research approach solidify, thought of various hypotheses and thought identified with an research region, planning tests for data collection, and perceiving affirmation of models in assembled information. Abductive research approach obviously enlightens certain deficient acknowledgments and dumbfounding substances related with a specific research. Therefore this kind of research approach spins around discovering answers for the strategies of certain deficient tests and staggering substances.
For this specific research an inductive research approach is picked. Since the research did not depend upon speculation, deductive research approach isn’t picked.
3.3.1. Defense for picking Inductive Approach
The analyst has discovered inductive method as real for this research since the research depends upon the dissecting the impact of versatile working in Malaysian division. The subject is major and not astonishing and thusly the addictive research approach isn’t picked for the research. Since the research did not depend upon any theory, the deductive research approach isn’t considered in this exploration. The research is generally settled on discovering answers to a lot of research questions and in like way the decision of inductive research approach is fitting for this research think about.
3.4 Research Design
Research configuration is a fundamental bit of research consider as it helps in prominent proof of set of methodologies and strategies that can be put to use for social occasion and estimation of the parts related with the perceived research issue. It can thusly be depicted as a precise procedure utilized by an analyst for planning a particular research consider. Thusly, the ID of research plan for an research consider ought to be suitable with the target that it can sincerely control the researcher for fitting information social occasion and research.
There are commonly three research structures that are utilized for quick scientists. These are valuable research plan, clear research structure and explorative research plan. The exploratory research configuration overviews the varying bits of an research think about dependent on the area of the exploration. This sort of research is predominantly determined for issues that have not been centered considerably more unquestionably in past and along these lines, it infers being made of necessities even more plainly. The informative research then again can be depicted as an endeavor to relate the insights for understanding the research issue that has been perceived. Verifiable research obviously can be portrayed as an research framework that bases on “what” of the research subject.
The researcher has settled on a sensible research plan for investigating the advantages of timber and stone work. The going with an area of this region gives the security against the decision of that exploration plan.
3.4.1. Defense for picking Descriptive research structure
The decision of realistic research configuration supposedly is fitting in this setting primaryly in light of the way that it goes about as an informative contraption for the scientist to investigate the apparent research issue. With the assistance of explaining research plan, the analyst had the capacity to get ready for the information amassing and precise research of the gathered information. In like way, the decision of this research configuration apparently is suitable.
3.5 Data Collection Method
For discovering answers to the apparent research questions, it is essential to figure an authentic information social occasion process. This research that is tried is a data based research and accordingly it is essential for the researcher to collect in any case much data as could reasonably be required to see and value the upsides of timber and stone work. The going with area of the research report gives a thought of the data gathering system that is followed in this research.
3.5.1. Gathering of Data gathering Methodology
The information get-together procedure related with any exploration falls under two standard classes, which are essential information amassing framework and discretionary information gathering philosophy (Brannen 2017). The information gathering system is sub mentioned in this two procedures subject to the technique for data getting.
Essential Data Collection: Primary data amassing suggests the technique for data gathering from those sources that have a firsthand information about the research that is being driven (Bernard 2017). There are various procedures that can be utilized for get-together and social occasion of essential information. These join, holding meeting, perceptions and utilizing review to perform reviews. This wellsprings of data is hinted as essential sources overwhelmingly in light of the manner in which that it will when all is said in done be sufficiently coordinated. Get-togethers for essential information get-together can be performed eye to eye or can be performed on telephonic way (Punch 2013). The most thoroughly utilized framework for essential information social occasion wires aggregation of information from studies and get-togethers.
Auxiliary Data Collection: The discretionary data social affair procedure is a strategy for data gathering from the sources that have been starting late passed on, for example, books, diaries and research papers. Along these lines from the optional sources a great deal of data can be collected (Brannen 2017). In any case, the data that are picked up from the discretionary sources are solid yet can’t be conveyed as stand-out. The optional information gathering process typically ends up valuable for a researcher by and large since it helps in get-together of immense extent of information that are significant and genuine.
Once in a while the scientists utilize both essential information and optional information as the information collection framework with a point of get-together of information from both essential and optional sources. This kind of research strategy is called blended research method.
Picked Data Collection Method
The information gathering strategy that is picked for this research is both essential and auxiliary information accumulation technique. The researcher has played out a social occasion to collect information that would react to the research questions. The whole research has been liable to the data that could be totaled from the social event. The reaction of the respondents helped in sorting out the research towards culmination. After sensible information gathering it is essential to pick definite information analyze process that will help in finding the responses for the perceived research questions.
3.6 Sample Size
Information has been gathered from both essential and auxiliary information accumulation strategy. The example estimate for the essential information accumulation technique have been 100 workers from four SME advanced innovation organizations. There has been online overview finished with these members and 10 close finished inquiries have been incorporated into the review poll. Study structure has been readied utilizing Google shapes and transferred on the web. The example measure for meeting procedure have been finished with three directors of SMEs. There have been three open finished inquiries posed amid the meeting. Their reactions have been gathered as information for the exploration.
3.7 Data Analysis Method
Information research in research is essentially of two sorts, abstract information ask about and quantitative information investigate (Silverman 2016). Abstract information explore is look into the information that can’t be evaluated. Abstract information research looks for after a degree of philosophy and systems and depends after social affair of s as indicated by the specific properties and characteristics (Marczyk, DeMatteo and Festinger 2017). In abstract information investigate is collected in basically nothing and unrepresentative models in an unstructured manner (Flick 2015). The abstract information analyze procedure is exploratory and the disclosures of emotional research are express to the subject that is being considered. For information gathering in emotional research, researchers everything considered make open finished solicitation. In this research, the researchers has driven social affair to amass information identified with impact of versatile working in Malaysian portion.
Thusly, emotional information research is a hypothetical research that is logically worried over the non quantifiable information. This sort of information research is in a general sense attempted in gets some information about that manage the course toward understanding the event of various marvel. In abstract information ask about, the model check is near nothing and non administrator.
Quantitative Data Analysis is basically worried over the research of quantitative information. It is a target research that surveys information. The information amassed for quantitative research merge unquestionable aggregates, for example, length, size, weight and mass. The exploration is for the most part worried over the methodology by which certain wonder happens (Walter and Andersen 2013). Thusly, in quantitative information investigate system the point of reference measure is ordinarily extensive and is a great part of the time summed up to cover the whole individuals. Quantitative information research routinely administers testing the perceived speculations that will give future gauge. Regardless, the quantitative research is limited by strategy of guidelines or numbers and along these lines this technique is wide gone and as regularly as conceivable multi faceted (Noble and Smith 2015). Besides, there are sure necessities related with the quantitative information ask about (Neuman 2013). For instance, the quantitative information investigate technique can’t be utilized for summing up the majority. The abstract research everything considered blueprints with close finished solicitation and the collected information experiences genuine research, for example, lose the faith, SPSS and others.
The right information examine system is singled out reason of the necessities of the research contemplate. This undertaking centers in finding impact of versatile working in Malaysian part. In that capacity the researcher has picked an exploration framework, which can be on a fundamental dimension utilized for discovering answers to the perceived research questions.
3.7.1. The Chosen Method: Quantitative
The researcher has picked quantitative technique for data gathering. Online survey has been done in the research with the help of individuals. Survey have been made using google shapes and exchanged over the web.
3.8 Ethical Consideration
Any philosophical research is associated with a lot of good concludes that are set up by instructive chambers. Preceding the exploration, each scholastic establishments request the adherence to certain essential rules which are as indicated by the going with
1. While driving the exploration examine, it is basic to regard the security and insurance of research people.
2. It is the dedication of the researcher and the research people to keep up the security of the data shared till the exploration is finished.
3. It is vital to get consent from the people before continuing with the information social occasion outlines.
4. The analysts ought to be able to guarantee and keep up namelessness in information get-together and information research process.
5. Keeping up the straightforwardness in information collection procedure is a central smart thought in instructive research. In this manner misquoting the data that is shared by the people ought to be totally denied.
Chapter 4: Data Findings and Analysis
4.1 Quantitative data analysis
Quantitative information research has been centered around the information gathered from essential information accumulation technique. The utilization of online study has been feast so as to gather information from members. In this way, online study has been finished with 100 workers of various computerized innovation SMEs in the market. There have been 10 close finished inquiries been posed to them. Following are the referenced review inquiries with appropriate information portrayals:
Question 1: Please specify your gender
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Male | 61 | 61 % | 100 |
| Female | 39 | 39 % | 100 |
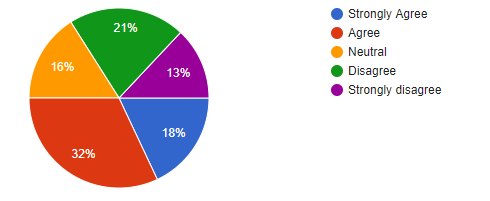
Figure 4.1.1: Please specify your gender
Analysis: As mentioned in graph and table, 61% of the participants are male and 39% of the participants are female. Therefore, this can be analyzed that the companies have been providing employment to male employees than female employees.
Question 2: What is your age?
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Below 20 years | 13 | 13 % | 100 |
| 21-30 years | 29 | 29 % | 100 |
| 31-40 years | 26 | 26 % | 100 |
| 41-50 years | 22 | 22 % | 100 |
| Above 51 years | 10 | 10 % | 100 |
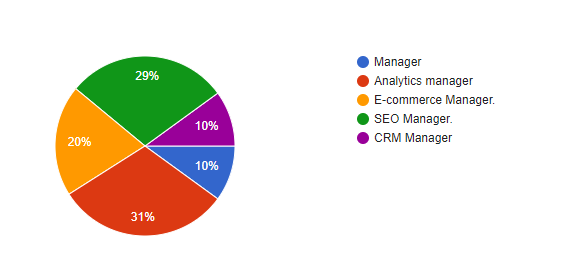
Figure 4.1.2: What is your age?
Analysis: As per table and chart, 29% of the participants have been ageing between 21-30 years. 26% of the participants have age between 31-40 years. Therefore, it can be analysed that most of the employees are of young ages between 21 years to 40 years. Therefore, companies have been hiring new employees in their workforce. Solid ties empower minimal effort access to the fine-grained informations and implicit learning while the frail binds give access to the novel informations. In spite of the fact that there are no such examines giving the proportion in the middle of the two however has been viewed as that depending more on solid ties serves in strengthening the current learning, that can adversely influence the imaginative capacities of the firm and furthermore incite division inside the nearby entertainers. According to the research done by (), it very well may be contended that depending more on associations with feeble ties could make it troublesome in recognizing and sifting through the significant informations. Based on the researchs directed on the collaborating spaces it very well may be said that the above bits of knowledge are significant on the grounds that they uncover that various systems should be considered during the time spent information creation that thus would rely upon the various sorts of the system connections that is available in the middle of the associates. According to the exploration done by (), it tends to be accepted that the colleagues in the littler conditions will get the chance to connect all the more frequently in this manner solid ties will be created inside the cooperating spaces. This will stay away from the as often as possible composed systems administration occasions so as to cultivate the tie developments. In spite of this, these activities could fill in as an effective technique bound in the enormous cooperating spaces where the associates will probably have less significant communications in the middle of them as a result of the size identified with the space and the populace. According to the exploration done by (), collaborators are principally profited by one another inferable from the cooperations, criticism, associations, trust, referrals and learning while some other exact researchs are of the feeling that colleagues hope to make developments in their system of the potential joint efforts and clients by the vehicle of social communications that are occurring in the premises of the collaborating spaces. Introductory researchs on the so-working spaces stressed on the way that simply giving spaces isn’t adequate to elements accordingly to develop among the collaborators. The solid ties or feeble ties or being worldwide or neighborhood, a cooperating space needs to concentrate on the correspondence in the middle of its clients or associates as the communication among the collaborators is viewed as essential during the time spent information creation. Treating the collaborating space as drop-in workplaces won’t profit the collaborators as it very well may be considered as a divider between co-task and connection.
Question 3: For how many years you are working in the company?
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| 0-2 years | 16 | 16 % | 100 |
| 3-5 years | 26 | 26 % | 100 |
| 6-8 years | 22 | 22 % | 100 |
| 9-11 years | 27 | 27 % | 100 |
| Above 12 years | 9 | 9 % | 100 |
Figure 4.1.3: For how many years you are working in the company?
Analysis: According to graphs and charts, 26% of the participants have been working for 3-5 years in the company. 22% of the participants have been working for 6-8 years. Therefore, companies have been including experienced employees in the workforce.
Question 4: What is your working position in your company?
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Manager | 10 | 10 % | 100 |
| Analytics Manager | 31 | 31 % | 100 |
| E-commerce manager | 20 | 20 % | 100 |
| SEO manager | 29 | 29 % | 100 |
| CRM manager | 10 | 10 % | 100 |
Figure 4.1.4: What is your working position in your company?
Analysis: According to the diagram and outline, 31% of the members have been filling in as research administrator. 29% of the members have been functioning as SEO chief. In the figuring stage Artificial Intelligence holds a vital spot as the fundamental objective of AI is to make advance machines whose work relies upon the human learning. The basic objective of this creation is to develop such machined who thinks similarly as goes about as shown by the general population. In order to pass on such improvement advancement it is fundamental for the machines to learn and think the human activities (Latah et al., 2016). At the point when all is said in done words to envision the machines which rely upon counterfeit understanding it is exceedingly basic to complete the ventures into the machines which rely upon the human showing and results.
Question 5: Are you agree in working at a co-working space?
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Strongly Agree | 18 | 18 % | 100 |
| Agree | 32 | 32 % | 100 |
| Neutral | 16 | 16 % | 100 |
| Disagree | 21 | 21 % | 100 |
| Strongly Disagree | 13 | 13 % | 100 |
Figure 4.1.5: Are you agree in working at a co-working space
Analysis: According to the research done by (), however feeble ties have a help of different focal points, there is a need to concentrate on the accessible constrained exact proof that is a help for the impact of these connections dependent on the formation of nearby information inside the enterprises. There is a requirement for reexamining of the hypothesis of the bunches according to its present ramifications of abnormal state of the communications that are nearby while observational proof propose that scarcely any actualities are there all together that the above supposition that is ” the more confined collaboration, the better” be considered. It has been discovered that the grouped firms generally favor solid social ties to make learning. The solid social ties have a trademark highlight of high feeling of correspondence, shared trust and genuinely closer connections that are pivotal so as to increase minimal effort access to the basic assets, particularly for those organizations that are in their underlying period of improvement. The organizations in their initial improvement stage are implanted with abnormal state of vulnerability that they need to stand up to bringing about specific exercises, for example, critical thinking and the trading of fine-grained inferred learning and important information’s. Despite the fact that it has been accepted that there exists an intrinsic nearby segment identified with the formation of solid ties, ongoing research have uncovered that these kinds of connections are presently progressively being created by the vehicle of virtual correspondence in the middle of spatially separated researchers. Therefore, the researchers contend that by just having similar qualities and having a mutual practice can be adequate for making solid ties in the middle of the removed entertainers. So as to increase ideal access to the accessible basic assets the system connections in cooperating firms should be created in understanding to both solid just as feeble ties.
Question 6: The positive impacts of co-working on physiological behaviour of employees
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Strongly Agree | 18 | 18 % | 100 |
| Agree | 32 | 32 % | 100 |
| Neutral | 16 | 16 % | 100 |
| Disagree | 21 | 21 % | 100 |
| Strongly Disagree | 13 | 13 % | 100 |
Figure 4.1.7: The positive impacts of co-working on physiological behaviour of employees
Analysis: The general population having a place with these various networks are keen on bringing individuals sharing same interests together. These people group help discover customers and acquire conceivable development pay and ability. Encompassed by dedicated experts in collaborating spaces, people will be enlivened to be focussed and buckle down. The collaborating spaces are a domain out of the solace of home where work should be possible in a spotless and expert condition. Cooperating spaces likewise positively affect wellbeing and way of life as individuals telecommuting for the most part experience the ill effects of sleep deprivation as they can’t separate from the work and the home condition however receiving the collaborating idea this perspective can be changed. It is compelling in cost cutting for the business visionaries as it can spare the cost done on the service bills. The collaborating spaces don’t load its clients with researcher co-ops and fixes and accordingly leasing a cooperating space is less expensive when contrasted with conventional workplaces.
The groups involves powerless social binds that are viewed as the fundamental in addition to point. The system hypothesis demonstrates that if there should be an occurrence of associations with the feeble ties for instance colleagues require less interests through setting up cozy connections dependent on trust and can fill in as essential wellspring of data that is novel and employment opportunities. Frail ties are being created by the mechanism of day by day cooperations in the middle of the grouped firms or if there should be an occurrence of parties for instance occasions that help in making the connections innately neighborhood. The powerless social ties require less ventures and support, it has been a theme of ion that this licenses for additional to get set up, the medium being organizing exercises that can be viewed as positive during the time spent sourcing the reciprocal hotspots for making information since it furnishes the grouped firms with numerous choices that can be browsed. With regards to each powerless bind identifying with some other groups of friends, along these lines giving the bunched firms adaptable, more extensive and differing systems. Feeble ties can help bunched firms to access pools of learning that exist past the effectively open neighborhood safe places that thusly is significant for the intensity of the firm. It very well may be contended that the associations with the frail ties could support and furthermore reinforce the nearby communication permitting extension for data and more learning that is living from somewhere else required to siphon into the inner systems bringing about the dynamic buzz that can be gainful for the grouped firms.
Question 8: Coworkers will bring about increased effectiveness in the organization
| Options | Responses | Responses% | Total respondents |
| Strongly Agree | 19 | 19 % | 100 |
| Agree | 38 | 38 % | 100 |
| Neutral | 16 | 16 % | 100 |
| Disagree | 20 | 20 % | 100 |
| Strongly Disagree | 7 | 7 % | 100 |
Figure 4.2.8: Co-workers will bring about increased effectiveness in the organization
Analysis: Vis-à-vis associations are significant in the part of the formation of the information inside the groups of the innovative business. The collaborating space is committed to the forlorn business people the individuals who are looking for mingling openings. “As indicated by a 2007 CDW review of more than, 2000 laborers demonstrated that 79% of researchers utilized in the private division and half of researchers utilized in the open part were stressed over inclination disconnected and missing human communication if they somehow managed to begin a working from home”. According to the research done by (), cooperating does not manage only the course of action of room but instead incorporates the development of way of life. With the new ages ruling the workforce, new thoughts and viable methodologies have been created identified with life and work. With the headway of innovation liberating individuals from the built up work areas, includes a more noteworthy sense identified with independence in the midst of the workforce present today. the cooperating spaces make more prominent independence and give Thoughts and obligations identified with proprietorship. Still there is a feeling of having a place that is profoundly covetous along these lines helping the development of the cooperating spaces that are an augmentation to the mutual conservative mindset. Being founded on participation, the cooperating spaces are equipped for gathering both way of life needs that identify with the developing workforce in particular the network, adaptability and singularity. The earth of the collaborating spaces gives the correct surroundings so as to concentrate on the current and the future objectives in the meantime winding up progressively profitable. Cooperating spaces depend on networks and subsequently is an ideal stage to make proficient contacts that thusly can help extend the business.
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Recommendations
The foundation of the structures impact the trading of learning by giving fundamental designs that thus offer collaboration in the middle of the laborers. It has been bantered for the capability of open-plan workplaces to cultivate coordinated effort and cooperation between the researchers. In contrast with the conventional office spaces, the open-plan workplaces have a trademark highlight of no divider premises that don’t separate the researchers from one another in this manner bringing about setting up designs where the people can cooperate under one major rooftop. This normal for setting the people near one another and expelling the physical obstructions regarding correspondence and association between the laborers as it encourages the collaborators to share informations identified with their undertaking, make open doors for fellowship and advance input. The researchs in regards to social effect of the open-plan workplaces show that these structures keep the possibility to encourage the casual collaborations among the researchers. While these structures were at first surveyed to be a wellspring of diversion and wastefulness from the genuine work, that animates casual connections in the middle of the laborers that have turned into a significant piece of the administration work so as to expand participation inside the groups, and in the meantime to impact the rate of the advancements being made in the associations. Perceiving the advantages of the casual informations, it has been a subject of enthusiasm among the researchers just as the experts so as to comprehend the way toward cultivating the equivalent. The casual collaborations can’t be managed or be arranged yet the likelihood of their occurrence can be influenced by the vehicle of aberrant methods for instance through the physical engineering. The new research structures are too much being created in manners by the designers so that these fundamentally animate the casual cooperations by the mechanism of open regions and the gathering spaces. it has been guaranteed that these structures should concentrate on giving the fundamental there things so as to encourage the collaboration among the laborers to be specific gathering territories, nearness and visual availability. The thought identified with visual or aural openness is tied in with holding the guidelines, for example, the structures should cease from physical boundaries so as to make it simple for the laborers to impart in that condition. Then again, closeness can be obtained by putting the laborers intently in the open-plan workplaces. concerning the relationship in the middle of the casual communications and the gathering regions, three primary viewpoints have been referenced to be specific the geology, physical engineering and capacity. Physical engineering implies how encased or open a space is. Two of the primary strands that are there as to the relationship in the middle of the casual connection and physical engineering with respect to a space are hypothesis of propinquity and protection. Hypotheses of security recommend that the encased spaces support and empower casual associations as they give the researchers the required solace so as to control their conversational limits while the speculations of propinquity propose that the halfway found open spaces bolster casual collaborations inferable from the way that they bring the collaborators closer to one another. The thoughts identified with geology and capacities are connected as both of these allude to the components of centrality. Thinking about the two ideas, physical centrality is an issue identified with topography and useful centrality is a piece of capacity of room. meeting places which are concentrated and are effectively available produce parcel of traffic that is capable to build the opportunity of making unconstrained experiences with each other.
Utilitarian centrality which concerns the capacity of the space identifies with those reasons that individuals have for visiting certain spots and the area of territory as for the other practically preeminent areas in the premises of the workplace that the laborers as often as possible visit for the duration of the day. during the time spent deciphering the way that how a few settings can manage the cost of the casual collaborations, the indicate that requirements be underscored on is to incorporate the social component in the hypothetical thinking. As expressed by a portion of the researchs a portion of the spaces that had certain perfect plans couldn’t rehearse casual communication until the social standards were built up that thusly enabled the researchers to do as such. The researchers contend for this situation that the laborers get the attitude that they are permitted to mingle and that they are permitted to collaborate with one another in explicit settings, or else no such genuine connections can be wanted. This social part of setting is called social assignment by the researchers. settings need right propinquity, social assignment and protection so as to manage the cost of the casual connection. Based on these experiences, the presumption that can be made is that the collaborating spaces that are halted from the physical boundaries to correspondence, for example, the stairs and the dividers, those that incorporate the open-plan workplaces and accessible gathering places, give an opportunity to the elements of the learning that happens in the middle of the individuals coming about because of casual communications that is encouraged by these conditions.
References
Alonzo, J., Kochemba, W. M., Pickel, D. L., Ramanathan, M., Sun, Z., Li, D., … & Kilbey II, S. M. (2013). Assembly and organization of poly (3-hexylthiophene) brushes and their potential use as novel anode buffer layers for organic photovoltaics. Nanoscale, 5(19), 9357-9364.
Annamareddy, A., & Eapen, J. (2017). Disordering and dynamic self-organization in stoichiometric UO2 at high temperatures. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 483, 132-141.
Bockhorn, H. (Ed.). (2013). Soot formation in combustion: mechanisms and models (Vol. 59). Springer Science & Business Media.
Capdevila, I. (2015). Co-working spaces and the localised dynamics of innovation in Barcelona. International Journal of Innovation Management, 19(03), 1540004.
Chandler, D. J., Gao, W. J., & Waterhouse, B. D. (2014). Heterogeneous organization of the locus coeruleus projections to prefrontal and motor cortices. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(18), 6816-6821.
Cornwell, J. (2012). Worker co‐operatives and spaces of possibility: an investigation of subject space at collective copies. Antipode, 44(3), 725-744.
Cummings, T. G., & Worley, C. G. (2014). Organization development and change. Cengage learning.
Dashti, Y., Grkovic, T., & Quinn, R. J. (2014). Predicting natural product value, an exploration of anti-TB drug space. Natural product reports, 31(8), 990-998.
Demetry, D. (2013). Regimes of meaning: The intersection of space and time in kitchen cultures. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography, 42(5), 576-607.
Dewyer, A. L., Argüelles, A. J., & Zimmerman, P. M. (2018). Methods for exploring reaction space in molecular systems. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Molecular Science, 8(2), e1354.
Eigen, M., & Schuster, P. (2012). The hypercycle: a principle of natural self-organization. Springer Science & Business Media.
Gandini, A. (2015). The rise of coworking spaces: A literature review. ephemera, 15(1), 193.
Hristopulos, D. T., & Mouslopoulou, V. (2013). Strength statistics and the distribution of earthquake interevent times. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 392(3), 485-496.
Komporozos-Athanasiou, A., & Fotaki, M. (2015). A theory of imagination for organization studies using the work of Cornelius Castoriadis. Organization Studies, 36(3), 321-342.
Liegl, M. (2014). Nomadicity and the care of place—on the aesthetic and affective organization of space in freelance creative work. Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW), 23(2), 163-183.
Matson, S. M., Rätzke, K., Shaikh, M. Q., Litvinova, E. G., Shishatskiy, S. M., Peinemann, K. V., & Khotimskiy, V. S. (2012). Macrochain configuration, stucture of free volume and transport properties of poly (1-trimethylsilyl-1-propyne) and poly (1-trimethylgermyl-1-propyne). Polymer Science Series A, 54(8), 671-677.
McIntosh, J. A., Farwell, C. C., & Arnold, F. H. (2014). Expanding P450 catalytic reaction space through evolution and engineering. Current opinion in chemical biology, 19, 126-134.
McQuoid, J., & Dijst, M. (2012). Bringing emotions to time geography: The case of mobilities of poverty. Journal of Transport Geography, 23, 26-34.
Merkel, J. (2015). Coworking in the city. ephemera, 15(2), 121-139.
Methot, J. R., Melwani, S., & Rothman, N. B. (2017). The space between us: A social-functional emotions view of ambivalent and indifferent workplace relationships. Journal of Management, 43(6), 1789-1819.
Owens, B. P., Baker, W. E., Sumpter, D. M., & Cameron, K. S. (2016). Relational energy at work: Implications for job engagement and job performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 101(1), 35.
Parrino, L. (2015). Coworking: assessing the role of proximity in knowledge exchange. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 13(3), 261-271.
Roine, U., Roine, T., Salmi, J., Nieminen‐Von Wendt, T., Leppämäki, S., Rintahaka, P., … & Sams, M. (2013). Increased Coherence of White Matter Fiber Tract Organization in Adults with A sperger Syndrome: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Autism Research, 6(6), 642-650.
Ross, P., & Ressia, S. (2015). Neither office nor home: Coworking as an emerging workplace choice. Employment Relations Record, 15(1), 42.
Schuermann, M. (2014). Coworking Space: A Potent Business Model for Plug ‘n Play and Indie Workers. epubli.
Schulze, B. M., Shewmon, N. T., Zhang, J., Watkins, D. L., Mudrick, J. P., Cao, W., … & Castellano, R. K. (2014). Consequences of hydrogen bonding on molecular organization and charge transport in molecular organic photovoltaic materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2(5), 1541-1549.
Segura, J. L., Juárez, R., Ramos, M., & Seoane, C. (2015). Hexaazatriphenylene (HAT) derivatives: from synthesis to molecular design, self-organization and device applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 44(19), 6850-6885.
Sengupta, D., & Kundu, S. (2012). Role of long-and short-range hydrophobic, hydrophilic and charged residues contact network in protein’s structural organization. BMC bioinformatics, 13(1), 142.
Sias, P. M., Pedersen, H., Gallagher, E. B., & Kopaneva, I. (2012). Workplace friendship in the electronically connected organization. Human Communication Research, 38(3), 253-279.
Snyder, D. L., & Miller, M. I. (2012). Random point processes in time and space. Springer Science & Business Media.
Sollitto, M. (2014). Why and How Organizational Members Encourage Their Peer Coworkers to Voluntarily Exit the Organization: An Investigation of Peer-Influence Exit Tactics. West Virginia University.
Tsao, S. C., & Lo, C. T. (2014). Photoresponsive behavior and self-organization of azobenzene-containing block copolymers. RSC Advances, 4(45), 23585-23594.
Tyner, J. A. (2012). Space, place, and violence: Violence and the embodied geographies of race, sex and gender. Routledge.
Veeraraghavan, R., & Gourdie, R. G. (2016). Stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy–based relative localization analysis (STORM-RLA) for quantitative nanoscale assessment of spatial protein organization. Molecular biology of the cell, 27(22), 3583-3590.
Wilhoit, E. D. (2018). Space, place, and the communicative constitution of organizations: A constitutive model of organizational space. Communication theory, 28(3), 311-331.
Xie, Y., Popa, B. I., Zigoneanu, L., & Cummer, S. A. (2013). Measurement of a broadband negative index with space-coiling acoustic metamaterials. Physical review letters, 110(17), 175501.