Introduction
The purpose of this report will be to review and summarise 2 decision models in practice to the field of sports. The decision-making models, the value added trio the businesses that are performed by the management of the organizations associated with the world of sports along with the management of different clubs and associates that are attached with the world of sports. Relevant assumptions through the models selected along with advantages and disadvantages of application of these models to the business scenario in this global business industry will also be discussed in this paper. It can be noted in this context that decision models plays an integral part in the sports industry, as it helps them to achieve the top spot along with earning profits, which helps them to perform better in future.
Decision Models
Advancement in the area of technology has increased both the competition level between the authorities associated with the world of sports along with increasing the level of satisfaction of the customers. The people who are associated with different bodies of sports need to take decisions according to the circumstances and situations. In this context, it can be stated that a decision model is like a prescription which states the process or procedure of arriving to any kind of fact-based conclusions of a particular business with following the business logic. It plays an integral part in the overall business operations of an organization related to sports. And to reach out to a decision, different decision models are used by the people who are associated with these institutes related to sports. One such model is Administrative model (Zikos 2013). This model can be regarded as a more realistic model which helps to describe the overall decision making process of a business house related to sports. For example, a football club in Australia will make decision regarding building the team for a new season, where they have to recruit managers and players in order to compete in the Australian League. Technology has also increased the competition level between the clubs along with increasing the level of satisfaction of the supporters. According to this model, decision makers possess various motivational level along with incentives and demands. They focus more on the satisfaction of the people rather than following the optimization of the overall businesses performed by them.
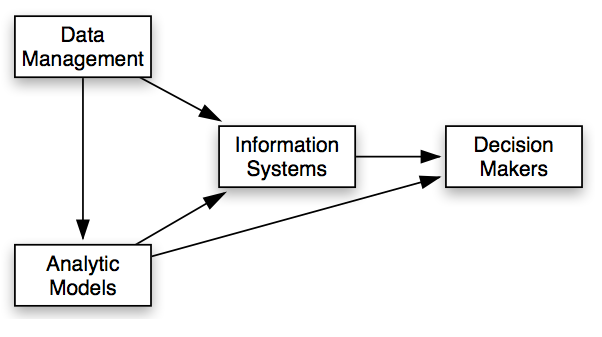
Fig 1: Decision Model System
Source: (Anderson-Cook 2018)
From the above diagram it can be seen that data management, analytical models and information systems are inter-related with each other and all the three help to take the dcecision making in the sports industry. It can be seen that the Standard Operating Procedures regarding the rules and regulations that are followed by the decision makers in order to save time while solving a problem or overcoming a challenge (Sałabun 2014). This model also helps to take decisions on uncertain conditions, which is very much relevant in the field of sports, though there are limited scope of gathering alternative decisions along with the desired outcomes from those decisions. But this decision model often results in conflicts between the people and consensus is lacked among the decision makers of different parent bodies attached with the world of sports. Alternative ways to reach to a decision are also limited in this Administrative model, which often hampers the quality of sports delivered by various clubs. As the level of competition has also increased the competition between the clubs and teams, limited options for coming to a decision often hampers the overall performance of these clubs and teams are deteriorated and the people associated in the decision making process of these clubs involves in conflicts which shows the limitations of the management bodies of these entities from the world of sports (Shah and Agrawal 2013).
On the other hand, Classical model help to provide information and use them while making decisions for the respective business entities related to sports. The Classical Decision Model is a decision-making approach which helps the managers in making the proper decisions. It is assumed by the approach that the managers think and work in a rational and logical manner. It is also assumed that the decisions of a manager will be taken by maintaining the best interests of an organization. Just like any other business ventures, the sports industry is not an exception from unethical actions and unwanted behavior (Gieseler 2017). There are numerous cases where unethical behavior has been noticed that includes a wide range of subjects such as the use performance enhancing drugs, cheating, monetary ramifications, blood doping, violence, legal issues, amateurism and many more. The decision-making process is used to maximize the moral consciousness across the employees who had received very less scholarly attention. Several popular sport managers depend entirely on the classical decision model by which they can take decisions in a practical way. Many of the issues mentioned above can be resolved by applying the decision-making process in sports management. In case of the decisions made by the coaches for any kind of sports, they are examined immediately by the media as well as the fans. They are often analyzed based on the results and not the real reason behind the decisions. Therefore, the art of decision-making plays a vital role while providing tactical, physical, psychological and technical guidance to an athlete with proper leadership and style (Rudychev, Nikitina and Gavrilovskaya 2013).
One of the best advantage that is enjoyed by the management and authorities who are associated with different sports entities is utilization of resources efficiently and effectively. As it has been already discussed that the competition between different sports organization related to different types of sports that are played across the world and it is necessary to use the resources in a planned way so that the maximum benefit can be gained through utilization of the available resources in the form of players, coaching staff, financial and infrastructural support. A healthy relationship can be maintained between the players, coaching staff, medical unit and other people associated with the sports with the decision makers, that is, the management of that sports entity who takes final decision regarding achieving the overall performance of that company. It can be stated in this context that efficient decisions can be taken through this decision model and better performances can be achieved by different teams and players in various sports that are played across the globe by following the classical decision model (Wachter, Mittelstadt and Floridi 2017).

Fig 2: Decision Making in Football
Source: (Chikish, Carrears and García 2019)
From the above diagram, it can be seen that cultural production, sporting performance, satisfaction of the stakeholders and monetization are inter-related with each other which helps to taken the best decision possible by following this classical decision model. But, the relevancy of this decision model restricts the team building efforts as it is more focused on the individual performances rather than focusing on the team effort. There is also less scope of following innovativeness by following this particular decision model in the world of sports, and it can be noted that creativity is important in sports industry to outshine others related to sports industry across the world.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it can be stated that the decision-making models, the value added trio the businesses that are performed by the respective management of the organizations associated with the world of sports are clearly described in this paper along with the management of different clubs and associates that are attached with the world of sports. Relevant assumptions through the models selected along with advantages and disadvantages of application of these models to the business scenario in this global business industry has also been discussed here, which helps the sports industry to adopt with the changes or alterations that are occurring according to the fluctuations in the level of competition along with in the satisfaction level of the supporters.
References
Anderson-Cook, C.M., 2018. The athlete at the center of sports statistics: Discussion for “The game insight group: A model for academic-industry partnerships for sports statistics innovation”. Quality Engineering, 31(LA-UR-18-22392).
Chikish, Y., Carrears, M. and García, J., 2019. eSports: A new era for the sports industry and a new impulse for the research in sports (and) economics. Spanish Economic Papers.
Gieseler, F., 2017. Decisions in the shadow of finitude of life:” Guided Decision-making”-A classical concept adapted to modern times. Divers Equal Health Care, 14, pp.63-68.
Rudychev, A.A., Nikitina, E.A. and Gavrilovskaya, S.P., 2013. Mathematical model of adoption of the administrative decision as means of increase of competitiveness of the industrial enterprise. World Applied Sciences Journal, 25(1), pp.113-118.
Sałabun, W., 2014. Application of the fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method to identify nonlinear decision models. Int. J. Comput. Appl, 89(15), pp.1-6.
Shah, M. and Agrawal, R., 2013. A review on classical and modern techniques with decision making tools for load forecasting. International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Development, (3), pp.174-184.
Wachter, S., Mittelstadt, B. and Floridi, L., 2017. Why a right to explanation of automated decision-making does not exist in the general data protection regulation. International Data Privacy Law, 7(2), pp.76-99.
Zikos, D., 2013. Data issues for clinical-administrative decision making in healthcare. Lecture Note.