Question 1
Main activities to be undertaken during the design stage of the project
Converting the three storey town house into 5 self-contained apartments, will involve many activities during the planning and redesign stage. The activities include;
- Establishing a design team
This will be the first thing to do. The client in consultation with the architect, will establish a design team. The core design will include an architect, a service engineer, a structural engineer, quantity surveyor and other specialist such as an acoustic consultant. Even though the core design team will be developed before the actual design work, the design team will continue growing as the design progresses leading to an increase in the level of details, which will bring in other professionals.
Developing a project brief
The client will explain to the design team his/her requirements, what he/she wants to be done and how. Through consultation of the client and the design team, the design team will develop a brief detailing all the project requirements and deliverables.
Carrying out a feasibility study
The feasibility study will involve carrying out a research about the legal and physical conditions of the existing building to be converted into 5 self-contained apartment. Carrying out a feasibility study will enable the design team to identify possible constraints, opportunities and risks. Through that the design team will understand the characteristic and nature of the building better. The feasibility investigation will basically involve;
- Surveying and assessing the structural components of the building
- Assessing and analyzing site topography
- Conducting ground investigations to establish the bearing capacity of the soil, availability of mineral deposits, and presence of flora & fauna. The main aim of carrying out ground investigations is to establish if there will be need to modify the foundation.
- Reviewing and analyzing the neighborhood.
Once all the information above has been collected the design time will be having an idea of how the design will look like.
Developing a design concept
Coming up with a design concept together with a design philosophy will be the first true stages of design. Coming up with a design concept is creatively responding to the project brief. During this stage all members of the design team will be expected to come up with estimated cost of the project, the safety measures to be observed, the buildability of the project and the project Programme.
Detailed design
This will involve on developing the approved concept by the client. During this stage the design team members describes all components of the building and how they will fit together. The detailed design will give enough information for applications for the statutory approvals. The design team will be deliver the following drawings and specification, when done with detailed design.
- The overall layout of the proposed 5 self-contained apartments
- The road layouts within the building site and in the neighborhood
- Schedules of accommodation
- The architectural drawings i.e. the plans, sections and elevations
- Building dimensions
- An outline of specifications
- Building service plans, elevations and sections.
- Room data sheets
- Structural drawings i.e. the plans, sections, elevations and specification
- Acoustic condition and acoustic separation
- A risk assessment plan having operational issues such cleaning of facades and roof atrium.
Tasks which would involve the services of an Acoustic Consultant
Acoustic Consultant will play an important role during the design stage. The Acoustic Consultant will take part in designing, assessing and give guidelines about the management and control of sounds and vibrations in the proposed building. Some of the activities that will require the service of an Acoustic Consultant include;
- Assessing noise levels in the building and the neighboring buildings, when a feasibility study is being carried out.
- Specifying the specific construction that might be required for the development of acoustic environments. Monitoring vibrations in the existing building and assessing the impact they.
- Assessing noise pollution levels and giving noise mitigation advice.
Existing construction/s and their performance,
The existing three storey town house was mainly designed for a single family dwellings. The existing three storey building is expected to have all basic amenities of a residential building and meet the required standards such as sufficient natural lighting of the building, sufficient natural ventilation, adherence to the building code standards such as adhering to the minimal dimensions of some building elements such the dimensions of the stairs.
The existing constructions performs well meeting all the functional requirements, health and requirements. Since the clients wants to convert current three storey town house to 5 self-contained apartments. The existing house was designed as a three storey town house to be occupied by a single family. The change of use of the building into 5 self-contained apartments, will mean that the building will now be occupied by more people i.e. five families, due to that the current amenities in the building will not be able to serve them hence, there will be need to increase the size of building elements such as stairs, balconies, water supplies among others.
Information exchange between the Architectural Technologist and the Acoustic Consultant
The architectural technologists will plan, design and even oversee the entire construction process of the project. On the other hand an Acoustic Consultant will be design the ambiance of the proposed apartments, by specifying the materials to be used and other specifications. Since both of them i.e. the architect and the acoustic consultant do design works, they will require to exchange information, so that each of them will effectively perform their duties. There are different ways through which they will exchange information such as;
The Acoustic Consultant will require the architectural drawings i.e. the building plans, sections and elevations to obtain information about the room or space he/she intends to develop its acoustic characteristics. The acoustic consultant will obtain a lot of information from the architectural drawings done by the architectural technologists such the room dimensions, the rom height, the material finishes and the location of services i.e. water and electricity.
Question 2
Noise is defined as “unwanted sound”, “a sound harmful to the human body, both physically and mentally” or just “undesired sound”. In the built environment, noise is considered as unwanted harmful sound in indoor and outdoor spaces, usually generated by human activities such as transport activities and industrial production. The design and structure of any building should help in keeping the noise to acceptable levels for the building to be comfortable. In residential buildings where the design and layout of the building helps keeping noise to acceptable levels, routine activities are carried out without or with minimal undue interference from external or internal noise.
To come up with an effective design for noise control in residential development, it is very crucial to understand the potential sources of noise with the building site, the type of noise and how noise moves throughout the site. Hence, there is need when carrying out a site assessment and analysis of a residential development to establish the potential sources of noise within the site, to help the architect and the acoustic consultant come up with better building design and layout to enhance the acoustic environment within the building.
Potential noise sources
The potential sources of noise in a building site can be categorized into two categories i.e. Industrial sources and non-industrial sources. The potential industrial sources of noise include the noise from big machines and industries which produces very high levels of noise intensity. While, the potential non-industrial sources of noise include the noise produced by vehicular/transport and all other noise sources from the neighborhood. Non-industrial sources of noise can further be divided into two categories i.e. Natural sources and manmade.
Potential manmade sources of noise include;
- Road traffic noise
Road traffic in the neighborhood can be a potential source of noise in the residential development. The motors and exhaust systems of autos, small trucks, motorcycles and buses passing near the building site produces a lot of noise.
- Aircraft noise
Low flying aircrafts can also be a potential sources of noise in building sites located near airports, military bases or in areas with frequent frying of large passenger, cargo or military aircrafts.
- Construction activities
Construction activities are also potential sources of noise in building sites located in areas where there is heavy construction activities in progress. Machines and equipment used in construction of roads, building, bridges and other structures normally produces a lot of noise.
- Noise from rail road.
Rail road is also another potential source of noise, in sites located near railways. The noise produced by locomotive engines, whistles and horns and switching and shutting operations in the rail yard can have a serious impact on the neighboring communities.
- Noise from neighboring buildings
Building neighboring the building site can also be a potential source of noise. The noise caused by routine human activities can also be a source of noise. Playing loud music, noise produced by household appliances such as a vacuum cleaner, children playing in the neighboring buildings are some of the potential sources of noise from the neighboring buildings.
The potential industrial sources of noise include;
- Manufacturing and processing plants
Manufacturing and processing plants can be potential sources of noise, when the building site of a residential development is located near noisy manufacturing plants such as motors, fans, compressor and other industrial components mounted on the building outside.
- Mining activities
There is normally high levels of noise produced in mining sites. The machines and equipment used in mining produces a lot of noise and vibration of the ground. During the assessment of the construction site, it is very important to analysis the mining sites near the site.
Potential noise mitigation methods
The best results in coming up with a design for noise control will be achieved , when noise mitigation techniques are implemented at early stage of planning and design and then followed right through the construction and post occupancy. Some of the potential mitigation methods that can be investigated before considering the make-up of the building envelope include;
- Increasing distance between the residential building (receiver) and the source of noise.
The level of noise can be greatly reduced by increasing the distance between the residential building to be developed and the source of noise. For instance the level of noise can reduced when the distance is increased between a residential building and a highway with heavy traffic.
- Proper orientation of the building
Before coming up with the layout or design of the building, it will be very important to investigate the orientation of the building in relation to the source of noise. The orientation of the building has a direct influence on the impact of noise. The investigation should be based on the location of spaces in relation to the source of noise. Additionally it will be important to investigate the location of openings such as windows. The residential building can also be oriented on a site in a manner which exploits the site’s natural features. In reference to the source of noise natural features can be exploited and the residential building to be placed in a low noise pocket.
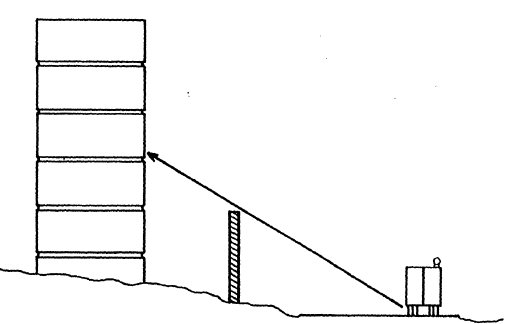
- Noise Compatible land uses as buffers
Before coming up with the layout and design of the residential building, it will be important to investigate the possibility of locating compatible land use between the source of noise and the residential building. The land use should be closest to the source of noise to be more effective. The figure below shows the use location of a compatible land use between a highway and a residential building.
- Application of noise barriers
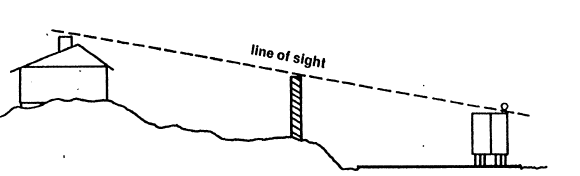
It will be important to investigate how different barriers can be utilized before coming up with the make-up of the building envelope. Barriers are obstacles that can be placed between the source of noise and the residential building, to block the path of noise. Different obstacles can be used such as;
- Fences and walls constructed using different materials such as wood, concrete, plastic, stucco or meatal.
- Slopping huge mounds of earth, called berms.
- Planting dense planting of trees or shrubs.
- The figure below illustrates how the use of obstacles can be used to control noise in a residential building site.
Question 3
Common design errors to look out for in block work separating partitions within Schools, Hospitals or residential developments.
Today’s commercial and residential property owners are mainly concerned with the safety and comfort of the interior environment of their buildings. Noise is among the factors which influences the safety and comfort of the interior spaces. The level of acoustics in a buildings depends on many factors the effect of poor workmanship and bad practices. This normally occurs due to mistakes of interpretation of construction details to be followed during the construction process. The installation of partitions in residential buildings, schools and hospitals also plays a very big role in the achievement of the intended acoustic levels. Even though it is a challenge for the builders to construct the construction details to reflect what is drawn on the detailed construction details, there are a lot of mistakes committed during the installation of partitions blocks both in schools, hospitals and even schools. This usually occurs because the construction drawings issued to the contractors or builders don’t contain sufficient construction drawings or does not have details on how the partitions are to be constructed. Also the revisions made to the constructions drawings when constructions is in progress and they are not cross-checked with other details issued such as for acoustic, fire regulations among others.
The use of partitioning blocks in hospitals, schools and residential buildings plays a vital role in realizing acoustical insulation. Nevertheless, the achievement of acoustic benefits associated with the partitioning blocks depends on installation and construction of details during the installation of the blocks. There are many errors committed during the design and installation of partitioning blocks in schools, hospitals and residential buildings, which directly contributes to poor acoustic in those spaces. Among the errors to be checked in partition blocks include;
- Absence of structural beams or riddles on the floor slabs above the partition.
- Failure of interruption in the inner of the external wall in correspondence with the junction with the partition.
- Failure to interrupt the attic rooms or roof in correspondence with the junction
- Absence of mortal in vertical joints , which leads to development of partially filled joints between the blockwork for the walls which require mortal in the vertical junctions.
- Damages made to the partitioning blocks to create paths for service such as electricity and fibre optics cables.
- Poor workmanship during fill of mortal
Issues which occurs due to mistakes or errors design errors in partitions
- Poor insulation of junctions between the partition blocks and the ceiling structural or the floor. Poor joining of the partition block and the ceiling or floor results to development of sound flanking paths. The figure below show how poor construction of joints brings about flanking.
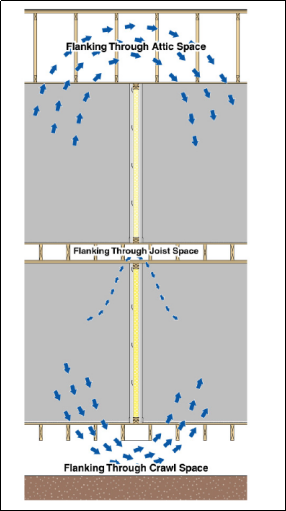
Fig: sound flanking paths
- Leakage of sound
Design errors committed during the design and installation of partition blocks leads to leakage of sound between different partitions in hospitals and schools. The sound leakage occurs due poor design and construction of partition blocks leading to development of sound leakage paths as shown in the figure below.
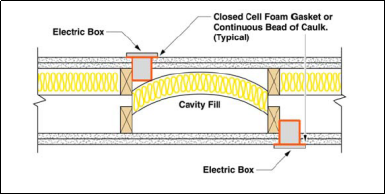
Fig: sound leakage paths
- Improper fastening of the partition blocks leading to structural short circuits, hence leading to transmission of sounds from one room to another. The figure below shows how poor fastening of the partition blocks leads to sound transmission from one room to another in hospitals, schools and residential buildings.
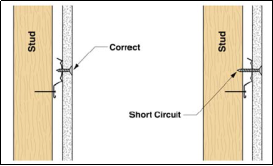
Fig: Fastener short circuits
Examples of good detailing practice
Good detailing of construction drawings for partitions, will prevent the issues identified above. This will increase the acoustical performance of different partition blocks such as; steel and wood studs, roof-ceiling systems and floor-ceiling assemblies used in hospitals, schools and residential buildings.
Combining dense sound barrier materials such as gypsum boards, wood framing, acoustical caulk and sheet metals can play a very crucial role in solving some of the issues identified above. The figures below shows some of good detailing practices that can be adopted.
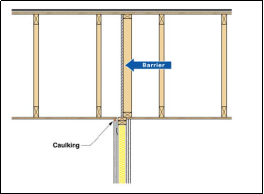
Fig: Gypsum board blocking
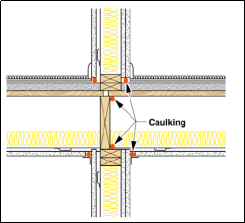
Fig: Between floor caulking
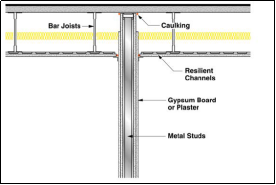
Fig: Partition wall height extension
The good detailing practices above ensured that the partitions are airtight, this is because sound in most cases takes the path where there is minimal resistance, no matter how small an opening or due to poor design or construction of partition. The good detailing of the partitions ensures that all perimeter joints are completely sealed with the use of acoustical caulk or gaskets. The framing members, electrical and plumbing conduits and the fastening systems be isolated from vibrations as much as possible in order to minimize structural borne sound energy transfer.
Workmanship issues which affects the performance of partition blocks
Good workmanship of the partitions in hospitals, schools and residential buildings enhances the acoustical performance of any space. With improved acoustical performance, partitions will greatly improve the quality of learning facilities, healthcare buildings and the residential dwellings. Unwanted sound has a great impact on the well-being of human beings. Noise affects all of us both psychologically and physiologically. Good workmanship of the partitions in hospitals will enhance the privacy and dignity of patients, hence promoting essential sleep patterns, which are key condition for healing. In schools building, good workmanship of partitions will enhance the acoustic characteristics of classrooms, library, offices among other facilities with the school, hence bringing many benefits in terms of learners and staff comfort and morale as well as enhanced efficiency and usability of equipment.
QUESTION 4
The main reason why old-fashioned building, used massive walls and massive floors was to reduce the possibility of noise transmission within the building. The given scenario of a scheme of four-in-a block houses, experiences problems of noise transmission from one dwelling to another. Just like the given case of Scottish housing association, noise transmission in multiple-dwelling buildings such as apartments is the fastest growing area of disputes and complains in urban areas globally. Hu8man exposure to high noise levels has been linked to annoyance, sleep deprivation among other health issues such as hypertension and hearth disease The living conditions in multiple-dwellings buildings across the world have not met the required health and safety standards and presence of excessive noise penetrating the dwellings through floors, ceiling , doors, windows and even through water supply pipes makes the use of such dwellings to be extremely unpleasant exposing the residents to many health risks.
The possible separating floor construction method
Noise produced by hard floors remains to be the greatest source of complains in many multiple-dwelling buildings. Poor installation and insulation of floor systems in multiple-dwelling buildings such as the scheme of four-in-a block houses Scotland, creates a lot of problems to the neighbors downstairs since they will be exposed to noise from scraping of furniture, residents walking around in heels, children playing with different objects among other human activities upstairs.
Suspended timber floor system is the most likely separating floor construction method that was used in scheme of four-in-a block houses. The suspended timber flor systems have timber joists that are suspended from the bearing walls .Once the structural stability of the suspended timber joists has been assessed and approved, they are covered with covered with floor boards to create a separating floor system. In the given case of scheme of four-in-a block houses., complains about noise by the occupants may be due to loosening of the flooring boards and the development of squeaks and creaks. The noise can also be easily transmitted from one dwelling to another easily if this separating flooring system was used, this is because the flooring boards used have a small thickness, through which noise can be transmitted if other insulating materials are not used.
Issues likely to occur due to the use of separating wood flooring system.
If the separating timber floor systems are properly installed and insulated properly, it will be possible to achieve sound proofing within individual dwellings. But if the separating timber systems are not well maintained they will deteriorate very fast and the flooring system will develop squeaks and creaks hence 8increasing the level of noise experienced in the building.
Possible remedial options
The high noise levels experienced in the given scheme of four-in-a block houses and other multiple-dwelling buildings across the world is really annoying. In order to address that issue of noise transmission, there is need to come up with ways on how to improve the acoustic qualities of the floors, ceiling and ceiling. The best way to block the transmission of noise is to separate the construction materials attached each other. Some of the possible solution include;
- Replacing the ceiling with an acoustic ceiling
To improve the acoustics of the dwellings there will be need to remove all ceiling materials attached to the main joints, the ceiling dry wall and all other parts of a ceiling that are in contact with the floor joists. This is aimed at blocking the transmission of noise produced upstairs.
Acoustic ceiling tiles will work perfectly in controlling noise from the upstairs floors and at the same time blocking sounds produced in a room from being transmitted to the neighboring dwellings. There are a wide variety of acoustic ceiling tiles and panels that can be used to control noise in the given scenario. Being residential buildings, acoustic ceiling tiles will be the better option, because the tiles are easy to easy to use and the same time they make the rooms they are used in more comfortable for the occupants.
- Changing the flooring system of the building to achieve better soundproofing
The best and the most effective option of reducing the noise produced as a result of footfall and moving furniture and other objects on the floor is to fix sound insulation objects which will be able to offer an excellent level of resilience. The sound insulation materials used will absorb the energy of the impact noise generated. There are different options of sound insulation that can be used to enhance the acoustic characteristics of the floor.
- Use of acoustic platform floors
Acoustic platform floors are generally made up of a resilient layer which acts as a backing to a deck system having tongue and groove edges, for example the compressed chipboards. The use of pre-bond resilient layer in the given building will ensure that the treatment of the floor is uniform and creating a hard surface that will reduce the possibility of the resilient layer being damaged.
- Replacing the existing floor system with a resilient cradle floor system
The resilient cradle floor system are mainly made up of a deck system which rests on the timer batters which will be held in Central positions using resilient supports.
- Use of acoustic underlays
This will involve separating the floor from the rest of the building. Separating the floor from the building structure will involve installation of an acoustic floating flor. The floor will be made up of a surface layer resting on a resilient acoustic underlay, which isolates the upper part of the floor from the lower part of the floor, and all the surrounding walls. The use of acoustic this option presents itself as the best option of improving the impact sound performance of the floor. The thickness of the acoustic sublays that can be used for the given scenario can vary depending the activities carried out in a given space.
Question 5
Performance requirements are for internal partitions in Scotland
- The strength and stability of the partition must be able to meet the requirements of BS 5234-2:1992 to the appropriate duty category. The duty categories range from the light duty for the partitions used in residential buildings, medium duty which is used in offices and the heavy duty which is used in public buildings such as schools and hospitals. The impact of small hard bodies, large soft bodies, door-slamming and crowd pressure; fixing methods Partitions are expected to have a service life of about 60 years
- The partition must meet all the acoustic requirements mentioned in SHTM 2045. Partition being very crucial to the building’s acoustical performance , all partitions must offer insulation from flanking, airborne and impact sounds, and the partitions must be able to control sound reverberation and absorption.
- All partitions must have a fire resistance of 120 minutes.Fire resistance of the partitions regarding their collapse, the transference of heat when exposed to fire, should be meet all the building (Scotland) Regulations 2004 and the relevant provisions of Fire code SHTM 81, SHTM 84 and SHTM 85.
- The cavity barrier in partitions should be located in the partition according to the Building (Scotland) Regulations 2004 and the relevant provisions of SHTM 81. Protection against mechanical damage should be considered in all areas where the partitions may be subjected to hard body impact from mobile equipment
- All the electrical installation in partitions should be carried out in accordance with the current IEE regulations for electrical installations.
- The space ( void) in the partitions must be able to accommodate all the major services which include the electrical installation, water piping network,. The diameter of all these services when running horizontally will be limited by the width of the cut-outs in the metal studs.
- Back to back fixing of all engineering terminals will be avoids as much as possible, especially in fire resisting partitions.
According to the information given by the plasterboard manufacturer showing the laboratory performance of different metal studs partitions. I would expect the following metal stud’s partitions to be suitable for internal partitions in Scotland.
Metal studs partition 1. Of one layer of board each side of 48mm. Gypframe ‘C’ studs at 600mm centres.
Metal studs partition 2. One layer of board each side of 48mm Gypframe ‘C’ studs at 600mm centres. 25mm ISOWO APR 1200 in the cavity.
Level of acoustic insulation these partitions would achieve if tested on site against the DnT,w criteria.
Dw is a term which is used to relate to the sound insulation between different rooms on-site. Simply Dw refers to the noise level in the source room minus the noise level in the receiving room. Dw is a performance standards which in most cases is used for describing the final requirements of the site. This is in most cases used to show the compliance with the building regulations for residential, hospital and school developments.
DnT,w refers to the performance parameter required for the schools and the healthcare buildings . The nT stands for normalization (n) of reverberation (T) which allows one to compare the sound insulation outcome objectively on a level field. For the given partitions given above will be able to achieve an acoustic insulation of 56 dB DnT,w if tested on site against the DnT,w criteria.
Reasons why it is difficult or impractical to test internal partitions within a residential building
It is challenging to test the internal partitions of a residential buildings because of the due to the following reasons.
The sounds produced in residential houses in most cases are unwanted sound. This is because the sounds produced by the house occupants does not affect each other.
The size of rooms or spaces in a residential building is small, making the internal conditions such as indoor temperature and humidity in all the rooms to be the same.
The nature of activities taking place in the rooms within the residential buildings is almost similar.
The number of occupants in residential buildings is small as compared to those in the public buildings such as hospitals and schools.
References
Austin & Simon, “Analytical design planning technique: a model of the detailed building design process.” Design studies 20.3 (1999): 279-296.
Barkokébas Jr and Béda. “Analysis of noise on construction sites of high-rise buildings.” Work 41.Supplement 1 (2012): 2982-2990.
Buchegger, Blasius, Heinz Ferk, and Martin Schanz. “Flanking sound transmission in connected panels of cross-laminated-timber at low frequencies.” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 140.4 (2016): 3281-3281.
Cornick, Tim. “Quality management for building design.” (1991).
Davy, John L.. “The prediction of flanking sound transmission below the critical frequency.” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 132.4 (2012): 2359-2370.
De Geetere, Lieven, Bart Ingelaere, and Monika Rychtarikova. “Flanking sound transmission measurements on a timber frame mock-up.” Proceedings of Internoise 2013 (2013).
Faber, Nathan D. “Costs and Benefits for Pipeline Acoustic Fiber Optic Monitoring.” Pipelines 2017. 2017. 12-22.
Gray, Colin, Will Hughes, and John Bennett. The successful management of design: A handbook of building design management. Centre for Strategic Studies in Construction, 1994
Hill, Jennifer G. “Centro and the monitoring board-legal duties versus Aspirational ideals in corporate governance.” UNSWLJ 35 (2012): 341.
Höller, Christoph. “Laboratory Study on Flanking Sound Transmission in Cold-Formed Steel-Framed Constructions.” INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings. Vol. 253. No. 7. Institute of Noise Control Engineering, 2016..
Jik Lee, Pyoung, and Michael J. Griffin. “Combined effect of noise and vibration produced by high-speed trains on annoyance in buildings.” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 133.4 (2013): 2126-2135.
Korkmaz, Sinem. “High-performance green building design process modeling and integrated use of visualization tools.” Journal of Architectural Engineering 16.1 (2010): 37-45.
Martello & N. Zuccherini “Analysis of direct and flanking sound transmission between rooms with curtain wall facades.” Energy Procedia 78 (2015): 164-169.
Miedema, Henk ME. “Relationship between exposure to multiple noise sources and noise annoyance.” The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 116.2 (2004): 949-957.
Patterson, Doug “New Acoustic Acquisition and Processing Method Assist in Delineating Structure in an Exploration Play in the Gulf of Mexico.” SPWLA 57th Annual Logging Symposium. Society of Petrophysicists and Well-Log Analysts, 2016.
Pierce, J. R. “Physical sources of noise.” Proceedings of the IRE 44.5 (1956): 601-608.
Secchi, Simone. “Sound transmission between rooms with curtain wall façades: a case study.” Building Acoustics 22.3-4 (2015): 193-207.
Sharland, I. Jr. “Sources of noise in axial flow fans.” Journal of Sound and Vibration 1.3 (1964): 302-322.
Tunstall, Gavin. Managing the building design process. Routledge, 2006.
Smyth, Fiona. “‘A Matter of Practical Emergency’: Herbert Baker, Hope Bagenal, and the Acoustic Legacy of the Assembly Chamber in Imperial Delhi.” Architectural History 62 (2019): 113-144.
Singh, Narendra, and Subhash C. Davar. “Noise pollution-sources, effects and control.” Journal of Human Ecology 16.3 (2004): 181-187.
Wax, Mati. “Detection and localization of multiple sources in noise with unknown covariance.” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 40.1 (1992): 245-249.
Zeitler, Berndt, Stefan Schoenwald, and Frances King. “Flanking sound insulation of wood frame assemblies with high axial and lateral load bearing capacity.” INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings. Vol. 247. No. 3. Institute of Noise Control Engineering, 2013.