- Introduction:
- Background of AI and Social Engineering-
With the increasing application of technologies and the implementation of digitally transformed approaches, organizations are heading towards the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, natural language processing and machine learning. According to the findings developed by Khan, Arif and Khan (2024), in organizations, AI is being used for multiple purposes, which include process automation, decision making, process optimization, as well as in cybersecurity practices. The application of AI in cybersecurity practices is helping organizations with threat detection, automatic responses to intrusions, as well as better decision-making to protect an organization from cybersecurity threats. It is highlighting the fact that cybersecurity professionals can utilize the feature of artificial intelligence technology to protect the organization from cybersecurity threats.
From the reports developed by Secureframe (2023), it has been highlighted that globally, there are different delivery methods and cybersecurity vulnerabilities that are causing ransomware infections.
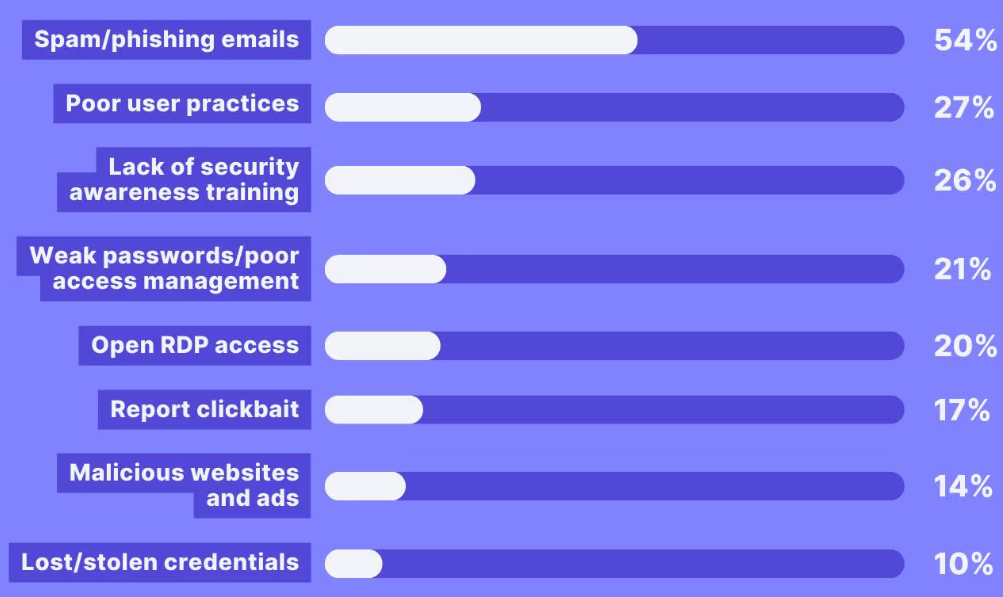
Figure 1: Contribution of Cyber security delivery methods and cybersecurity vulnerabilities to cause ransomware infections.
Source: Secureframe (2023)
In Figure 1, it is given that amongst all the delivery methods and cyber security vulnerabilities there is 54% Spam and phishing emails, 27% poor user practices, 26% lack of security awareness training, 21% weak password and poor management of data access, 20% open RDP access, 17% report clickbait, 14% malicious websites and advertisements whereas 10% is caused by lost or stolen credentials.
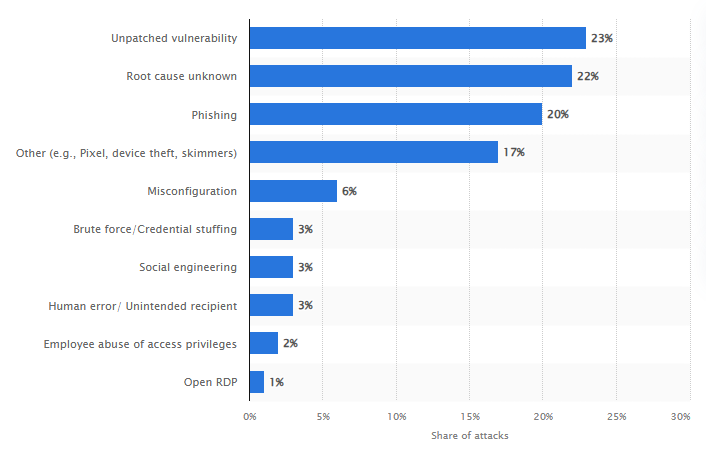
Figure 2: % of cybersecurity challenges experienced by Companies in the US.
Source: Statista (2023a)
From the reports published by Statista (2023a), in the United States, companies are experiencing an increasing number of cybersecurity challenges. Where, 23% of unpatched vulnerabilities, for 22% the root cause of the issue is unknown, 20% because of phishing attacks, 17% because of device theft and skimmers, 6% because of misconfiguration, brute force holds 3%, social engineering holds 3%, another 3% is caused by human error, 2% is contributed by employee abuse of access privileges and open RDP contributes 1% of these cyber-attacks encountered by companies in the United States in the year 2023.
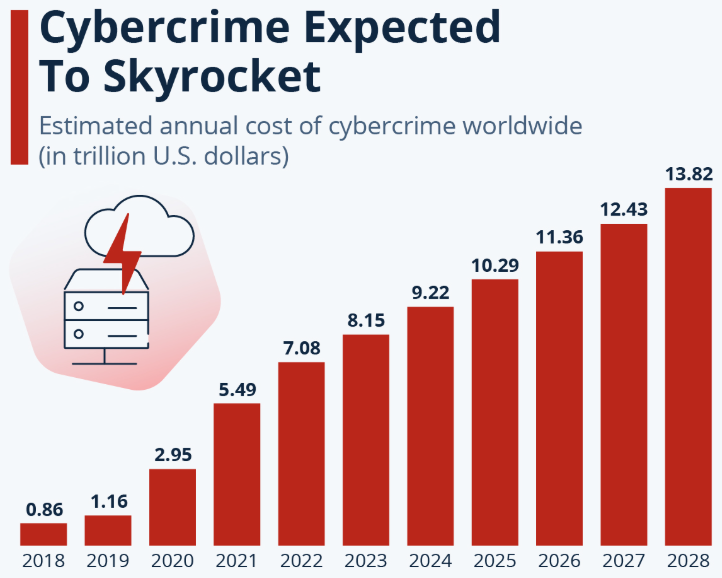
Figure 3: Estimated annual cost of cybercrime globally from 2018 to 2028.
Source: Statista (2023b)
Another report published by Statista (2023b) has highlighted that since 2018, the estimated annual cost of cybercrime globally has increased significantly. In the year 2020, the estimated annual cost of cybercrime globally was 2.95 trillion U.S. dollars; in the year 2024, it was 9.22 trillion U.S. dollars, and it is estimated that by the year 2028, it will reach 13.82 trillion U.S. dollars. In the reports published by Crane (2025), it is found that in the United States, approximately $12.5 billion in fraud-related losses were reported by consumers in the year 2024. Social engineering attacks are one of the attacks that have contributed to the loss of approximately $ 130,000 by stealing data or conducting monetary theft. In addition to the above, the report highlights the fact that although social engineering is not the number one threat experienced by the consumers of the United States, it is within the top three attacks, which are still damaging the data privacy and security of organizations.
Referring to this discussion, it can be stated that cybersecurity attacks are increasing day by day, which requires effective treatment. The existing mitigation strategies show that cyber security attacks are expensive, time-consuming and sometimes ineffective. It is thus anticipated to introduce the power of artificial intelligence technology in handling cybersecurity threats.
- Research problem and relevance-
It is found in the report developed by Johannes (2024) that social engineering attacks have a significant negative impact on the cybersecurity and financial infrastructure of an organization. The cybercriminals focus on understanding human psychology so that they can apply social engineering strategies to exploit and manipulate employees working in an organization to download malware or to hand over access to confidential documents. To date, no effective strategy or technology has been applied to offer full protection against this manipulative tactic of cybercriminals. In the year 2021 the social engineering attack compromised the high-profile Twitter accounts including the Twitter account of Barack Obama, Elon Musk and Bill Gates. the cybercriminals utilized the combination of phone vishing and phishing attack to get the access of the credentials and then used the high-profile Twitter accounts to post fraudulent tweets to advertise Bitcoin scam. In the reports published by Sajjad, (2023) it is mentioned that the organizations often fail to detect cyber threats because majority of the organizations are depending on the legacy devices as well as outdated software programmes which are not effective enough to detect anomalies and malicious activities in network caused by continuously evolving cyber security methods. Apart from the above, it is also found that because of the insider threat, human errors, as well as a lack of training amongst the staff, the organizations often fail to detect suspicious activities.
Referring to the above discussion, it can be stated that currently, there is a significant gap in the cybersecurity infrastructure of organizations where there is an absence of advanced technology to effectively detect malicious activities. Referring to Section 1.1, it can be stated that artificial intelligence technology has the feature of automatically detecting specific patterns, making data-based decisions, as well as optimizing and automating processes. The incorporation of artificial intelligence-enabled technologies in the cybersecurity infrastructure for the detection of malicious activities and the prevention of cybersecurity attacks, such as social engineering, can be helpful for organizations. Hence, it can be stated that the findings of this research can be helpful for organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity infrastructure to eliminate the occurrence and negative impact of social engineering attacks.
- Research questions-
The application of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing social engineering attacks can be helpful for organizations to improve their cybersecurity infrastructure. However, some barriers like staff resistance, lack of skilled employees to operate the technology, as well as the issue with the compatibility of the organizational infrastructure, can restrict the benefits of AI technology (Ojoh, 2025). Understanding the above-mentioned aspect, this research aims to answer the following research questions: –
RQ1- How can the use of artificial intelligence-enabled systems improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations?
RQ2- How should an organization be prepared to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen its cybersecurity infrastructure for effective detection and prevention of social engineering attacks?
- Aims and objectives-
Aim- The aim of this research is to determine the artificial intelligence-enabled systems to improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations as well as develop strategies to prepare the organization to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen its cybersecurity infrastructure.
Research Objectives-
- Research Objective 1- To determine the current issues experienced by organizations operating in the United States because of the occurrence of social engineering attacks.
- Research Objective 2- To determine the factors influencing the occurrence of social engineering attacks in the organizations of United States.
- Research Objective 3- To explore and determine artificial intelligence-enabled systems to improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations.
- Research Objective 4- To determine the strategies to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen the cybersecurity infrastructure for effective detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations.
- Scope and limitations-
The scope of the research includes the determination of strategies to use artificial intelligence-enabled systems improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations. In addition, it will help in developing strategies to prepare the organization to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen its cybersecurity infrastructure. However, the scope does not include practical implementation of the system.
- Literature Review:
- Overview of Artificial Intelligence-
Weng et al. (2024) have mentioned in the findings of the study that artificial intelligence is an emerging technology that is fundamentally restructuring the industries by improving their decision-making process, bringing automation, as well as optimizing organizational activities. Amongst all the transformative technologies introduced in the 21st century, artificial intelligence is one of the most effective technologies. According to the findings developed by Muneer et al. (2024), artificial intelligence-enabled models have the feature of data-driven decision making, maintaining transparency and interpretability. By analyzing the network data, an artificial intelligence-driven system can detect unique and suspicious activities and report them as an anomaly.
- Social Engineering Attacks-
According to the findings developed by Venkatesha, Reddy and Chandavarkar (2021), the increase in time spent by participants on online platforms also increases the vulnerability of social engineering. The social engineering attacks are nothing but a group of sophisticated and well-designed cybersecurity attacks by cybercriminals to exploit the innate human nature with the aim of penetrating the secure system of an organization. The cybercriminals use human psychology to manipulate humans, because of which the success rate of social engineering attacks is always high. Hijji and Alam (2021) have highlighted that during COVID-19, cybercriminals used social engineering-based cyberattacks, which include phishing, spamming, scamming, smishing, and vishing. In addition, fake emails, malicious website links, and scam mobile apps were used as weapons by the cyber criminals for conducting successful cyberattacks.
- Traditional Methods for Detecting Social Engineering-
According to the findings developed by He et al. (2022), in order to detect social engineering attacks, it is important to focus on monitoring human factors and behavior. However, the current detection methods used by organizations are not focusing on analyzing the behavior of human resources, but on analyzing the organizational network to detect malicious activities. Tang and Mahmoud (2021) have identified that the traditional methods for identifying social engineering attacks depend on the whitelists and backlists, which are not capable of detecting new methods. Since the cybercriminals are rapidly changing the pattern and strategies of social engineering attacks, the traditional systems are failing to detect the anomalies.
- Emergence of AI in Cybersecurity-
According to the findings developed by George (2024), there are several emerging trends in AI-driven cybersecurity which is helping organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity infrastructure. The integration of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is introducing the feature of real-time data analytics for developing decisions to adopt proactive responses, performing predictive analytics to offer a comprehensive understanding of the potential issues, as well as automating threat detection to reduce the time consumed by the organization in detecting malicious activities within the organizational network. It is also found in this study that generative adversarial networks can also be considered as one of the emerging technologies to strengthen the cybersecurity infrastructure of open organizations with real-time threat responses. It is found in the study findings developed by Jimmy (2021) that integration of artificial intelligence can help organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses with effective navigation of the right cybersecurity practices, as well as analyzing complex scenarios to make data-driven decisions.
- Applications of AI in Detecting Social Engineering Attacks-
It is found in the study findings developed by Metta et al., (2024) that Generative artificial intelligence (GAI) has a comprehensive impact on the current activities of cybersecurity frameworks and protocols, alongside safeguarding the digital infrastructure of an organization. Metta et al. (2024) have highlighted that the acceleration of GAI is assisting cybersecurity experts in improving their threat detection and response process. It is found in the study developed by Ojoh (2025) that the application of AI-powered tools has the potential to significantly improve the approaches of threat detection and response times, where the efficiencies of this technology can be examined through the use of effectiveness, usability and detection rates. According to the findings developed by Fakhouri et al., (2024) AI enhanced mechanism has the potential to improve the detection and mitigation of social engineering threats, where the advanced model focuses on developing decisions based on the results of behavioral analytics as well as helps in implementing the correct strategy to prevent organizations from the threat of social engineering. In addition to the above, behind the selection of AI technology for social engineering attack detection and mitigation, one of the key reasons is the continuously evolving nature of the technology, which ensures continuous development to remain up to date to deal with the cybersecurity threats.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations-
The findings developed in the study conducted by Alahmed, Abadla, and Al Ansari (2024) have highlighted that the introduction of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is prone to several challenges and ethical considerations. Staff resistance, poor technological infrastructure, and the absence of adequate talent are considered key challenges that can restrict the implementation of AI within organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity capability. Apart from the above, it is found that the ethical considerations associated with the implementation of AI in cybersecurity systems highlight the need to implement safe AI to ensure that the implemented system is solely working for the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks, and there is no third-party access to the organizational data. In addition to the above, when implementing technology, one of the primary ethical issues is the issue of job loss, as advanced technologies can replace human efforts. Although the integration of these technologies can also offer employment opportunities to skilled individuals to operate the system.
- Theoretical Framework-
According to the findings developed by Chatterjee et al. (2021) using the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), the acceptance of the proposed technology in the cybersecurity landscape can be examined. However, this model does not have the capability to examine the organisational readiness, as well as the organisational compatibility to accept the nominated technology.
- Gaps in the Literature-
After careful analysis of the above-mentioned literature, it is found that currently there is a significant gap in discussing the practices of Artificial Intelligence-enabled systems to detect as well as mitigate social engineering attacks. Although there is research conducted on the features of AI to strengthen the cybersecurity landscape, no detailed discussion is presented that is specifically for social engineering attacks. In the literature analysis, it is found that, in a social engineering attack, understanding human behavior is important. Understanding the above-mentioned factors, in this research, it is anticipated to examine the factors that are influencing the occurrence of social engineering attacks in organizations in the United States, as well as help organizations ensure their readiness to adopt AI to strengthen their cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Research Methodology:
3.1 Research Philosophy and Approach (Qualitative, Quantitative, or Mixed)-
In order to conduct the research, it is anticipated to follow the pragmatic research philosophical belief and the Abductive research approach. It is anticipated that to formulate the findings of this research, both qualitative and quantitative data are needed (King, 2022). Quantitative data offers a comprehensive understanding of factors and patterns, while qualitative data offers a deeper understanding of the context. Referring to the above understanding, it is anticipated that the selection of the pragmatist philosophical view and the abductive research approach to use both qualitative and quantitative data can be helpful in generating reliable and valid research outcomes.
3.2 Research Design and Strategy-
In order to conduct the research, it is anticipated to use an exploratory sequential mixed-methods design, where the findings of this research will be influenced towards the results of quantitative data analysis collected directly from the participants associated with the research (Chiarini and Kumar 2022). The exploratory sequential research design has the potential to bring a deeper understanding of the practical issues, as well as offer comprehensive control over the development of adequate strategies to address the identified issue.
3.3 Data Collection Methods (Primary and Secondary)-
In this research, both primary and secondary data will be collected. The primary data will be collected from 100 professionals working in the digitally transformed organizations of the United States to understand the factors that are influencing the occurrence of social engineering attacks, as well as the perspectives of the employees working in the organizations. The secondary data will be collected from peer-reviewed journals, industry reports, and newspapers so that the trending ideas can be explored for the development of the right strategy to integrate AI-enabled systems in the cybersecurity infrastructure for the detection and mitigation of social engineering attacks.
3.4 Sampling Techniques and Simple Size-
In this research, a purposive sampling strategy will be utilized to conduct the primary quantitative data collection process, specifically, cyber security professionals working in the digitally transformed organizations with a minimum of 5 years of experience will be engaged.
For the collection of secondary data, a specific search strategy will be used using keywords like AI in cybersecurity, trends of AI to strengthen cybersecurity, and others. It is anticipated to collect the secondary data from Google Scholar and the Google Internet search engine.
3.5 Data Analysis Techniques and Tools-
In order to analyses this primary quantitative data, SPSS software will be used, and techniques such as regression analysis, correlation analysis and descriptive statistics will be applied. In order to analyze the secondary qualitative data, a thematic data analysis framework will be used, where the collected data will be analyzed against specific themes derived from the research objectives and the collected data.
3.6 Ethical Considerations and Approvals-
Similar to every research, this research has ethical considerations. Since in this research, primary data will be collected from participants, at first, a consent form will be shared with the participants to ensure that before participating in the survey, they will have a comprehensive understanding of the research purpose. In addition to maintaining confidentiality, the personal identification data will not be collected. Alongside the above, the research will be conducted by following the ethical guidance of the university.
3.7 Limitations and Potential Pitfalls of the Methodology-
Small Sample size for the collection of primary data is the pitfall of the research. Gaining a deeper understanding of the issues faced by cybersecurity professionals in detecting and managing social engineering attacks from 100 professionals may not be adequate to represent the actual scenario.
- Implementation:
- Activities-
In the following table the key activities to conduct the research to examine the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting and Preventing Social Engineering Attacks is mentioned along with a Gnatt Chart: –
Table 1: Timeline and Gantt Chart
| Activities | Wk 1 | Wk 2 | Wk 3 | Wk 4 | Wk 5 | Wk 6 | Wk 7 | Wk 8 | Wk 9 | Wk 10 | Wk 11 | Wk 12 | Wk 13 | Wk 14 | Wk 15 | Wk 16 | Wk 17 |
| Gap Determination | |||||||||||||||||
| Proposal Submission | |||||||||||||||||
| Approval Received on Proposal | |||||||||||||||||
| Literature Review | |||||||||||||||||
| Primary Data Collection | |||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Data Collection | |||||||||||||||||
| Primary Data Analysis | |||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Data Analysis | |||||||||||||||||
| Formulation of Research findings | |||||||||||||||||
| Submission of the draft paper | |||||||||||||||||
| Feedback Received on Draft | |||||||||||||||||
| Final Work Submitted |
- Data collection-
The primary data will be collected from 100 professionals working in the digitally transformed organizations of the United States. The secondary data will be collected from peer-reviewed journals, industry reports, and newspapers. To conduct the primary quantitative data collection process, specifically, cyber security professionals working in the digitally transformed organizations with a minimum of 5 years of experience will be engaged.
- Challenges-
In this research to examine the role of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting and Preventing Social Engineering Attacks engaging 100 professionals can be challenges. Apart from this, there is not such potential challenges in this proposed research.
- Validation-
In the SPSS software the techniques such as Value Labels and Range Checks as well as the Cross-tabulation will be used to examine the logical consistency validation.
- Anticipated Results:
- Expected technical outcomes-
In this research it is anticipated to determine the artificial intelligence-enabled systems to improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations as well as develop strategies to prepare the organization to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen its cybersecurity infrastructure. The research will help is developing best practices of AI implementation in cybersecurity to help in detecting and mitigating the social engineering attacks in organizations.
- Practical implications-
The project scope does not include practical implementation of the system however, the research will determine the current issues experienced by organizations operating in the United States because of the occurrence of social engineering attacks, the factors influencing the occurrence of social engineering attacks in the organizations of United States, artificial intelligence-enabled systems to improve the detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations as well as the strategies to integrate artificial intelligence-enabled systems to strengthen the cybersecurity infrastructure for effective detection and prevention of social engineering attacks in organizations.
- Conclusion:
- Key findings-
The application of AI in cybersecurity practices is helping organizations with threat detection, automatic responses to intrusions, as well as better decision-making to protect an organization from cybersecurity threats. The cybersecurity attacks are increasing day by day, which requires effective treatment. There is a significant gap in the cybersecurity infrastructure of organizations where there is an absence of advanced technology to effectively detect malicious activities. Hence, it can be stated that the findings of this research can be helpful for organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity infrastructure to eliminate the occurrence and negative impact of social engineering attacks.
- Recommendations for future research-
It is suggested to conduct a practical experiment on organizations using the traditional methods and AI driven detection methods to compare the results and identified the comparative benefits of AI driven detection methods in cybersecurity.
- Reflection:
After completion of the above work, I would like to mention that the selection of the correct methodological approach to conduct the study was the most challenging part of this work, because the credibility of the findings of research depends on the accuracy of the selected research methodology. From the work I have learned that both primary and secondary data can be used in the research to strengthen the research findings. However, I feel that there is scope to conduct deeper background analysis to grasp a better understanding of the context.
References:
Alahmed, Y., Abadla, R. and Al Ansari, M.J., 2024, September. Exploring the Potential Implications of AI-generated Content in Social Engineering Attacks. In 2024 International Conference on Multimedia Computing, Networking and Applications (MCNA) (pp. 64-73). IEEE.
Chatterjee, S., Rana, N.P., Dwivedi, Y.K. and Baabdullah, A.M., 2021. Understanding AI adoption in manufacturing and production firms using an integrated TAM-TOE model. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 170, p.120880.
Chiarini, A. and Kumar, M., 2022. What is Quality 4.0? An exploratory sequential mixed methods study of Italian manufacturing companies. International Journal of Production Research, 60(16), pp.4890-4910.
Crane, C. (2025) ‘Social Engineering Statistics 2025: When Cyber Crime & Human Nature Intersect’, Hashed Out. The SSL Store™, 20 June. Available at: https://www.thesslstore.com/blog/social-engineering-statistics/ [Accessed: 9 July 2025].
Fakhouri, H.N., Alhadidi, B., Omar, K., Makhadmeh, S.N., Hamad, F. and Halalsheh, N.Z., 2024, February. Ai-driven solutions for social engineering attacks: Detection, prevention, and response. In 2024 2nd International Conference on Cyber Resilience (ICCR) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
George, A.S., 2024. Emerging Trends in AI-Driven Cybersecurity: An In-Depth Analysis. Partners Universal Innovative Research Publication, 2(4), pp.15-28.
He, D., Lv, X., Xu, X., Yu, S., Li, D., Chan, S. and Guizani, M., 2022. An effective double-layer detection system against social engineering attacks. IEEE Network, 36(6), pp.92-98.
Hijji, M. and Alam, G., 2021. A multivocal literature review on growing social engineering based cyber-attacks/threats during the COVID-19 pandemic: challenges and prospective solutions. Ieee Access, 9, pp.7152-7169.
Jimmy, F., 2021. Emerging threats: The latest cybersecurity risks and the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing cybersecurity defenses. Valley International Journal Digital Library, 1, pp.564-74.
Johannes, C. (2024) ‘The True Cost of Cybersecurity Failure – When Technology (and People) Fail’, NAVEX, 16 April. Available at: https://www.navex.com/en-us/blog/article/the-true-cost-of-cybersecurity-failure-when-technology-and-people-fail/ [Accessed: 9 July 2025].
Khan, M.I., Arif, A. and Khan, A.R.A., 2024. The most recent advances and uses of AI in cybersecurity. BULLET: Jurnal Multidisiplin Ilmu, 3(4), pp.566-578.
King, R., 2022. The utility of pragmatism in educational research. Creative Education, 13(10), pp.3153-3161.
Metta, S., Chang, I., Parker, J., Roman, M.P. and Ehuan, A.F., 2024. Generative AI in cybersecurity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.01674.
Muneer, S., Farooq, U., Athar, A., Ahsan Raza, M., Ghazal, T.M. and Sakib, S., 2024. A critical review of artificial intelligence based approaches in intrusion detection: A comprehensive analysis. Journal of Engineering, 2024(1), p.3909173.
Ojoh, O., 2025. A Comparative Analysis of the Influence of Artificial Intelligence Tools in Cybersecurity.
Sajjad, F. (2023) ‘Why are organizations failing to detect cybersecurity threats?’, LevelBlue Security Essentials, 19 October. Available at: https://levelblue.com/blogs/security-essentials/why-are-organizations-failing-to-detect-cybersecurity-threats [Accessed: 9 July 2025].
Secureframe. (2023) 27 social engineering statistics you need to know. [Online] Available at: https://secureframe.com/blog/social-engineering-statistics [Accessed 9 July 2025].
Statista. (2023a) Share of companies experiencing cyber attacks in the United States in 2022, by type. [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1406484/cyber-attacks-experienced-by-us-companies/ [Accessed 9 July 2025].
Statista. (2023b) Expected cost of cybercrime worldwide from 2023 to 2028. [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/chart/28878/expected-cost-of-cybercrime-until-2027/ [Accessed 9 July 2025].
Tang, L. and Mahmoud, Q.H., 2021. A survey of machine learning-based solutions for phishing website detection. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 3(3), pp.672-694.
Venkatesha, S., Reddy, K.R. and Chandavarkar, B.R., 2021. Social engineering attacks during the COVID-19 pandemic. SN computer science, 2, pp.1-9.
Weng, Y., Wu, J., Kelly, T. and Johnson, W., 2024. Comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence applications in modern industries. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.13059.
